2 operation, 1 overview, 2 laser exposure process – Konica Minolta 5430 DL 5440 DL 5450 User Manual
Page 41: Operation -4, Overview -4, Laser exposure process -4
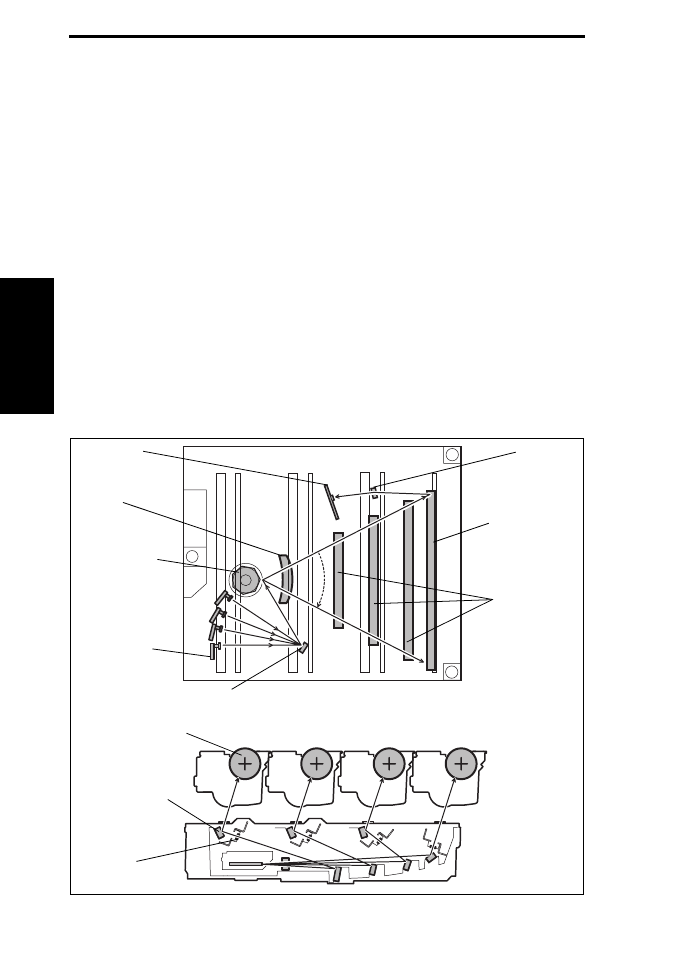
Print Head (PH)
Main Unit Theory of Operation
2-4
II Co
mpo
siti
o
n/
Op
er
atio
n
2.2
Operation
2.2.1
Overview
• Four semiconductor lasers provided, one for each of the four different colors. A single
Polygon Motor is used to make a scan motion.
• Each Photo Conductor is irradiated with a laser light so that an electrostatic latent image
is formed on it.
NOTE
• The magicolor 5430 DL/5440 DL uses a different PH unit than does the magicolor
5450. When replacing the PH unit, be sure to use the PH unit for the appropriate
model. Using the incorrect PH unit will adversely affect image quality.
2.2.2
Laser exposure process
1.
The laser light emitted by each of the Semiconductor Laser/Y, M, C, and K is reflected
onto the Polygon Mirror via the Synthetic Mirror.
2.
Since the angle of incidence for each color of laser light varies, the laser light reflected
by the Polygon Mirror is reflected at a different angle for each color.
3.
The condensing angle of each color of laser light is corrected by the G1 Lens before
reaching each Return Mirror.
4.
The K laser light is condensed on the surface of the Photo Conductor through the Sep-
aration Mirror and G2 Lens.
5.
The Y, M, or C laser light is condensed on the Photo Conductor through the Separation
Mirror, G2 Lens, and Return Mirror.
SOS Lens
4138to2502c0
G1 Lens
G2 Lens
Synthetic Mirror
Polygon Mirror
Separation Mirror
Photo Conductor
Semiconductor
Laser
Return Mirror/2nd
SOS Sensor
Return Mirror/1st
Y
M
C
K
Y
M
C
K
K
C
M
Y
K
C
M
Y
M
C
K
Y
