Pin description (continued) – Rainbow Electronics MAX3420E User Manual
Page 5
Register Description
The SPI master controls the MAX3420E by reading and
writing 21 registers (Table 1). For a complete descrip-
tion of register contents, please refer to the “MAX3420E
Programming Guide.” A register access consists of the
SPI master first writing an SPI command byte, followed
by reading or writing the contents of the addressed
register. All SPI transfers are MSB (most significant bit)
first. The command byte contains the register address,
a direction bit (Read = 0, Write = 1), and the ACKSTAT
bit (Figure 4). The SPI master addresses the
MAX3420E registers by writing the binary value of the
register number in the Reg4 through Reg0 bits of the
command byte. For example, to access the IOPINS
(R20) register, the Reg4 through Reg0 bits would be as
follows: Reg4 = 1, Reg3 = 0, Reg2 = 1, Reg1 = 0, Reg0
= 0. The DIR (direction) bit determines the direction for
the data transfer. DIR = 1 means the data byte(s) will
be written to the register, and DIR = 0 means the data
byte(s) will be read from the register. The ACKSTAT bit
sets the ACKSTAT bit in the EPSTALLS (R9) register.
The SPI master sets this bit to indicate that it has fin-
ished servicing a CONTROL transfer. Since the bit is
frequently used, having it in the SPI command byte
improves firmware efficiency. In SPI full-duplex mode,
the MAX3420E clocks out eight USB status bits as the
command byte is clocked in (Figure 5). In half-duplex
MAX3420E
USB Peripheral Controller
with SPI Interface
_______________________________________________________________________________________
5
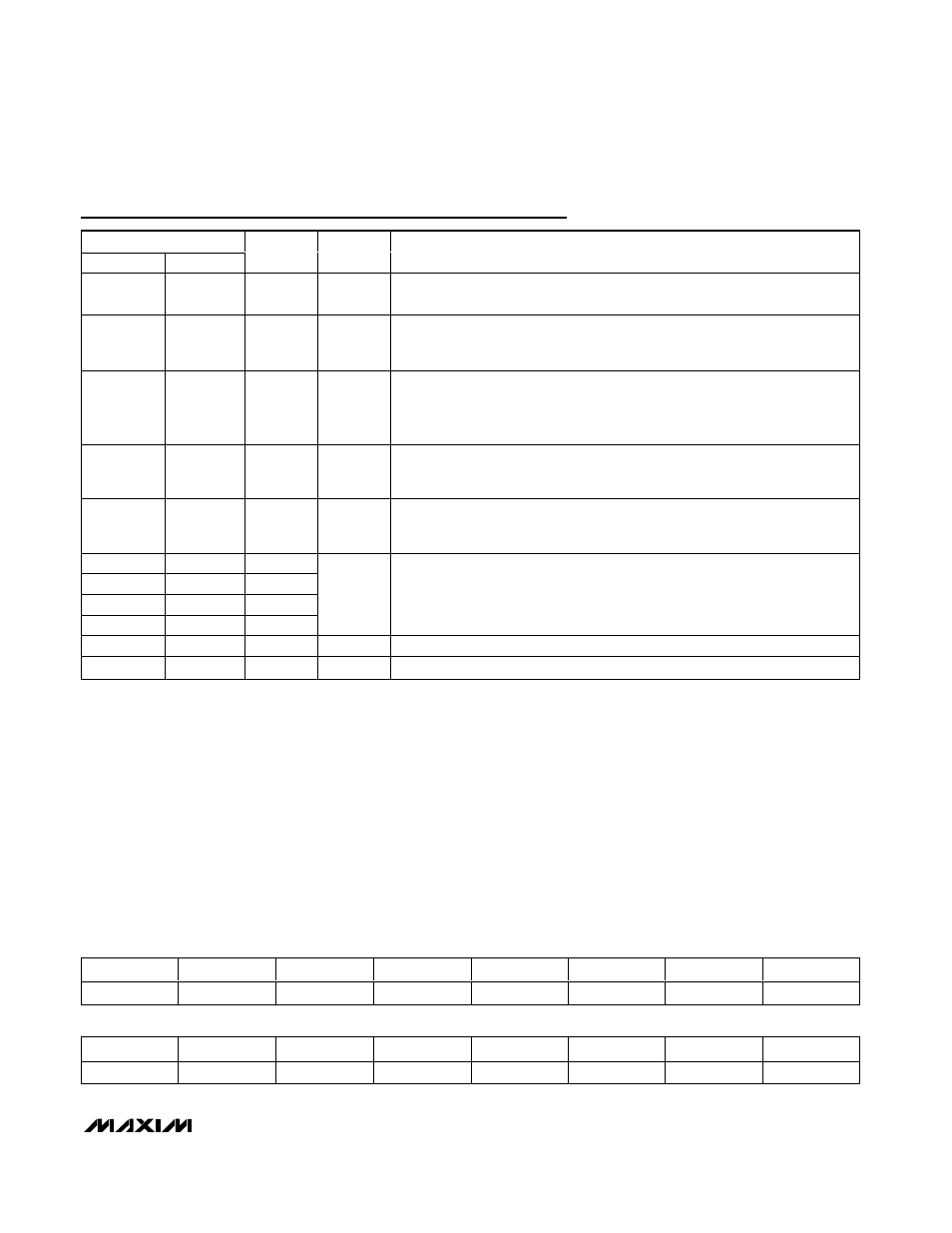
Pin Description (continued)
PIN
TQFN
TQFP
NAME
INPUT/
OUTPUT
FUNCTION
16
21
D+
Input/
Output
