Usb data formats, 1 usb data formats – HP D315 User Manual
Page 105
Technical Reference Guide
5.7.1 USB DATA FORMATS
The USB I/F uses non-return-to-zero inverted (NRZI) encoding for data transmissions, in which a
1 is represented by no change (between bit times) in signal level and a 0 is represented by a
change in signal level. Bit stuffing is employed prior to NRZ1 encoding so that in the event a
string of 1’s is transmitted (normally resulting in a steady signal level) a 0 is inserted after every
six consecutive 1’s to ensure adequate signal transitions in the data stream. The USB
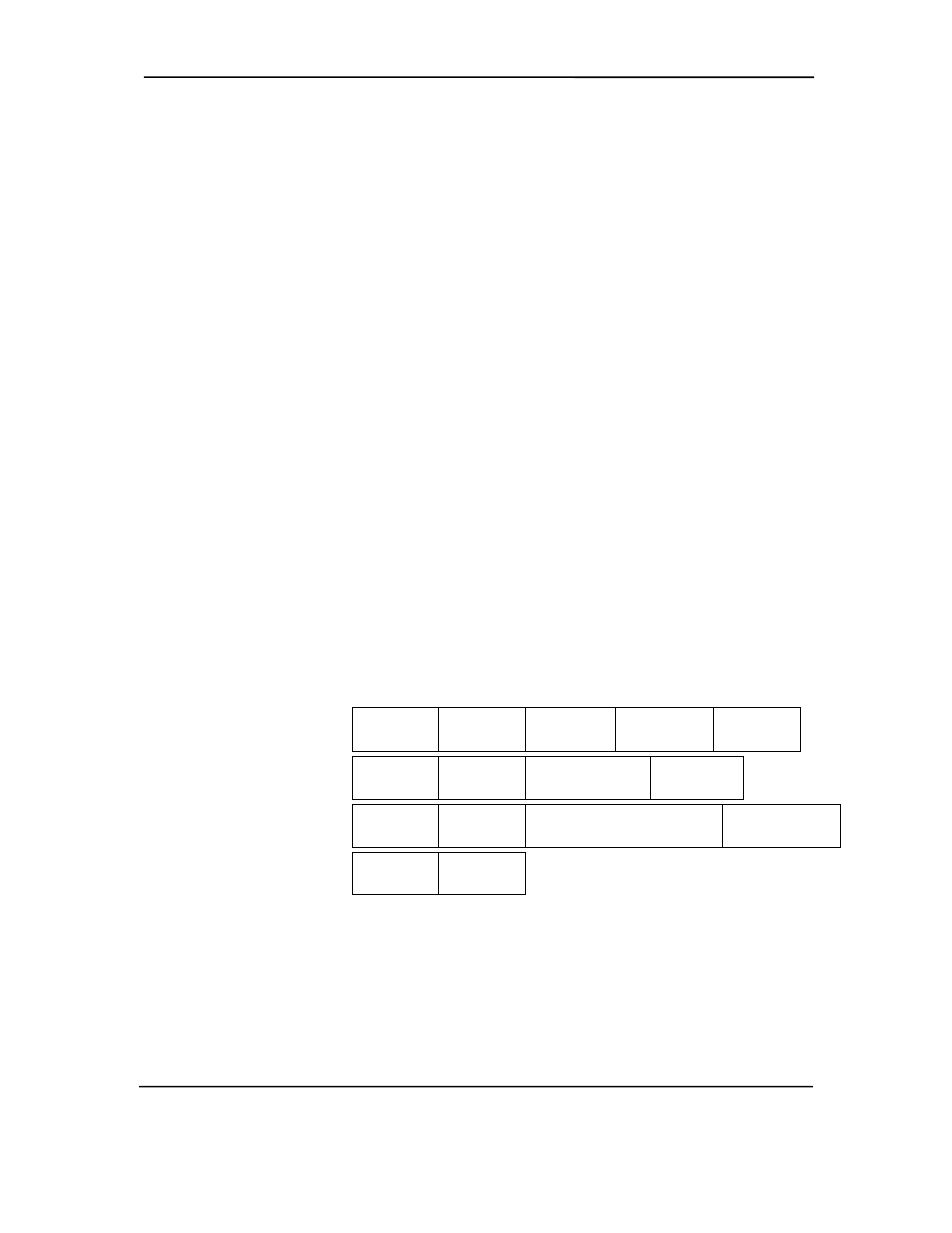
transmissions consist of packets using one of four types of formats (Figure 5-8) that include two
or more of seven field types.
♦
♦
♦
♦
♦
♦
♦
Sync Field – 8-bit field that starts every packet and is used by the receiver to align the
incoming signal with the local clock.
Packet Identifier (PID) Field – 8-bit field sent with every packet to identify the attributes (in.
out, start-of-frame (SOF), setup, data, acknowledge, stall, preamble) and the degree of error
correction to be applied.
Address Field – 7-bit field that provides source information required in token packets.
Endpoint Field – 4-bit field that provides destination information required in token packets.
Frame Field – 11-bit field sent in Start-of-Frame (SOF) packets that are incremented by the
host and sent only at the start of each frame.
Data Field – 0-1023-byte field of data.
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) Field – 5- or 16-bit field used to check transmission
integrity.
Sync Field
(8 bits)
PID Field
(8 bits)
Sync Field
(8 bits)
CRC Field
(16 bits)
Data Field
(0-1023 bytes)
PID Field
(8 bits)
Sync Field
(8 bits)
CRC Field
(5 bits)
Frame Field
(11 bits)
PID Field
(8 bits)
Sync Field
(8 bits)
CRC Field
(5 bits)
ENDP. Field
(4 bits)
Addr. Field
(7 bits)
PID Field
(8 bits)
Token Packet
SOF Packet
Data Packet
Handshake Packet
Figure 5-8. USB Packet Formats
Data is transferred LSb first. A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is applied to all packets (except a
handshake packet). A packet causing a CRC error is generally completely ignored by the receiver.
Compaq D315 and hp d325 Personal Computers
Featuring the AMD Athlon XP Processor
Second Edition - April 2003
5-23
