Traffic shaping – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 55
5-3
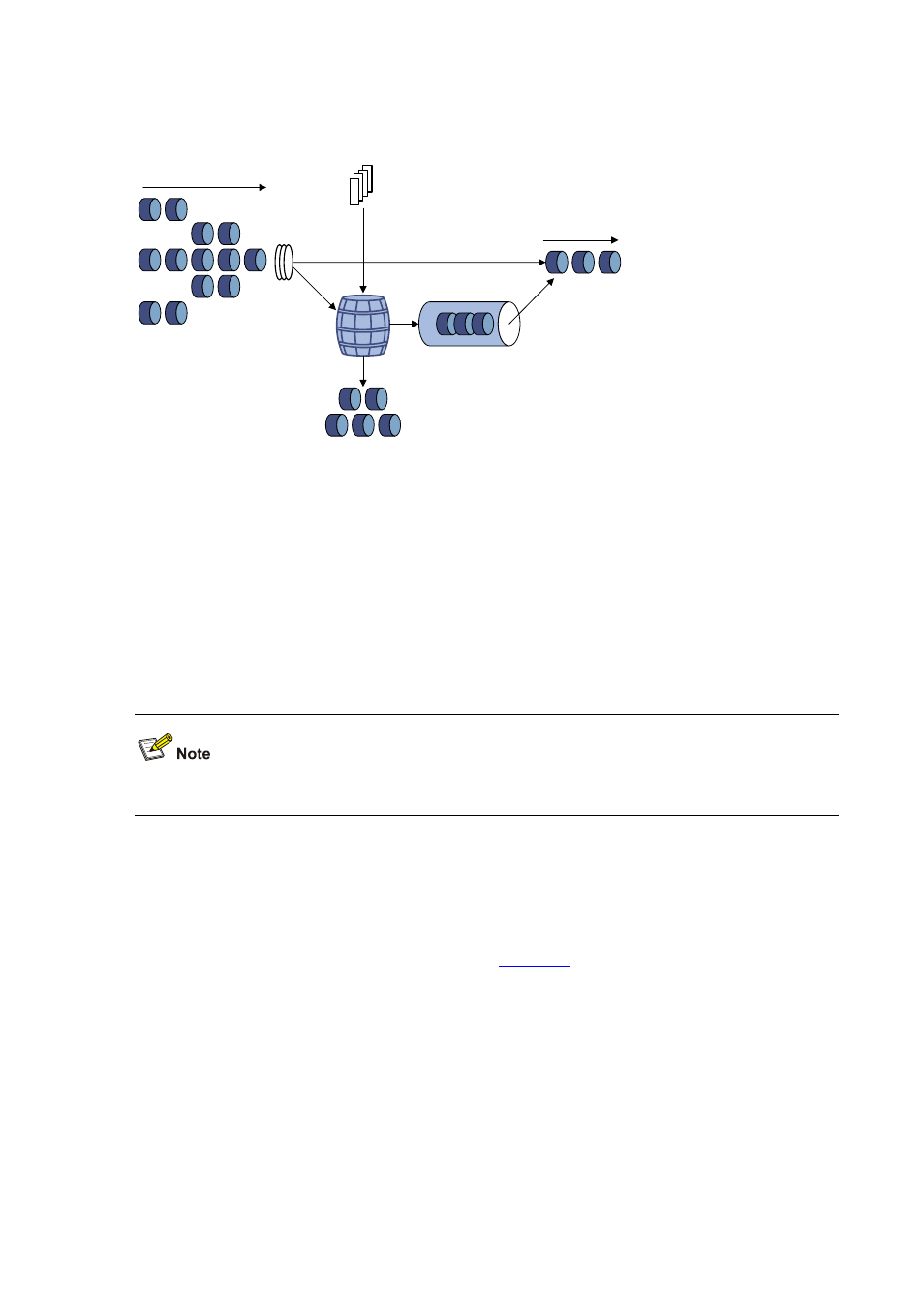
Figure 5-1 Schematic diagram for traffic policing
Token
bucket
Packets dropped
Packet
classification
Packets to be sent
through this interface
Packets sent
Tokens are put into the
bucket at the set rate
Queue
Traffic policing is widely used in policing traffic entering the networks of internet service providers
(ISPs). It can classify the policed traffic and take pre-defined policing actions on each packet
depending on the evaluation result:
z
Forwarding the traffic if the evaluation result is “conforming.”
z
Dropping the traffic if the evaluation result is “excess.”
z
Modifying the DSCP priority of the conforming traffic and forwarding it.
Traffic Shaping
Traffic shaping supports shaping traffic to the outgoing traffic.
Traffic shaping provides measures to adjust the rate of outbound traffic actively. A typical traffic
shaping application is to limit the local traffic output rate according to the downstream traffic policing
parameters.
The difference between traffic policing and GTS is that packets to be dropped with traffic policing are
retained in a buffer or queue with GTS, as shown in
. When there are enough tokens in the
token bucket, the buffered packets are sent at an even rate. Traffic shaping may result in additional
delay while traffic policing does not.
