Monitoring functions, The monitor call – IBM SC33-1683-02 User Manual
Page 362
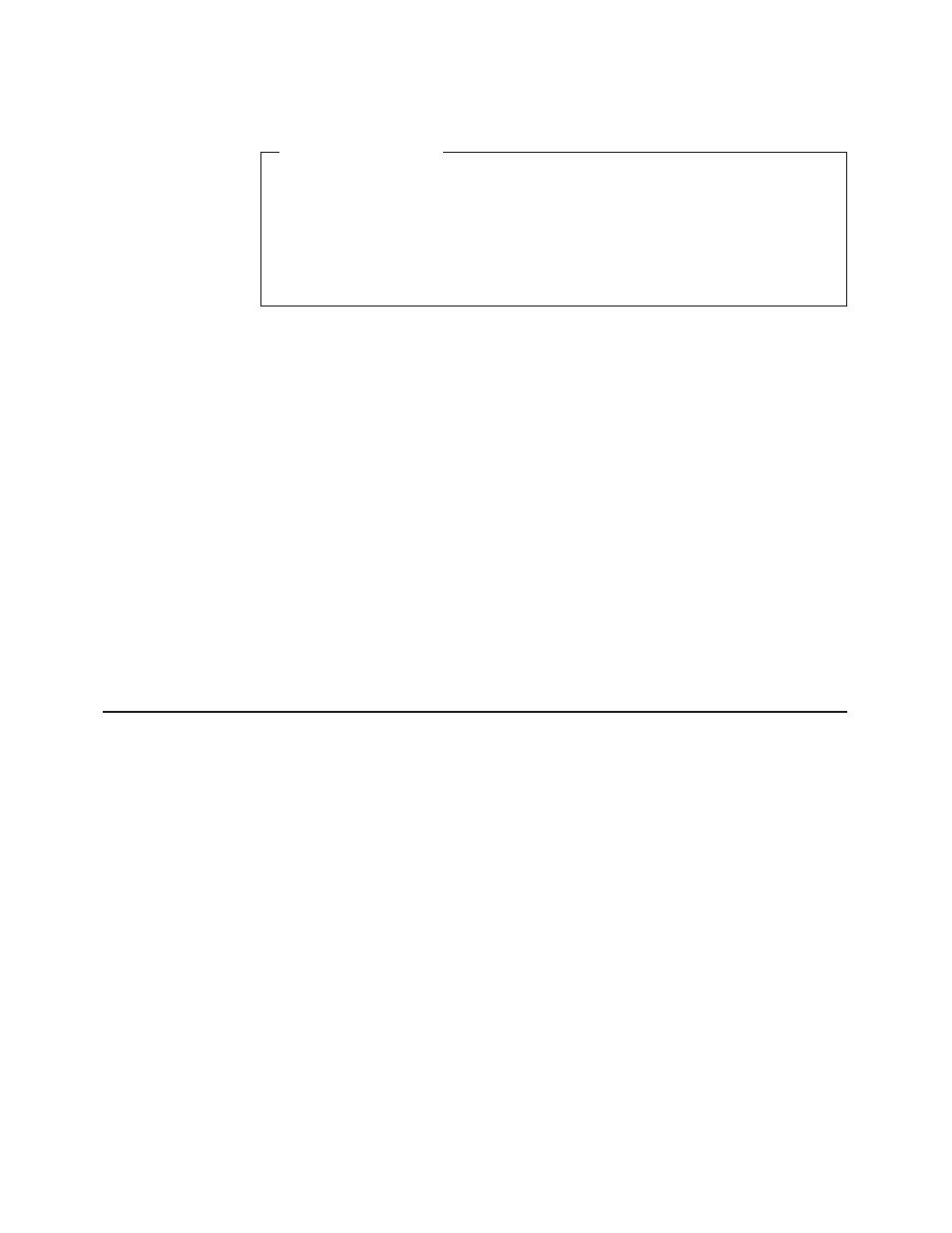
SET_PARAMETERS
DFHLGPAX [CALL,]
[CLEAR,]
[IN,
FUNCTION(SET_PARAMETERS),
[KEYPOINT_FREQUENCY(name4 | (Rn) ),]]
[OUT,
RESPONSE(name1 | *),
REASON(name1 | *)]
KEYPOINT_FREQUENCY(name4 | *)
specifies the activity keypointing frequency of the CICS region.
Permitted values are 0, or any integer between 200 and 65535 inclusive.
name4
The name of a 4-byte location that contains the new frequency value.
(Rn)
A register that contains the new frequency value.
RESPONSE and REASON values for SET_PARAMETERS:
RESPONSE
REASON
OK
None
EXCEPTION
OUT_OF_RANGE
DISASTER
None
INVALID
None
KERNERROR
None
Note: For more detail, refer to the explanation of RESPONSE and REASON in
“General form of an XPI call” on page 286.
Monitoring functions
There are two XPI monitoring functions. These are the DFHMNMNX calls
MONITOR and INQUIRE_MONITORING_DATA.
DFHMNMNX calls cannot be used in any exit program invoked from any global
user exit point in the:
v
Dispatcher domain
v
Dump domain
v
Monitor domain
v
Statistics domain
v
Transient data program.
INQUIRE_MONITORING_DATA calls cannot be used in any exit program invoked
from any global user exit point in DFHTCP or DFHZCP (that is, at any of the exit
points named “XTCx...” or “XZCx...”).
The MONITOR call
The MONITOR XPI call is similar to the EXEC CICS MONITOR command. It
enables you to invoke user event-monitoring points (EMPs) in your exit programs.
log manager functions
330
CICS TS for OS/390: CICS Customization Guide
