Specifications – Atec Agilent-4284A_4285A User Manual
Page 15
15
q
accuracy is given as:
±[(180/p) x (A
e
/100)] (absolute degrees)
where: 1.
A
e
= [A + (K
a
+K
b
+K
c
) X 100]
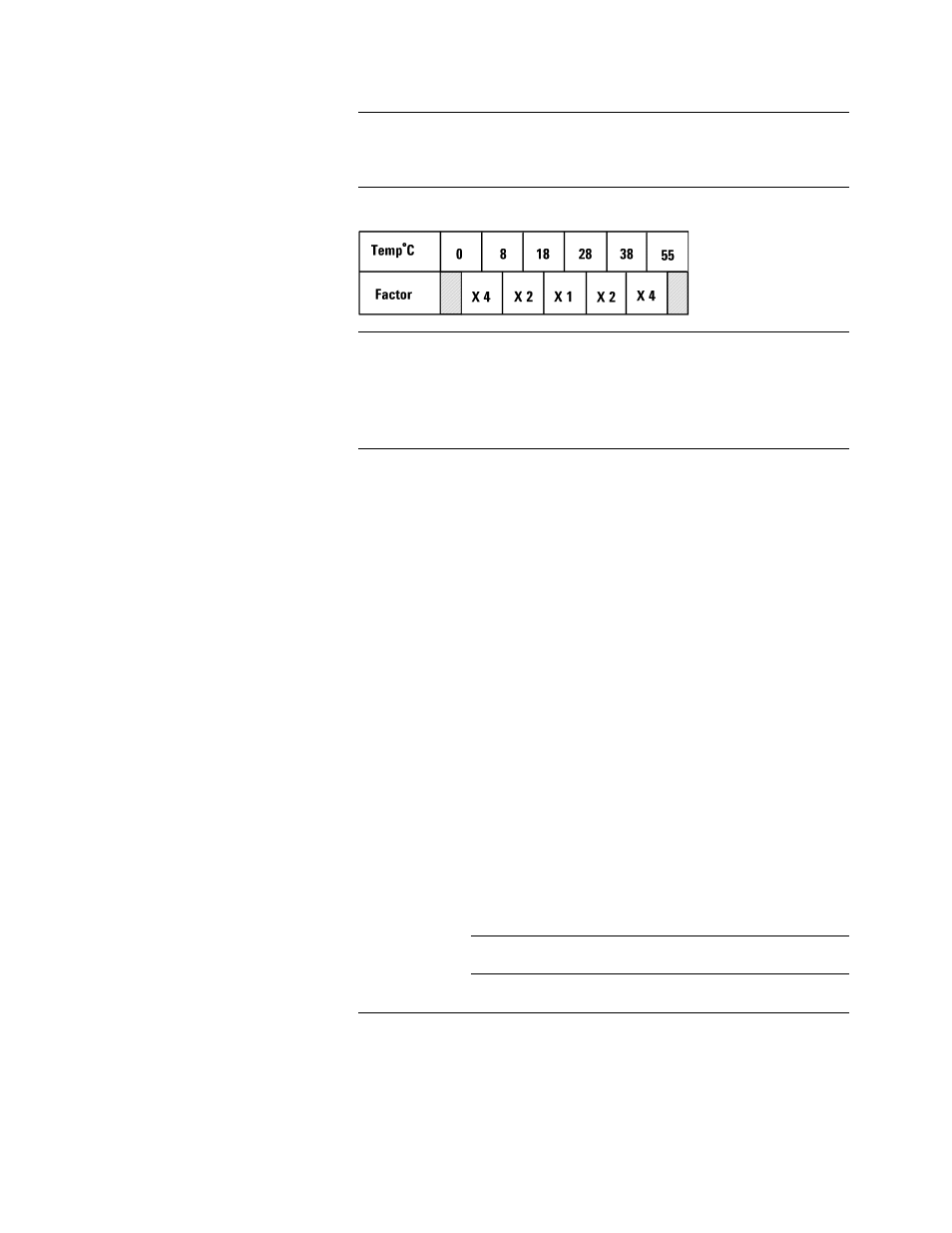
Additional error due to temperature:
Multiply the measurement accuracy by the following temperature factors.
Example C and D accuracy calculation
Measurement conditions:
Frequency: 1
kHz
Capacitance value:
100 nF
Test signal level:
1 Vrms
Integration time:
Medium
Calculation:
Step 1:
Use Figure 1 to determine A and Z
m
.
a. Find the frequency along the X-axis.
b. Find the capacitance value along a diagonal.
c. Note the intersection of the values from steps a and b.
Interpolation may be necessary.
d. Each shaded area has two values for A; the upper
number is for medium and long integrations, the
lower number is for short integration. A = 0.05%.
Find Z
m
by extrapolating horizontally to the Y-axis
(impedance axis). Z
m
= 1590
Ω
Step 2:
Use Tables 1 and 2 to find K
a
, K
b
and K
c
.
a. Use the equations in Table 2 to find K
a
and K
b
.
K
a
= (1 x 10
-3
/1590)(1+(200/1000)) = 7.5 x 10
-7
K
b
= (1590(1 x 10
-9
) (1 + 70/1000)) = 1.67 x 10
-6
b. Use Table 1 to find K
c
for the given frequency.
K
c
= 0
Step 3:
Calculate C and D accuracy.
C = 0.05 + (7.5 x 10
-7
+ 1.67 x 10
-6
+ 0) x 100% = 0.05%
D = 0.05/100 = 0.0005
Table 1. Kc : Calibration interpolation factor
Frequency
Kc
Direct correction frequencies
0
All other frequencies
0.0003
Note: Direct calibration frequencies are 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80, 100, 120, 150, 200Hz.
Sequence repeats for each decade up to 1 MHz. 48 frequencies total.
Specifications continued on page 16
Specifications
Continued
from page 14
