B&B Electronics MODSCAN32 - Manual User Manual
Page 67
67
Serial Connections
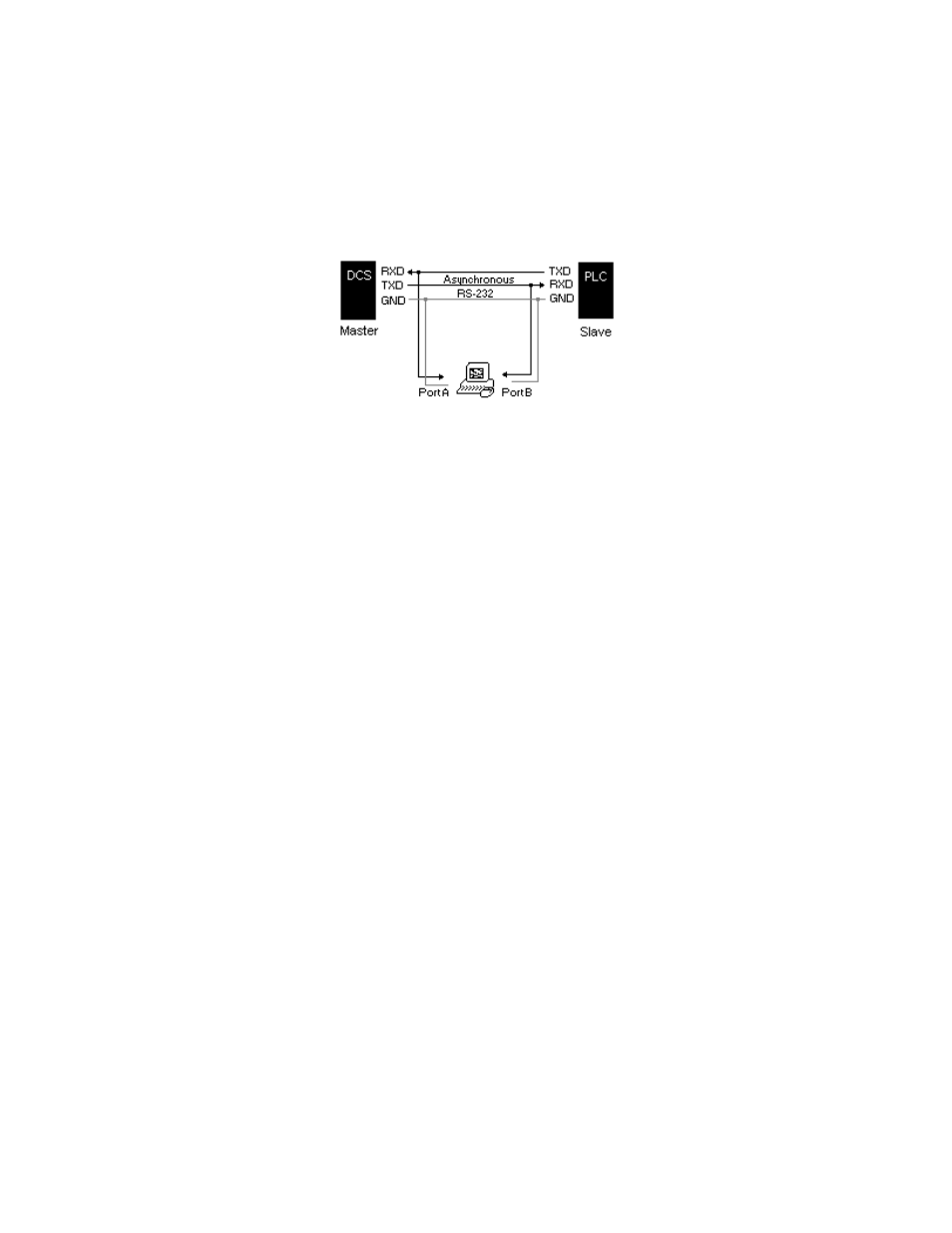
MNetMon uses a very simple concept. The nature or RS-232 allows multiple receivers to be connected to a
single transmitter. As long as the total cable length does not exceed the RS-232 specification, a listening
device, (in this case MNetMon), may tap into the transmit signal of an existing communications link and
‘hear’ everything that’s being said. By using two PC COM ports and listening the transmit from both the
master and slave device, MNetMon is able to capture data passed back and forth.
RS-232 devices are classified as DTE or DCE, (Data Terminal Equipment or Data Communications
Equipment). The standard pin-out arrangement allows a straight 25-pin cable to be attached between an
DCE device and a DTE device. If a DCE device is attached to another DCE device, (or DTE to DTE), the
cabling conductors must be switched such that the proper active pins are connected to the proper passive
pins on the corresponding device, (i.e. Transmit to Receive, Request to Send to Clear to Send, etc.).
The three primary RS-232 signals are located on pins 2,3 & 7 of a twenty-five pin “D” connector. Pin 7 is
ground; 2&3 are either Transmit & Receive or Receive & Transmit, depending on the configuration of
DCE/DTE. On 9-pin connectors 2,3 & 5 are used, with 5 being ground.
The connections to the monitoring device consists of two serial connectors, each with two conductors,
(Receive & Ground for port 1, and Receive and ground for port 2). The two receive lines may be connected
to either end of an RS-232 cable segment on pins 2&3. Both Grounds may be connected to pin 7. In this
configuration, MNetMon can receive data from device A on port 1, and data from device B on port 2.
Network Connections
MNetMon utilizes the built-in networking capabilities of Windows to access the plant LAN. MNetMon is
a Windows Sockets application. During start-up, MNetMon opens a TCP service port at address 52 and
awaits connection attempts from other network devices. As MBAP client applications connect, separate
communications threads are created to handle each communications link concurrently. Each connection has
full, (Read-Only), access to data captured and collected by MNetMon.
