Xerox 721P88200 User Manual
Page 105
AFP PRINT FLOWS
DOCUPRINT IPS SOLUTIONS GUIDE
D-3
RS/6000 data flow
The RS/6000 connection accepts ASCII, ditroff, MO:DCA-P, PCL 5e,
EUC (Extended UNIX commands), DBASCII (double-byte ASCII),
1403 line-mode (EBCDIC) data, PostScript level 2 and 3, SAP ABAP
line data, and SAP OTF data streams. In turn, it outputs IPDS,
PostScript (from AIX or BSD attached printers), PPDS, and PCL 4/5/
5c data streams.
To create resources in the RS/6000 environment, you may use the
PPFA/6000 program. The RS/6000 connection supports both AFP
and non-AFP printers, and enables printer sharing between System/
390 and AIX systems.
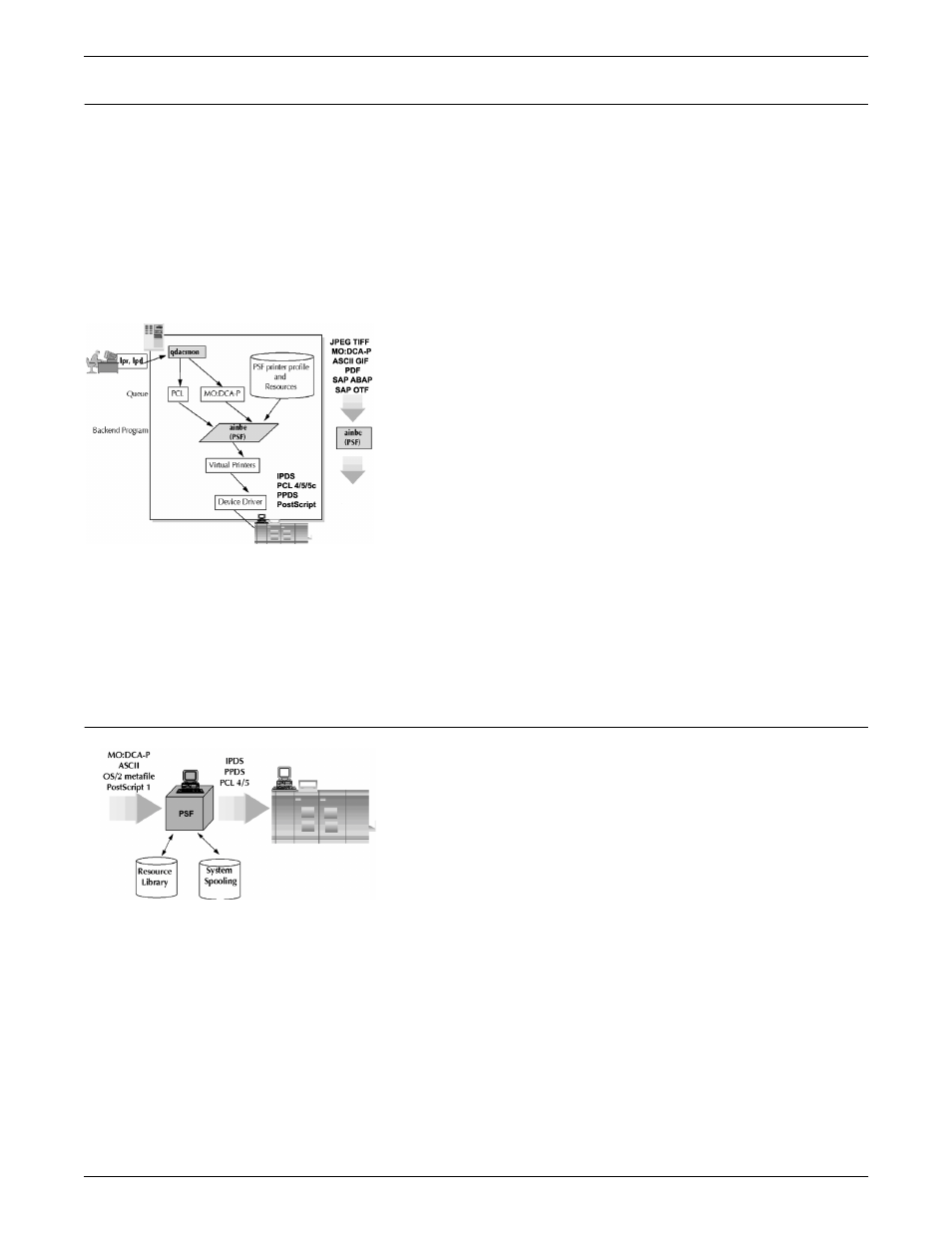
AIX print flow
1. An application creates the print output.
2. An lpr or lpd command is issued to transfer the output into the
qdaemon.
3. The qdaemon determines what the input data stream to PSF is.
If required, the qdaemon transforms the data stream to the
necessary format.
4. When the specified printer is available according to job control
parameters, the qdaemon schedules the job to PSF. This PSF
task is identified as “ainbe” on the RS/6000.
5. PSF identifies and retrieves any necessary AFP resources
stored on DASD.
6. PSF (ainbe) composes the data stream into IPDS and directs
the output to a virtual printer, which in turn writes the data to a
device driver on the IPDS printer.
PS/data flow
The PS/2 connection accepts ASCII, MO:DCA-P, OS/2 metafile, and
PostScript 1 data streams. In turn, it outputs IPDS, PPDS, and PCL
4/5 data streams.
1. An application creates the print output.
2. The print job is submitted for printing.
3. When the specified printer is available according to the job
parameters, PSF/2 identifies and retrieves any necessary AFP
resources from the resource libraries.
4. PSF composes the data stream into IPDS and directs the
output to the printer.
