Rainbow Electronics MAX9216 User Manual
Page 12
MAX9210/MAX9212/MAX9214/MAX9216/MAX9220/MAX9222
Programmable DC-Balance
21-Bit Deserializers
12
______________________________________________________________________________________
bias resistors, along with the 100
Ω ±1% tolerance ter-
mination resistor, provide +15mV of differential input.
However, the +15mV bias causes degradation of
RSKM proportional to the slew rate of the clock input.
For example, if the clock transitions 250mV in 500ps,
the slew rate of 0.5mV/ps reduces RSKM by 30ps.
Unused LVDS Data Inputs
In non-DC-balanced mode, leave unused LVDS data
inputs open. In non-DC balanced mode, the input fail-
safe circuit drives the corresponding outputs low and no
pullup or pulldown resistors are needed. In DC-balanced
mode, at each unused LVDS data input, pull the inverting
input up to V
CC
using a 10k
Ω resistor, and pull the nonin-
verting input down to ground using a 10k
Ω resistor. Do
not connect a termination resistor. The pullup and pull-
down resistors drive the corresponding outputs low and
prevent switching due to noise.
PWRDWN
Driving PWRDWN low puts the outputs in high imped-
ance, stops the PLL, and reduces supply current to
50µA or less. Driving PWRDWN high drives the outputs
low until the PLL locks. The outputs of two deserializers
can be bused to form a 2:1 mux with the outputs con-
trolled by PWRDWN. Wait 100ns between disabling one
deserializer (driving PWRDWN low) and enabling the
second one (driving PWRDWN high) to avoid con-
tention of the bused outputs.
Input Clock and PLL Lock Time
There is no required timing sequence for the applica-
tion or reapplication of the parallel rate clock (RxCLK
IN) relative to PWRDWN, or to a power-supply ramp for
proper PLL lock. The PLL lock time is set by an internal
counter. The maximum time to lock is 32,800 clock
periods. Power and clock should be stable to meet the
lock time specification. When the PLL is locking, the
outputs are low.
Power-Supply Bypassing
There are separate on-chip power domains for digital
circuits, outputs, PLL, and LVDS inputs. Bypass each
V
CC
, V
CCO
, PLL V
CC
, and LVDS V
CC
pin with high-fre-
quency, surface-mount ceramic 0.1µF and 0.001µF
capacitors in parallel as close to the device as possi-
ble, with the smallest value capacitor closest to the
supply pin.
Cables and Connectors
Interconnect for LVDS typically has a differential imped-
ance of 100
Ω. Use cables and connectors that have
matched differential impedance to minimize impedance
discontinuities.
Twisted-pair and shielded twisted-pair cables offer
superior signal quality compared to ribbon cable and
tend to generate less EMI due to magnetic field cancel-
ing effects. Balanced cables pick up noise as common
mode, which is rejected by the LVDS receiver.
Board Layout
Keep the LVTTL/LVCMOS outputs and LVDS input sig-
nals separated to prevent crosstalk. A four-layer PC
board with separate layers for power, ground, LVDS
inputs, and digital signals is recommended.
