Gcd( gcd( 1 – Texas Instruments TI-73 EXPLORER User Manual
Page 42
36
Chapter 2: Math Operations
7302ENG.DOC CH2 Math Operations, English Julie Hewlett Revised: 07/29/98 11:58 AM Printed: 05/19/99 8:58
AM Page 36 of 32
Add
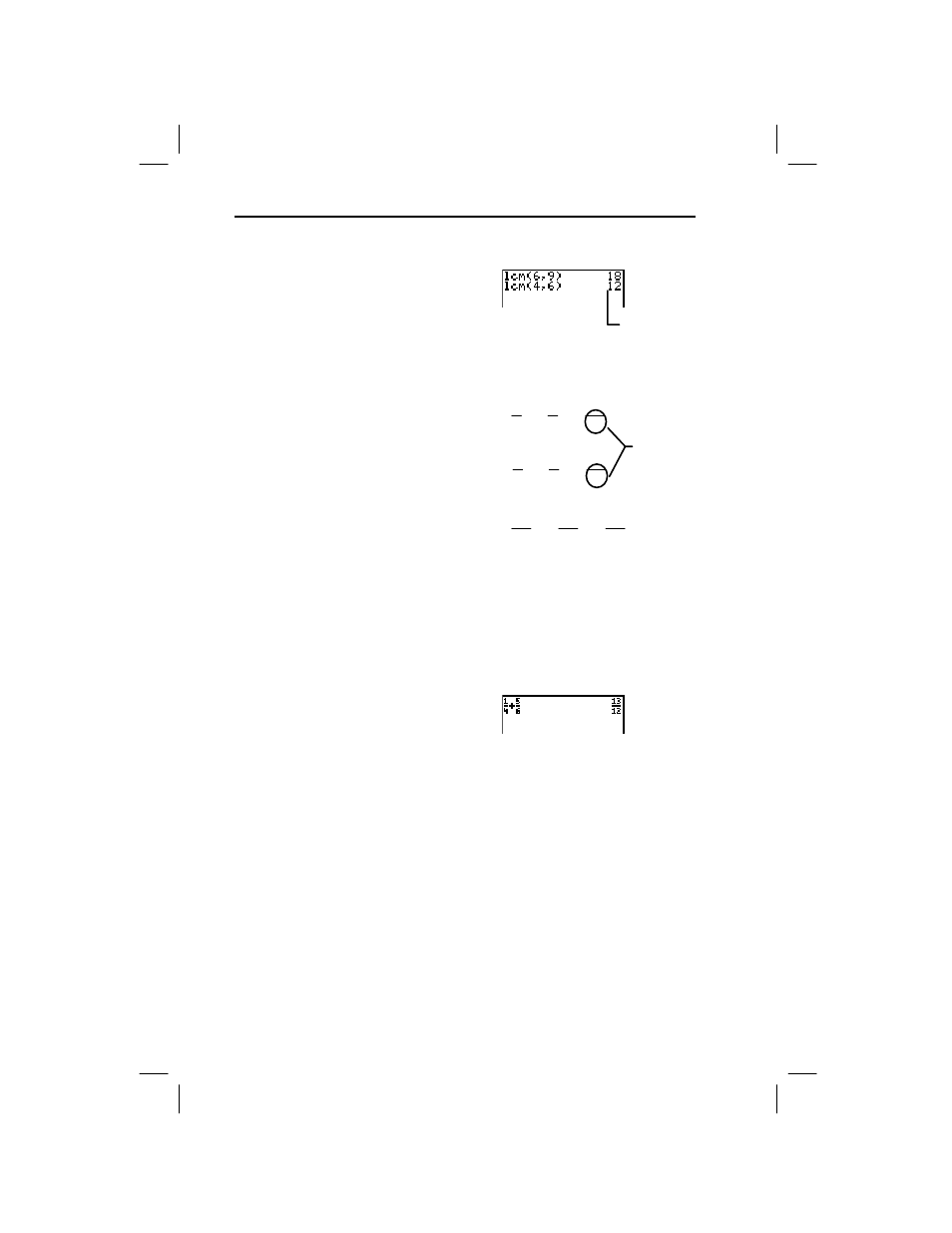
1
/
4
+
5
/
6
(using LCM).
1. Find the LCM of the
denominators.
1
1
4
¡
6
E b
2. Use the LCM to convert
1
/
4
and
5
/
6
to fractions where
12 is the common
denominator (without using
the calculator).
3. Add the newly converted
fractions (without using the
calculator).
4. Verify your answer by
adding the original fractions
on the calculator. Select the
b/c
Display Format mode
setting and clear the Home
screen, if desired.
. # # # " b
- l :
1
=
4
" \
5
=
6
b
gcd(
gcd( 1
2
2
The greatest common divisor (GCD) function returns the
largest number that divides into two positive whole numbers
or lists of positive whole numbers evenly. If both arguments
are lists, they must have the same number of elements. If one
argument is a list and the other a non-list, the non-list is paired
with each element of the list, and a list is returned.
This is frequently used with fractions to reduce them to lowest
terms. See Chapter 2: Fractions for more information on
entering fractions.
³
3
12
+
10
12
=
13
12
5
6
Q
2
2
=
10
12
1
4
Q
3
3
=
3
12
LCM=12
Therefore, 12 is
the common
denominator.
