Site 1 site 2, Gdps/pprc hyperswap, Planned – IBM 990 User Manual
Page 185: Unplanned, Remote copy (pprc), Chapter 7. sysplex functions, Figure 7-8 gdps/pprc (no extended distance rpq), Zseries
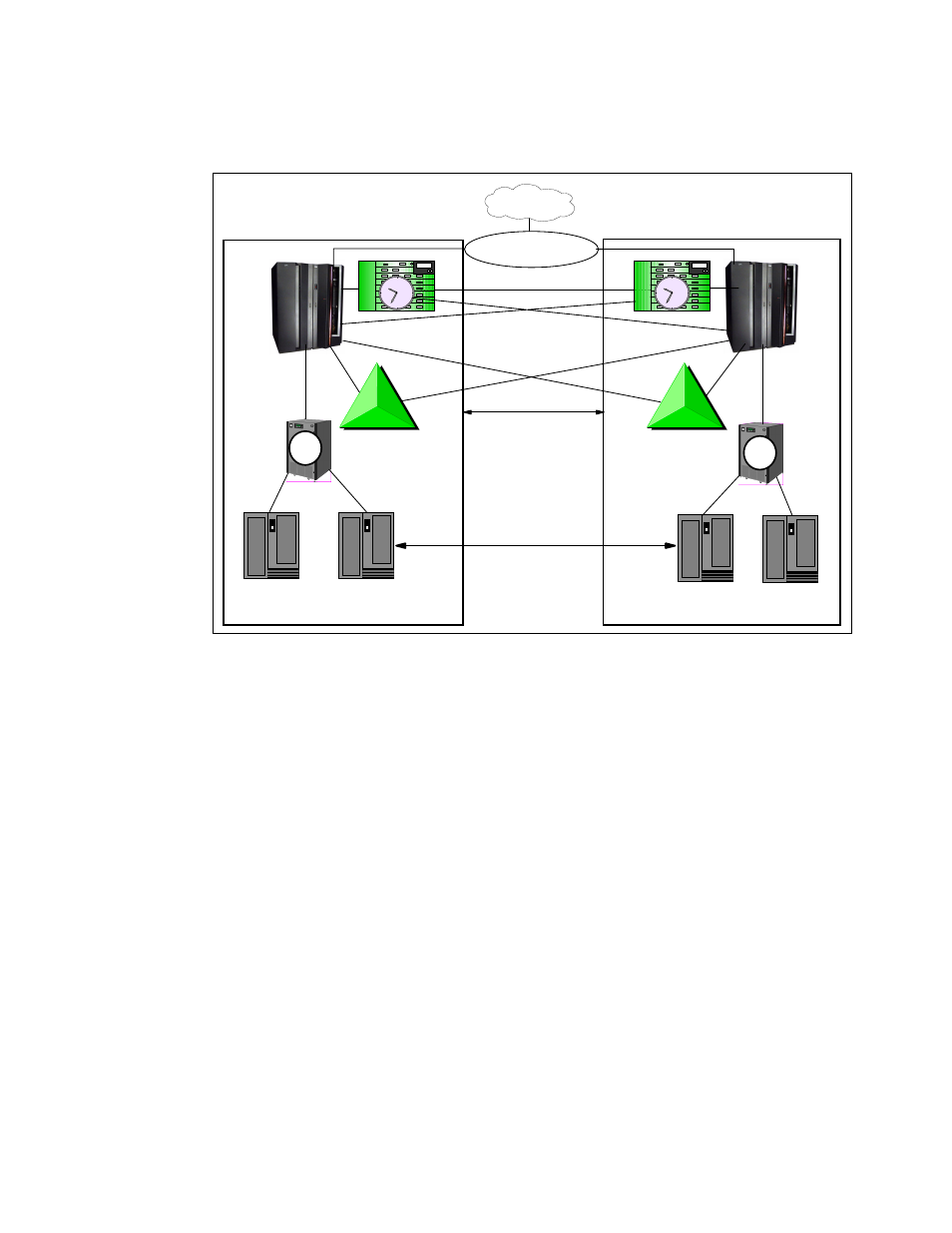
Chapter 7. Sysplex functions
173
Parallel Sysplex cluster must be configured with redundant hardware (for example, a Coupling
Facility and a Sysplex Timer in each site), and the cross-site connections must be redundant.
Figure 7-8 GDPS/PPRC (no extended distance RPQ)
All critical data resides on storage subsystems in site 1 (the primary copy of data) and is
mirrored to site 2 (the secondary copy of data) via PPRC synchronous remote copy.
GDPS/PPRC is capable of the following attributes:
Continuous availability
Near-transparent disaster recovery
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) less than an hour
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) of zero (optional)
Protects against localized area disasters
GDPS/PPRC HyperSwap™
The GDPS/PPRC HyperSwap function is designed to broaden the continuous availability
attributes of GDPS/PPRC by extending the Parallel Sysplex redundancy to disk subsystems.
The HyperSwap function can help significantly reduce the time needed to switch disks
between sites and the time to switch sites. GDPS/PPRC HyperSwap provides the ability to
transparently switch all primary PPRC disk subsystems with the secondary PPRC disk
subsystems for a
planned
or
unplanned
reconfiguration, as shown on Figure 7-9 on
CF01
CF02
Site 1
Site 2
Network
High Performance
Routing
Remote copy
(PPRC)
40km max
with DWDM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11 12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11 12
SW
SW
Primary disk
subsystems
Secondary disk
subsystems
zSeries
zSeries