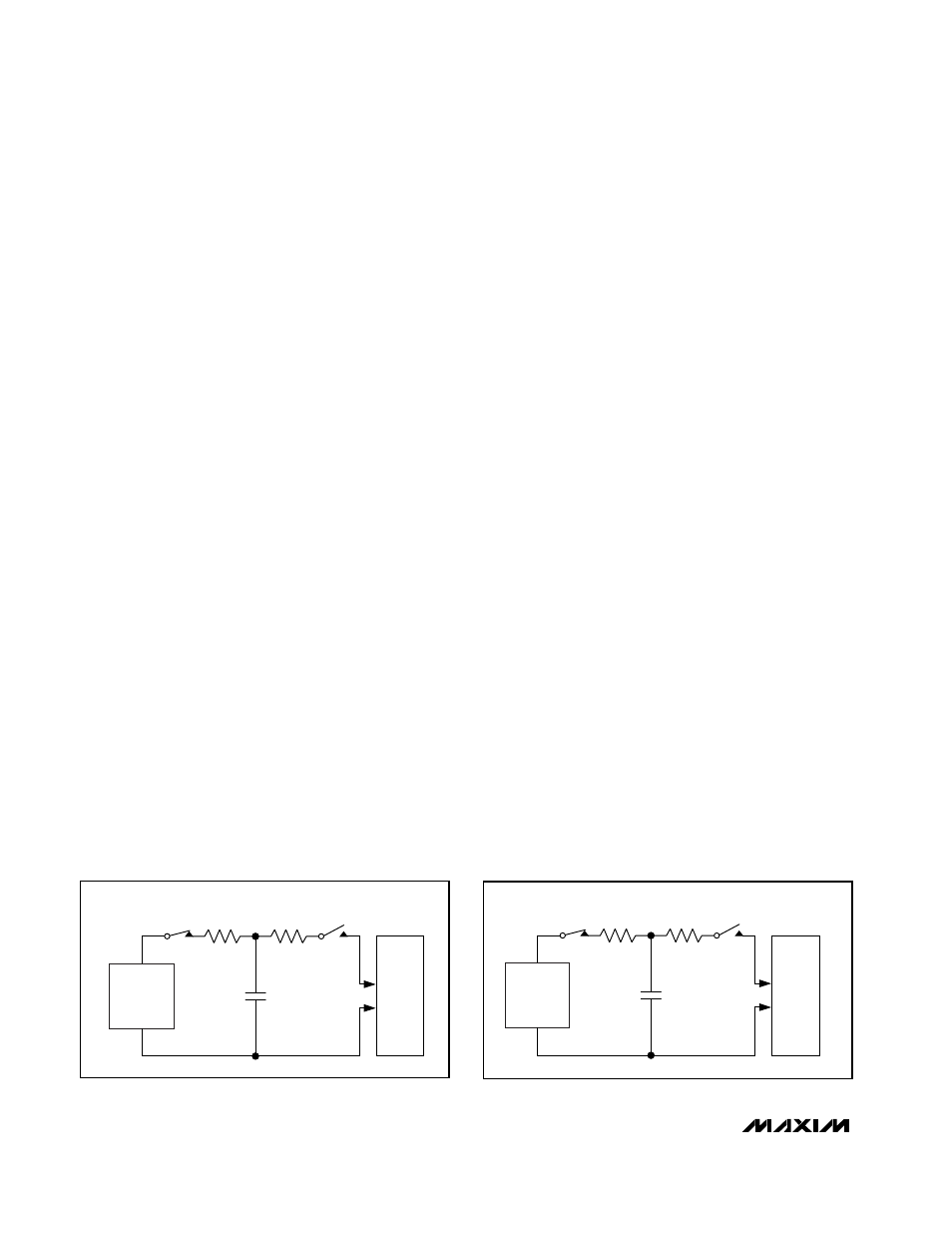
IEC 61000-4-2 Level 4 ESD Protection
The IEC 61000-4-2 standard specifies ESD tolerance
for electronic systems. The IEC 61000-4-2 model
(Figure 14) specifies a 150pF capacitor that is dis-
charged into the device through a 330
Ω resistor. The
MAX9210/MAX9212/MAX9214/MAX9216/MAX9220/
MAX9222 LVDS inputs are rated for IEC 61000-4-2
level 4 (
±8kV contact discharge and ±15kV air dis-
charge). IEC 61000-4-2 discharges higher peak current
and more energy than the HBM due to the lower series
resistance and larger capacitor. The HBM (Figure 15)
specifies a 100pF capacitor that is discharged into the
device through a 1.5k
Ω resistor. All pins are rated for
±5kV HBM.
STORAGE
CAPACITOR
HIGH-
VOLTAGE
DC
SOURCE
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
CHARGE-CURRENT-
LIMIT RESISTOR
DISCHARGE
RESISTANCE
R1
50
Ω TO 100Ω
R2
330k
Ω
C
S
150pF
Figure 14. IEC 61000-4-2 Contact Discharge ESD Test Circuit
STORAGE
CAPACITOR
HIGH-
VOLTAGE
DC
SOURCE
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
CHARGE-CURRENT-
LIMIT RESISTOR
DISCHARGE
RESISTANCE
R1
1M
Ω
R2
1.5k
Ω
C
S
100pF
Figure 15. Human Body ESD Test Circuit
