Esa/390 mode – IBM 990 User Manual
Page 80
68
IBM
^
zSeries 990 Technical Guide
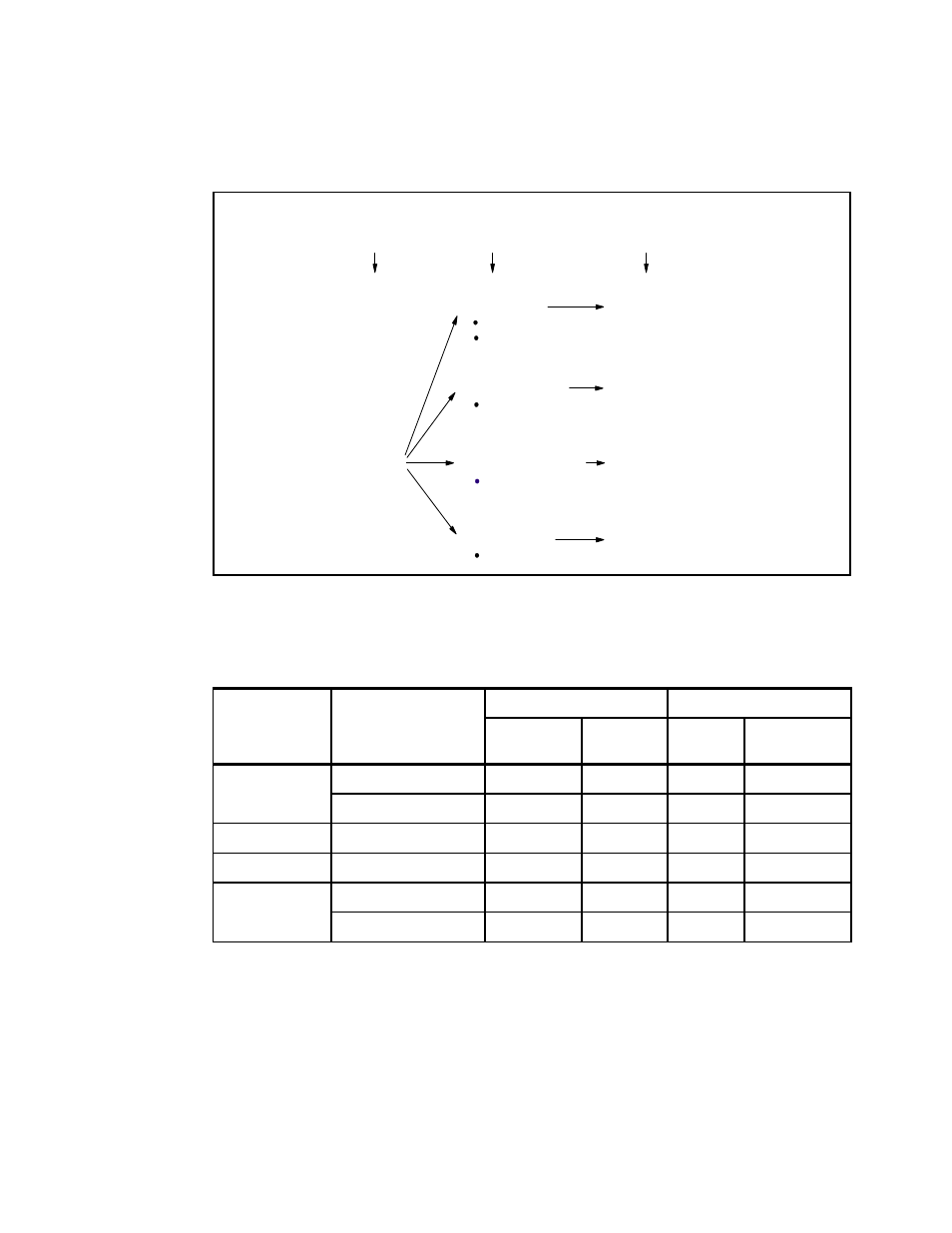
Figure 2-18 shows the z990 modes and memory diagram, summarizing all image modes,
with their processor types and the Central Storage (CS) and Expanded Storage (ES)
definitions allowed for each mode.
Figure 2-18 Modes and memory diagram
Table 2-9 shows the z990 storage
allocation
and
usage
possibilities, which depend upon the
image and architecture modes.
Table 2-9 Storage definition and usage possibilities
Remember that either a z/Architecture mode or an ESA/390 architecture mode operating
system can run in an ESA/390 image mode on a z990. Any ESA/390 image can be defined
with more than 2 GB of central storage
and
can have expanded storage. These options allow
you to configure more storage resources than the operating system is capable of addressing.
ESA/390 mode
In ESA/390 mode, storage addressing can be 31- or 64-bits, depending on the operating
system architecture
and
the operating system configuration.
Image mode
Architecture mode
(addressability)
Maximum central storage
Expanded storage
Architecture
z990
definition
z990
definable
Operating
system usage
ESA/390
z/Architecture (64-bit)
16 EB
128 GB
yes
only
by z/VM
ESA/390 (31-bit)
2 GB
128 GB
yes
yes
ESA/390 TPF
ESA/390 (31-bit)
2 GB
128 GB
yes
yes
Coupling Facility
CFCC (64-bit)
16 EB
128 GB
no
no
Linux Only
z/Architecture (64-bit)
16 EB
128 GB
yes
only
by z/VM
ESA/390 (31-bit)
2 GB
128 GB
yes
yes
z990
Mode
Logically
Partitioned
Mode
ESA/390 Mode
ESA/390 TPF Mode
Coupling Facility Mode
Linux Only Mode
CPs
CPs only
ICFs and/or CPs
IFLs or CPs
Image
Modes
CS < = 128 GB
ES = Yes
CS < = 128 GB
ES = Yes
CS < = 128 GB
ES = No
CS < = 128 GB
ES = Yes
CPs and zAAPs
Definable Central Storage (CS)
and Expanded Storage