USB D+ Signal. Connect D+ to a USB “B” connector through a 33
Ω (±1%)
series resistor. The 1.5k
Ω D+ pullup resistor is internal to the device.
17
22, 23
V
CC
Input
USB Transceiver Power-Supply Input. Connect V
CC
to a positive 3.3V power
supply. Bypass V
CC
to ground with a 1.0µF ceramic capacitor as close to the
V
CC
pin as possible.
18
24
VBCOMP
Input
V
BUS
Comparator Input. VBCOMP is internally connected to a voltage
comparator to allow the SPI master to detect (through an interrupt or checking
a register bit) the presence or loss of power on V
BUS
. Bypass VBCOMP to
ground with a 1.0µF ceramic capacitor.
19
26
XI
Input
Crystal Oscillator Input. Connect XI to one side of a parallel resonant 12MHz
(±0.25%) crystal and a capacitor to GND. XI can also be driven by an external
clock referenced to V
CC
.
20
27
XO
Output
Crystal Oscillator Output. Connect XO to the other side of a parallel resonant
12MHz (±0.25%) crystal and a capacitor to GND. Leave XO unconnected if XI
is driven with an external source.
21
29
GPIN0
22
30
GPIN1
23
31
GPIN2
24
32
GPIN3
Input
General-Purpose Inputs. GPIN3–GPIN0 are connected to V
L
with internal
pullup resistors. GPIN3–GPIN0 logic levels are referenced to the voltage on V
L
.
The SPI master samples GPIN3–GPIN0 states by reading bit 7 through bit 4 of
the IOPINS (R20) register. Writing to these bits has no effect.
—
9, 16, 25, 28
N.C.
—
No Internal Connection
EP
—
GND
Input
Exposed Paddle on the Bottom of the TQFN Package. Connect EP to GND.
Figure 4. SPI Command Byte
b7
b6
b5
b4
b3
b2
b1
b0
Reg4
Reg3
Reg2
Reg1
Reg0
0
DIR
ACKSTAT
Figure 5. USB Status Bits Clocked Out as First Byte of Every Transfer (Full-Duplex Mode Only)
b7
b6
b5
b4
b3
b2
b1
b0
SUSPIRQ
URESIRQ
SUDAVIRQ
IN3BAVIRQ
IN2BAVIRQ
OUT1DAVIRQ
OUT0DAVIRQ
IN0BAVIRQ
