How the arcoptix anir works, Overview principle of operation, Appendix a – Ocean Optics ARCoptix ANIR User Manual
Page 31: Overview, Principle of operation
ARC-00000-000-02-0310 23
Appendix A
How the ARCoptix ANIR Works
Overview
The ARCoptix ANIR is a miniaturized Fourier Transform Spectrometer (FTS). It is based on the
principle named “Lamellar Grating Interferometer” (LGI). The active part of the LGI is driven by a
micrommechanical System. A Fourier Transform Spectrometer (FTS) has distinct advantages
compared to grating spectrometer in terms of throughput and Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR).
The principle of the LGI was invented by Strong [J. Strong, and G. A. Vanasse, “Lamellar grating far-
infrared interferometer”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 50, 113-118 (1960). The implementation of the LGI using
the emerging technology of micro-machining is unique.
Principle of Operation
An FTS splits the in-coming light in two beams, which are then recombined after having been shifted
in phase. The output modulation of the light is recorded as a function of time and called
interferogram. The interferogram contains all information about the spectra but contrary to grating
spectrometers the information is encoded via a Fourier transform. To obtain the spectra the recorded
data have to be Fourier transformed.
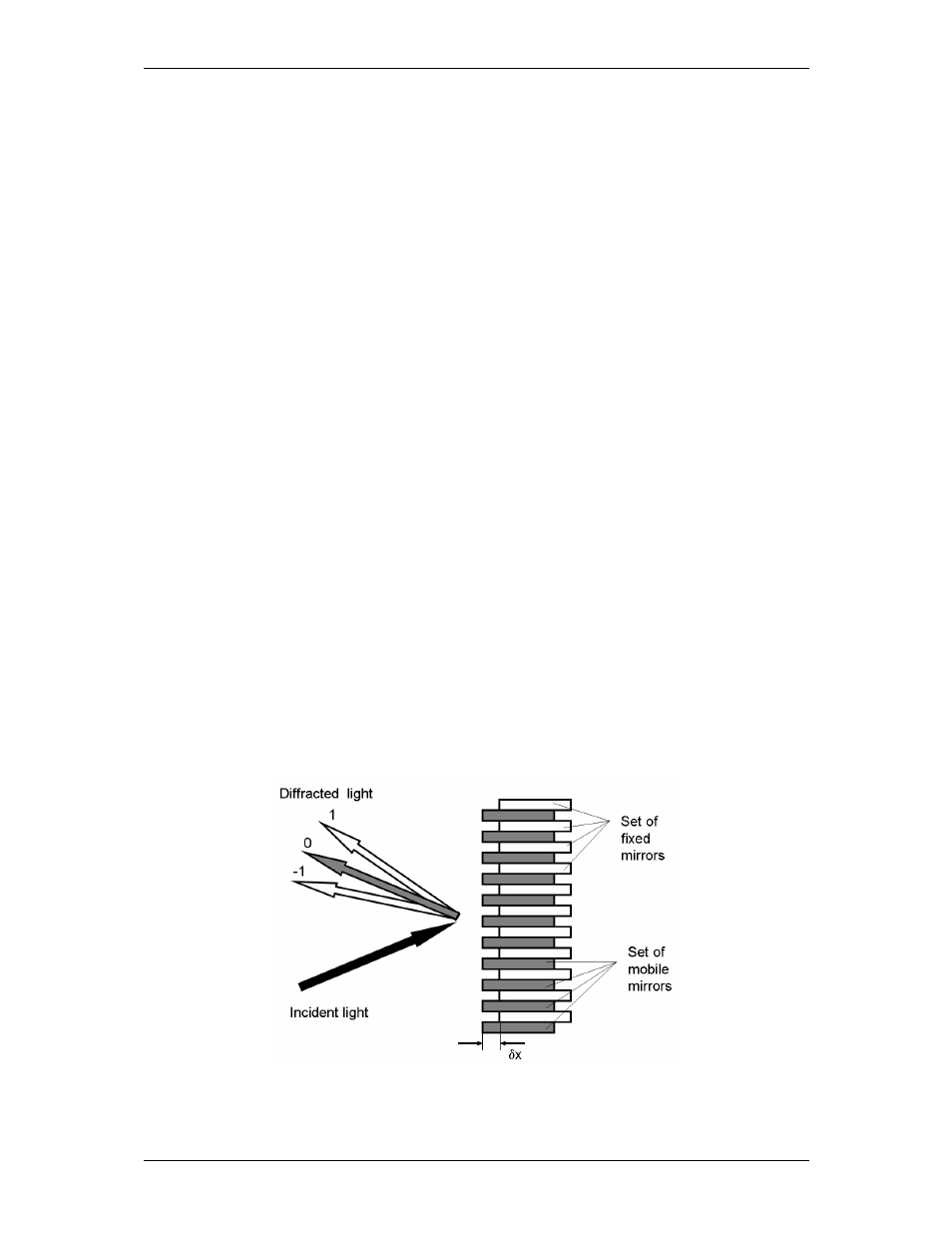
The particularity of the instrument developed by ARCoptix consists in using the so-called Lamellar
Grating Interferometer (LGI) configuration to produce the interferogram. Instead of using the
conventional Michelson interferometer (more precisely, the Twyman-Green interferometer) where
two mirrors and a beam splitter are used, the LGI consists of a series of mirrors that from a grating as
shown in Fig. A - 1.
Figure A- 1. The principle of operation of an LGI
