Operation, Caution, B-8 multiple arc system considerations – Lincoln Electric POWER WAVE 11124 User Manual
Page 46: Basic modes of operation, Constant current (cc), Constant voltage (cv)
B-8
OPERATION
B-8
MULTIPLE ARC SYSTEM
CONSIDERATIONS
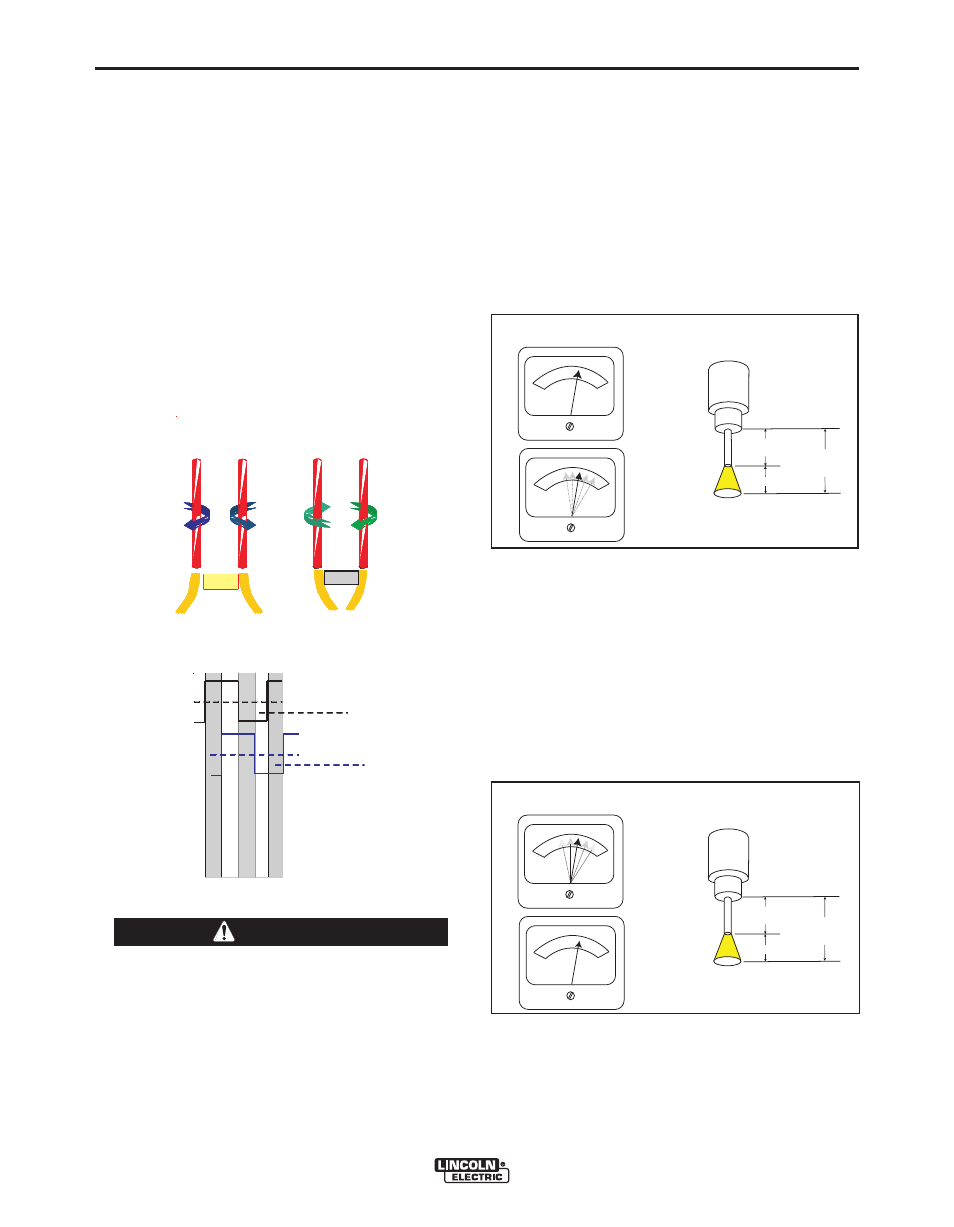
Large scale SAW applications often employ multiple
arcs to increase deposition rates. In multiple arc sys-
tems, magnetic forces created by like and opposing
weld currents of adjacent arcs can result in arc inter-
action that can physically push or pull the arc columns
together. To counteract this effect, the phase relation-
ship between adjacent arcs can be adjusted to alter-
nate and equalize the duration of magnetic push and
pull forces. This is accomplished by the use of an
optional K2282-1 Power Wave System Interface,
which not only synchronizes the arcs, but also
enables adjustment of the phase relationship between
them. Ideally, the net result is a cancellation of the
interacting forces.
FIGURE B.2
FIGURE B.3
Never simultaneously touch electrically "hot"
parts in the electrode circuits of two different
welders. The electrode to electrode no load volt-
age of multiple arc systems with opposite polari-
ties can be double the no load voltage of each arc.
Consult the Safety information located at the front
of the Instruction Manual for additional informa-
tion.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
BASIC MODES OF OPERATION
CONSTANT CURRENT (CC)
• Operator presets Current and desired Voltage.
• The Power Source:
- Goal is to maintain a constant arc length.
- Drives a constant Current.
- Synergically Controls WFS to Maintain Voltage
at the desired Set point.
• Arc Length is proportional to Voltage.
• Traditionally used for larger diameter wires and
slower travel speeds.
CONSTANT VOLTAGE (CV)
• Operator presets Wire Feed Speed and desired
Voltage
• The Power Source:
- Goal is to maintain a constant arc length.
- Commands constant wire feed speed
- Synergically Controls Current to Maintain
Voltage at the desired Set point
• Arc Length is proportional to Voltage
• Traditionally used for smaller diameter wires and
faster travel speeds.
POWER WAVE® AC/DC 1000
+
-
-
+
PUSH
+
+
-
-
PULL
+
-
-
+
+
-
+
PUSH
+
+
-
-
PULL
PUSH
+
+
-
-
+
+
-
+
+
-
-
PULL
Lead Arc
Trai l Arc
P
o
s
it
iv
e
N
e
g
a
ti
v
e
P
o
s
it
iv
e
P
o
s
it
iv
e
N
e
g
a
ti
v
e
N
e
g
a
ti
v
e
P
o
s
it
iv
e
N
e
g
a
ti
v
e
P
o
s
it
iv
e
N
e
g
a
ti
v
e
Lead Arc
Trai l Arc
P
U
S
H
P
U
S
H
P
U
S
H
P
U
L
L
P
U
L
L
CAUTION
Extension
Heating= Vir
Arc Length= Varc
Total Electrical
Stick out
V= Vir+Varc
TO
MAINTAIN CONSTANT
ARC LENGTH
AND
WIRE FEED
SPEED VARIED
CURRENT HELD
CONSTANT
AMPS
CONSTANT CURRENT (CC)
WIRE FEED SPEED
Extension
Heating= Vir
Arc Length= Varc
Total Electrical
Stick out
V= Vir+Varc
TO
MAINTAIN CONSTANT
ARC LENGTH
AND
WIRE FEED SPEED
HELD CONSTANT
CURRENT VARIED
AMPS
CONSTANT VOLTAGE (CV)
WIRE FEED SPEED
