Using ° and r to specify degrees and radians, Using, 1 and 4 – Texas Instruments TI-73 EXPLORER User Manual
Page 222
216
Chapter 11: Trigonometry
7311ENG.DOC CH 11 Trigonometry, English Julie Hewlett Revised: 05/26/98 11:12 AM Printed: 05/19/99 9:02
AM Page 216 of 12
Using
Using
¡
and
and
r
to Specify Degrees and Radians
to Specify Degrees and Radians
-
u
"
1 and 4
1 and 4
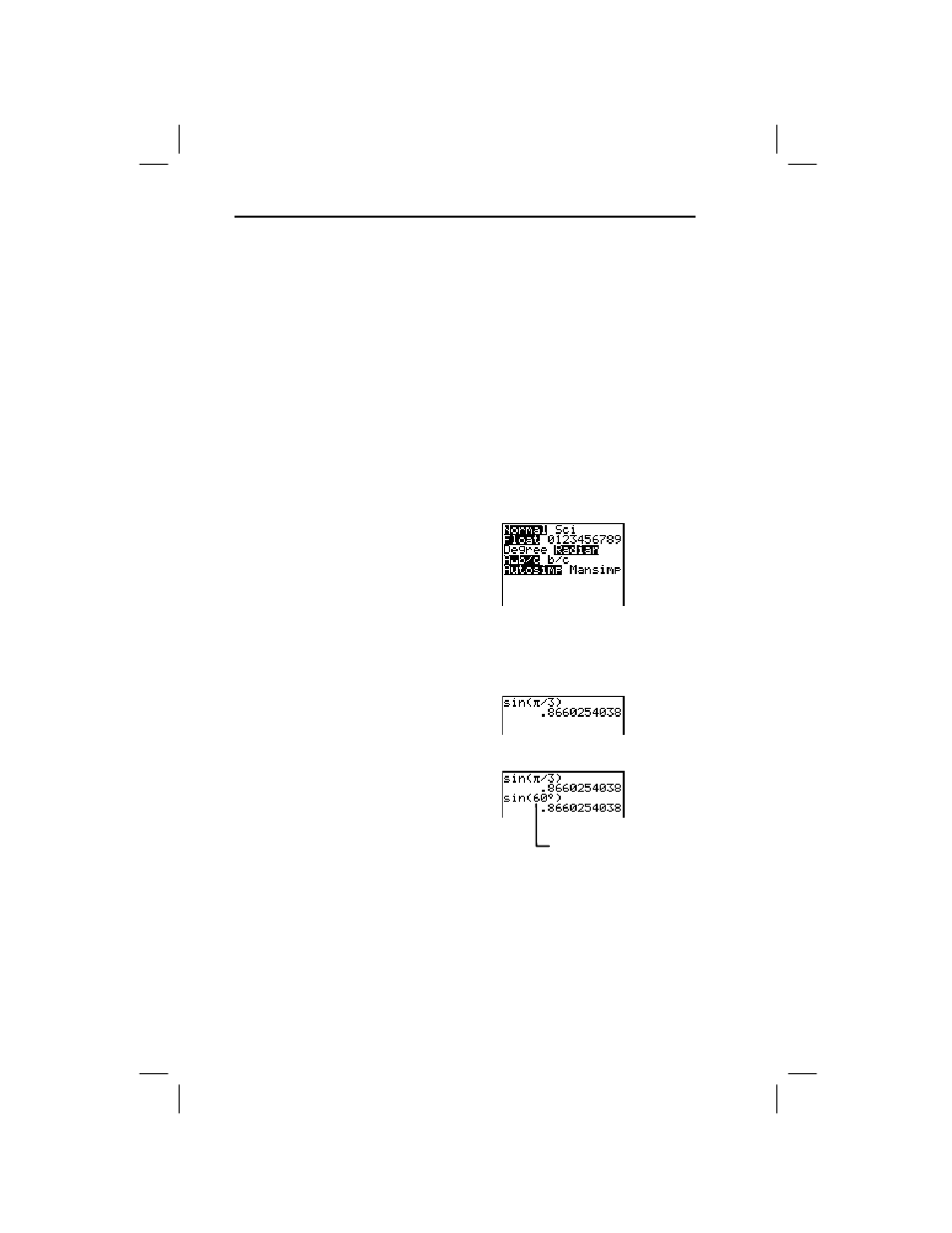
Normally, angles are interpreted according to the Angle mode
setting. However, you can specify an angle as degrees or
radians regardless of the Angle mode.
Suppose a series of trig calculations uses radians, but a few
use degrees. Rather than change from
Radian
to
Degree
Angle
mode and then back again, you can stay in the
Radian
Angle
mode and specify some angles as degrees.
In
Radian
Angle mode, calculate sin(p/3). Then, without
changing to the
Degree
Angle mode, calculate sin(60¡).
1. Select
Radian
Angle mode.
. # # " b
2. Return to the Home screen,
and clear it, if desired.
- l :
3. Enter
sin(
p
/3)
.
- u
1
- „ F
3
E b
4. Use the
¡
designator to
enter
sin(60
¡
)
.
- u
1
6 0
- u "
1
E b
Likewise, you can use
r
to specify an angle as radians in the
Degree
Angle mode.
³
60 is specified as degrees
even in Radian angle mode.
p
/3r=60
¡
.
