IBM SC34-6814-04 User Manual
Page 242
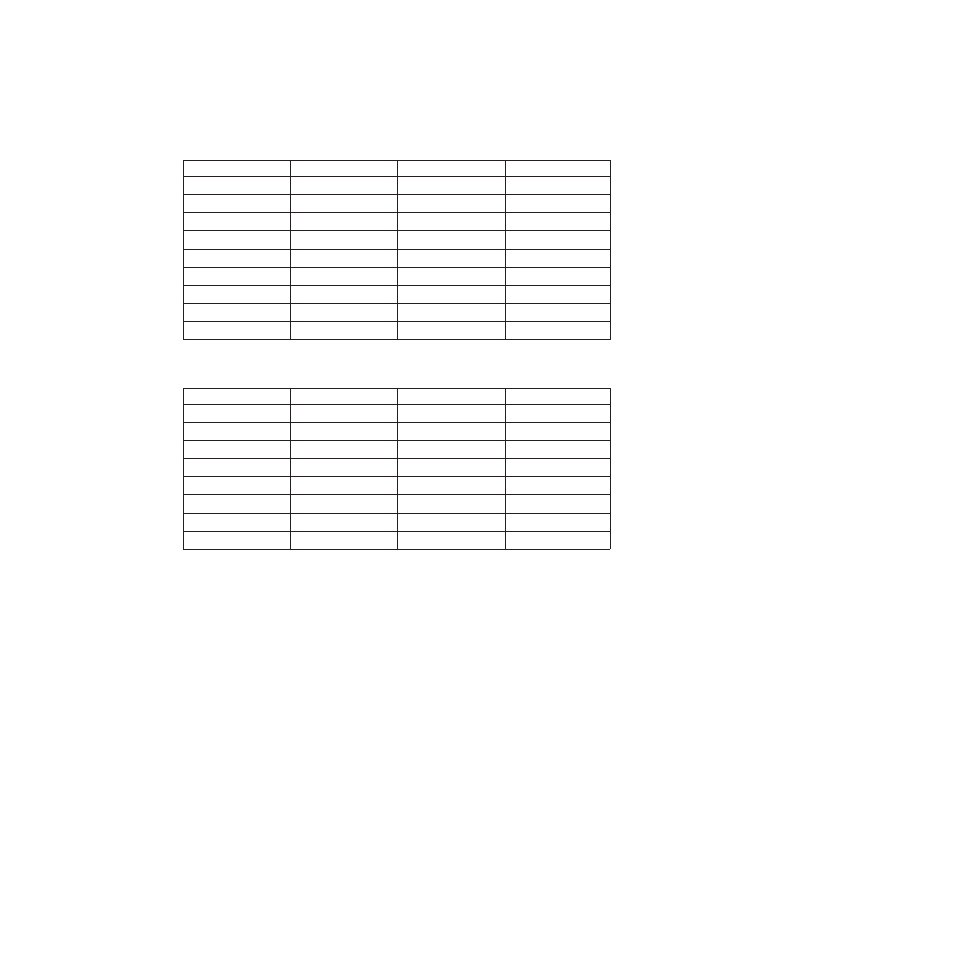
Table 11. READQ TS: User arguments and associated keywords, data types, and
input/output types
Argument
Keyword
Data type
Input/output type
Arg1
QUEUE
CHAR(8)
input
Arg1
QNAME
CHAR(16)
input
Arg2
SET
DATA-AREA, PTR
output
Arg2
INTO
DATA-AREA
output
Arg3
LENGTH
BIN(15)
input/output
Arg4
NUMITEMS
BIN(15)
output
Arg5
ITEM
BIN(15)
input
Arg6
*
*
Arg7
SYSID
CHAR(4)
input
Table 12. DELETEQ TS: User arguments and associated keywords, data types, and
input/output types
Argument
Keyword
Data type
Input/output type
Arg1
QUEUE
CHAR(8)
input
Arg1
QNAME
CHAR(16)
input
Arg2
*
*
*
Arg3
*
*
*
Arg4
*
*
*
Arg5
*
*
*
Arg6
*
*
*
Arg7
SYSID
CHAR(4)
input
Modifying user arguments: User exit programs can modify user arguments, as
follows:
For input arguments, the user exit program should obtain sufficient storage to hold
the modified argument, set up that storage to the required value, and set the
associated pointer in the parameter list to the address of the newly acquired area.
For output arguments, and for input/output arguments, the user exit program can
update the argument in place, because the area of storage is represented by a
variable in the application which is expected to receive a value from CICS.
Note:
1. CICS does not check changes to argument values, so any changes must
be verified by the user exit program making the changes.
2. It is not advisable for XTSEREQ to modify output arguments or for
XTSEREQC to modify input arguments.
Adding user arguments: Global user exit programs can add arguments
associated with the SYSID keyword. You must ensure that the arguments you
specify or modify in your exit programs are valid.
Assuming that the argument to be added does not already exist, the user exit
program must:
220
Customization Guide
