Experiment 4: intermediate transformers – PASCO SF-8616_8617 COILS SET User Manual
Page 15
scientific
13
012-03800A
Experiment 4: Intermediate Transformers
Introduction
In this lab you will continue investigating transformers. You will investigate additional core
configurations and work into d.c. power supplies, one of the key applications of transformer
technology.
Equipment Needed - Supplied
1.
The PASCO SF-8617 Complete Coils Set
Equipment Needed - Not Supplied
1.
Low voltage ac power supply 0-6 VAC, 0-1 amp such as PASCO Model SF-9582
2.
AC voltmeter 0-6 VAC
3.
AC ammeter 0-2 A
4.
Oscilloscope
5.
Two diodes 1 amp, 50 PIV (min) rectifiers such as 2N4007
6.
Resistor 1000
Ω
, 2 Watt
7.
Capacitor 470
µ
F
8.
Banana connecting leads for electrical connections
Procedure A
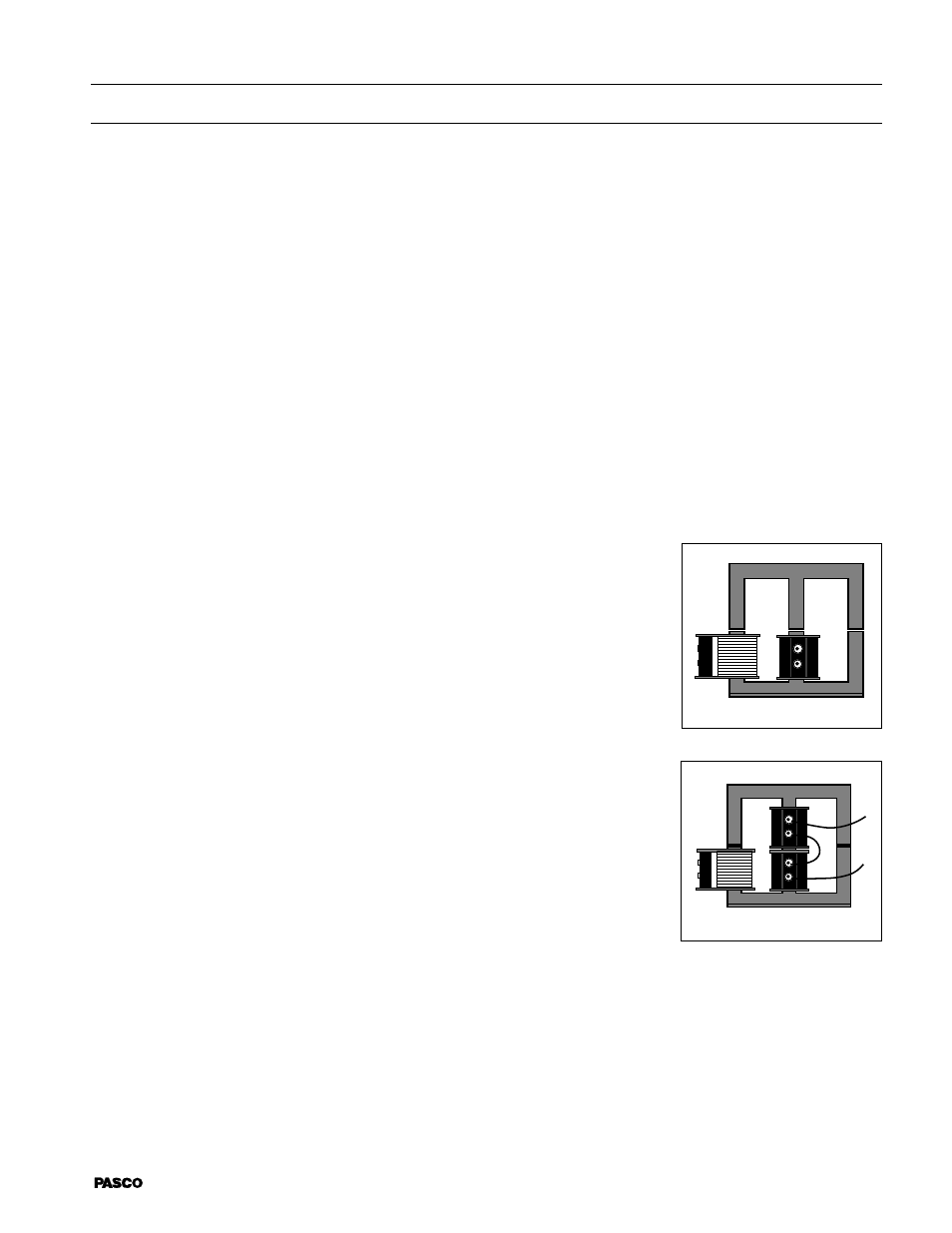
1.
Set up the coils and core as shown in Figure 1. In the diagram, the
coil to the left will be referred to as the primary coil, and the center
one will be the secondary coil.
2.
With the 200-turn coil as the primary and the 800-turn coil as the
secondary, adjust the input voltage to 6.0 volts a.c. With a resistance
of 1000
Ω
connected to the secondary, measure the input current, the
output voltage and the output current. Record your results in Table
4.1.
3.
Now replace the 800-turn coil with the two 400-turn coils, stacked on
the same arm of the E-shaped core. With the two coils connected as
shown in Figure 2, with a load resistance of 1000 ohms, measure the
input and output currents and voltages. Record your results in Table
4.1.
4.
Reverse the leads to one of the coils and re-measure the currents and
voltages. Record your results. How did the results compare with step
3? What did you change and why did you get the results you did?
5.
Now move the two 400-turn coils to the third arm of the core. How
do the values for current and voltage compare to those seen in the
previous position of the coils? How would these values compare with
a single 800-turn coil? Set up the single 800-turn coil and test your
hypothesis.
6.
Measure the individual voltages and currents of the 400-turn coils of
the secondary when they are connected to the 1000-
Ω
resistance in
the configuration which gave you the biggest output voltage and
current. How do the two values compare with one another? Do they
add or subtract to any specific values? Do the values you obtain in
the experiment support your understanding of basic series circuits?
Change the leads on one coil and re-measure the individual voltages
and the total voltage. Why do you get your end result?
Figure 2
Figure 1
Primary
Secondary
Primary
Secondary
