NEC PD78058FY(A) User Manual
Page 365
365
CHAPTER 17 SERIAL INTERFACE CHANNEL 0 (
µ
PD78058FY SUBSERIES)
2
3
4
5
6
7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
R/W
Transfer direction
specification
SCL
8
1
SDA0(SDA1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
R/W
Address
SCL
SDA0(SDA1)
H
SCL
SDA0(SDA1)
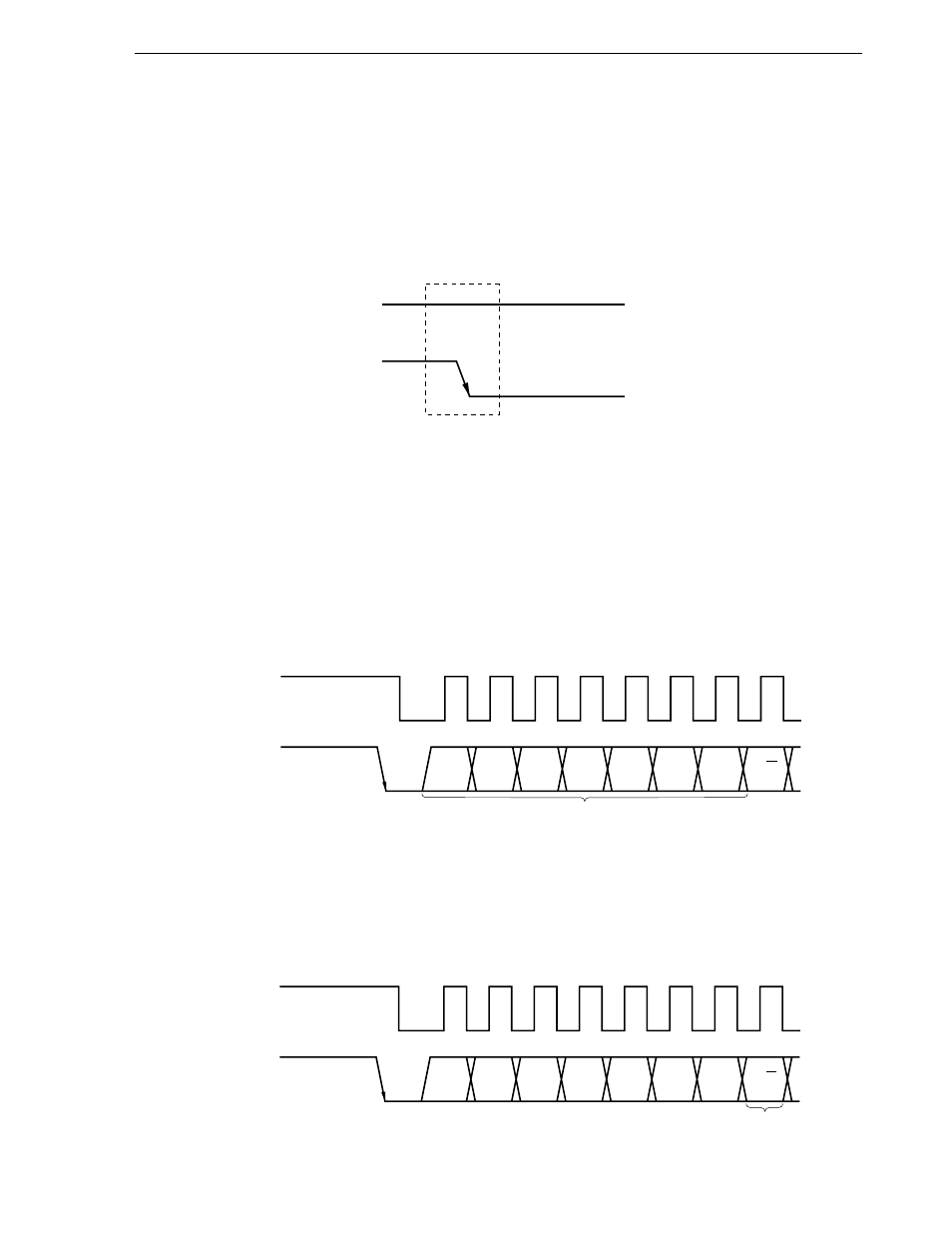
(a) Start condition
When the SDA0 (SDA1) pin level is changed from high to low while the SCL pin is high, this transition is
recognized as the start condition signal. This start condition signal, which is created using the SCL and
SDA0 (or SDA1) pins, is output from the master device to slave devices to initiate a serial transfer. See
section 17.4.5 Cautions on use of I
2
C bus mode for details of the start condition output.
The start condition signal is detected by hardware incorporated in slave devices.
Figure 17-15. Start Condition
(b) Address
The 7 bits following the start condition signal are defined as an address.
The 7-bit address data is output by the master device to specify a specific slave from among those
connected to the bus line. Each slave device on the bus line must therefore have a different address.
Therefore, after a slave device detects the start condition, it compares the 7-bit address data received
and the data of the slave address register (SVA). After the comparison, only the slave device in which
the data are a match becomes the communication partner, and subsequently performs communication
with the master device until the master device sends a start condition or stop condition signal.
Figure 17-16. Address
(c) Transfer direction specification
The 1 bit that follows the 7-bit address data will be sent from the master device, and it is defined as the
transfer direction specification bit. If this bit is 0, it is the master device which will send data to the slave.
If it is 1, it is the slave device which will send data to the master.
Figure 17-17. Transfer Direction Specification
