Measurement Computing CIO-DAS08-AOH User Manual
Page 14
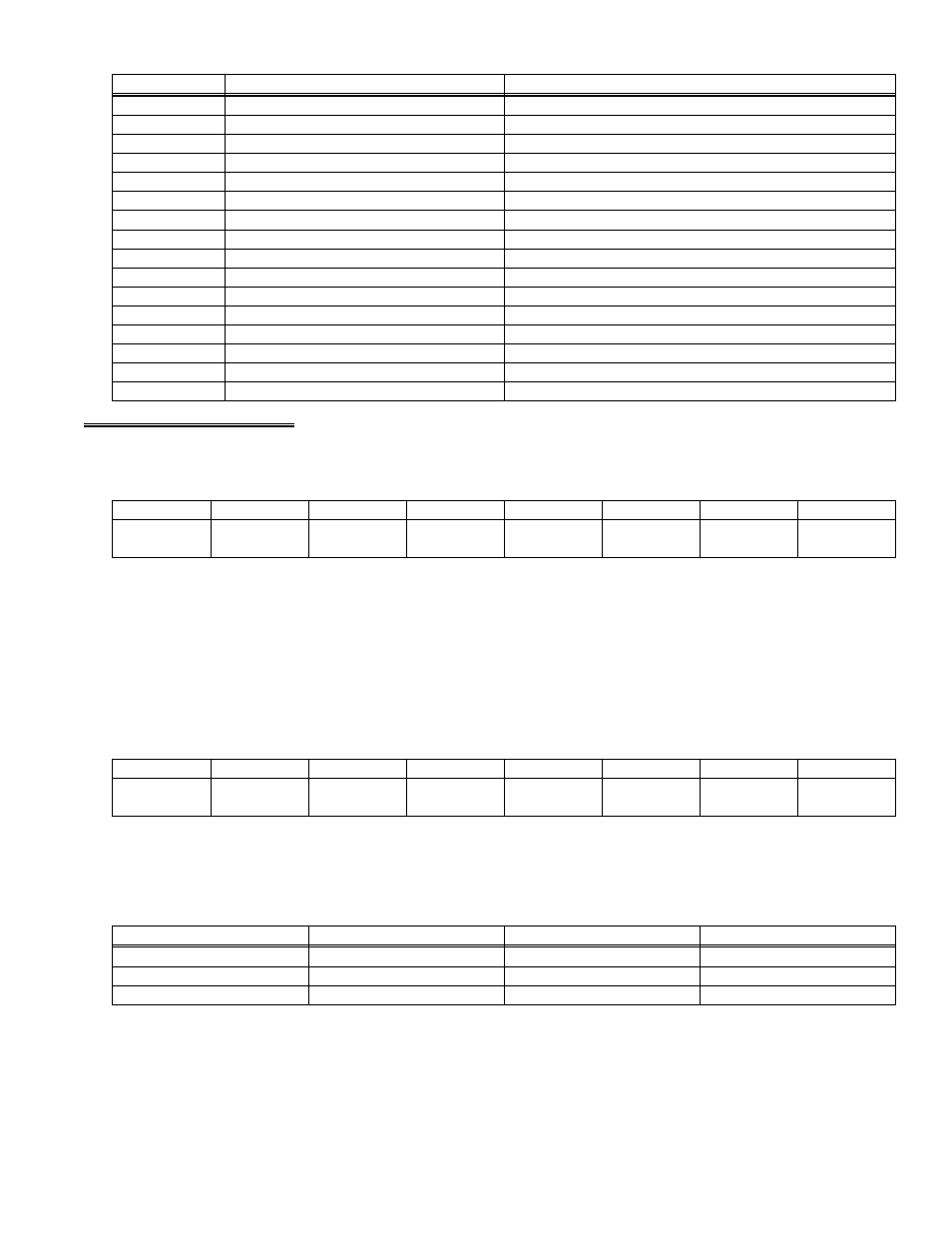
Table 6-2. Register Functions
82C55 Control
None
BASE + 15
PORT C 82C55
PORT C 82C55
BASE + 14
PORT B 82C55
PORT B 82C55
BASE + 13
PORT A 82C55
PORT A 82C55
BASE + 12
DAC 1 High Byte (& individual update)
Simultaneous Update
BASE + 11
DAC 1 Low Byte
Simultaneous Update
BASE + 10
DAC 0 High Byte (& individual update)
Simultaneous Update
BASE + 9
DAC 0 Low Byte
Simultaneous Update
BASE + 8
Counter Control
Not used
BASE + 7
Load Counter 2
Read Counter 2
BASE + 6
Load Counter 1
Read Counter 1
BASE + 5
Load Counter 0
Read Counter 0
BASE + 4
Programmable gain control
Channel MUX and Gain Status
BASE + 3
OP1 - OP4, INTE & MUX Address
EOC, IP1 - IP3, IRQ, MUX Address
BASE + 2
Start 12 bit A/D conversion
A/D Bits 1 (MSB) - 8
BASE + 1
Start 8 bit A/D conversion
A/D Bits 9 - 12 (LSB)
BASE
WRITE FUNCTION
READ FUNCTION
ADDRESS
6.2 A/D DATA REGISTER
BASE ADDRESS (Read / Write)
0
0
0
0
A/D12
LSB
A/D11
A/D10
A/D9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
READ
On read, it contains the least significant four digits of the analog input data.
These four bits of analog input data must be combined with the eight bits of analog input data in BASE + 1, forming a
complete 12 bit number. The data is in the format 0 = minus full scale. 4095 = +FS.
WRITE
Writing any data to the register causes an immediate 8-bit A/D conversion.
BASE ADDRESS + 1 (Read / Write)
A/D8
A/D7
A/D6
A/D5
A/D4
A/D3
A/D2
A/D1
MSB
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
READ
On read the most significant A/D byte is read.
The A/D Bits code corresponds to the voltage on the input according to the table below.
0 Volts
- Full Scale
0
0
½ Full Scale
0 Volts
800
2048
+ Full Scale
+ Full Scale
FFF
4095
UNIPOLAR
BIPOLAR
HEX
DECIMAL
WRITE
Writing to this register starts a 12-bit A/D conversion.
A note of caution: Place several NO-OP instructions between consecutive 12-bit A/D conversions to avoid overrunning the
A/D converter.
10
