HP 5400ZL User Manual
Page 286
Quality of Service: Managing Bandwidth More Effectively
Globally-Configured QoS
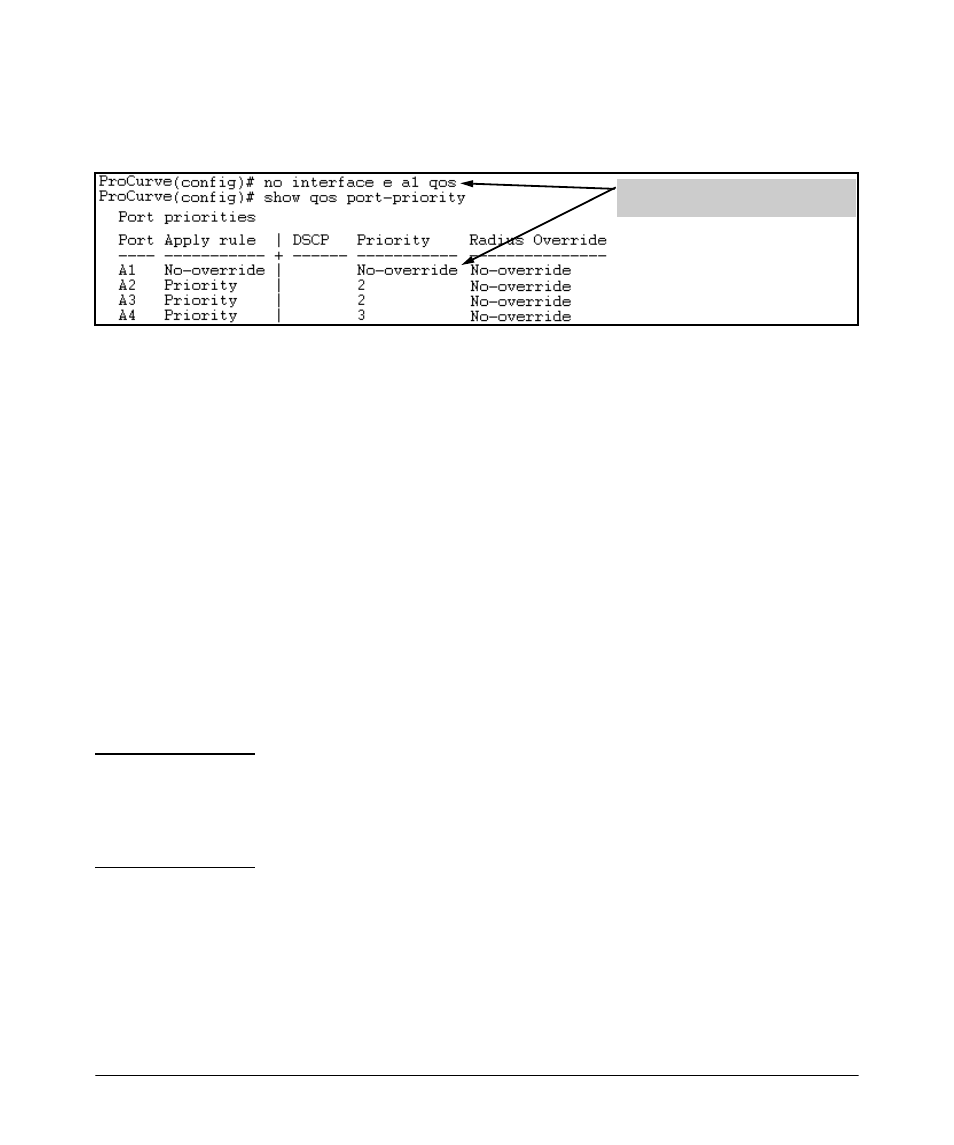
If you later decided to remove source-port A1 from QoS prioritization, you
would enter the following command:
In this instance, No-override indicates
that port A1 is not prioritized by QoS.
Figure 6-29. Returning a QoS-Prioritized VLAN to “No-override” Status
Assigning a DSCP Policy for a Global Source-Port Classifier
This global QoS packet-marking option assigns a previously configured DSCP
policy (codepoint and 802.1p priority) to outbound IP packets received from
the specified source-ports. The switch:
1. Selects an incoming IP packet on the basis of its source-port.
2. Overwrites the packet’s DSCP with the DSCP configured for matching
packets.
3. Assigns the 802.1p priority associated with the new DSCP. (See “Differen
tiated Services Codepoint (DSCP) Mapping” on page 6-88.)
4. Forwards the packet through the appropriate outbound port queue.
For more on DSCP, refer to “QoS Terminology” on page 6-7.
Creating a Policy Based on Source-Port Classifiers.
C o n f i g u r a t i o n
You can configure only one DSCP per source-port to mark matching packets.
N o t e s
Configuring a new DSCP for a source-port automatically overwrites (replaces)
any previous DSCP or 802.1p priority configuration for that source-port
classifier.
1. Identify the source-port classifier to which you want to assign a DSCP
policy.
2. Determine the DSCP policy for packets having the selected source-port:
a. Determine the DSCP you want to assign to the selected packets. (This
codepoint will be used to overwrite the DSCP carried in packets
received through the source-port from upstream devices.)
6-64
