3 calibration with scream – Guralp Systems CMG-5TD User Manual
Page 32
Calibration
calculated using a Fourier transform. Because the input signal has
predominantly low-frequency components, this method generally gives
poor results. However, it is simple enough to be performed daily.
•
Injecting a sinusoidal current of known amplitude and frequency
allows the system response to be determined at a spot frequency.
However, before the calibration measurement can be made, the system
must be allowed to reach a steady state; for low frequencies, this may
take a long time. In addition, several measurements must be made to
determine the response over the full frequency spectrum.
•
Injecting white noise into the calibration coil gives the response of the
whole system, which can be measured using a spectrum analyser.
You can perform calibration using the built-in CMG-DM24 digitizer, which
can generate step and sinusoidal calibration signals.
6.3
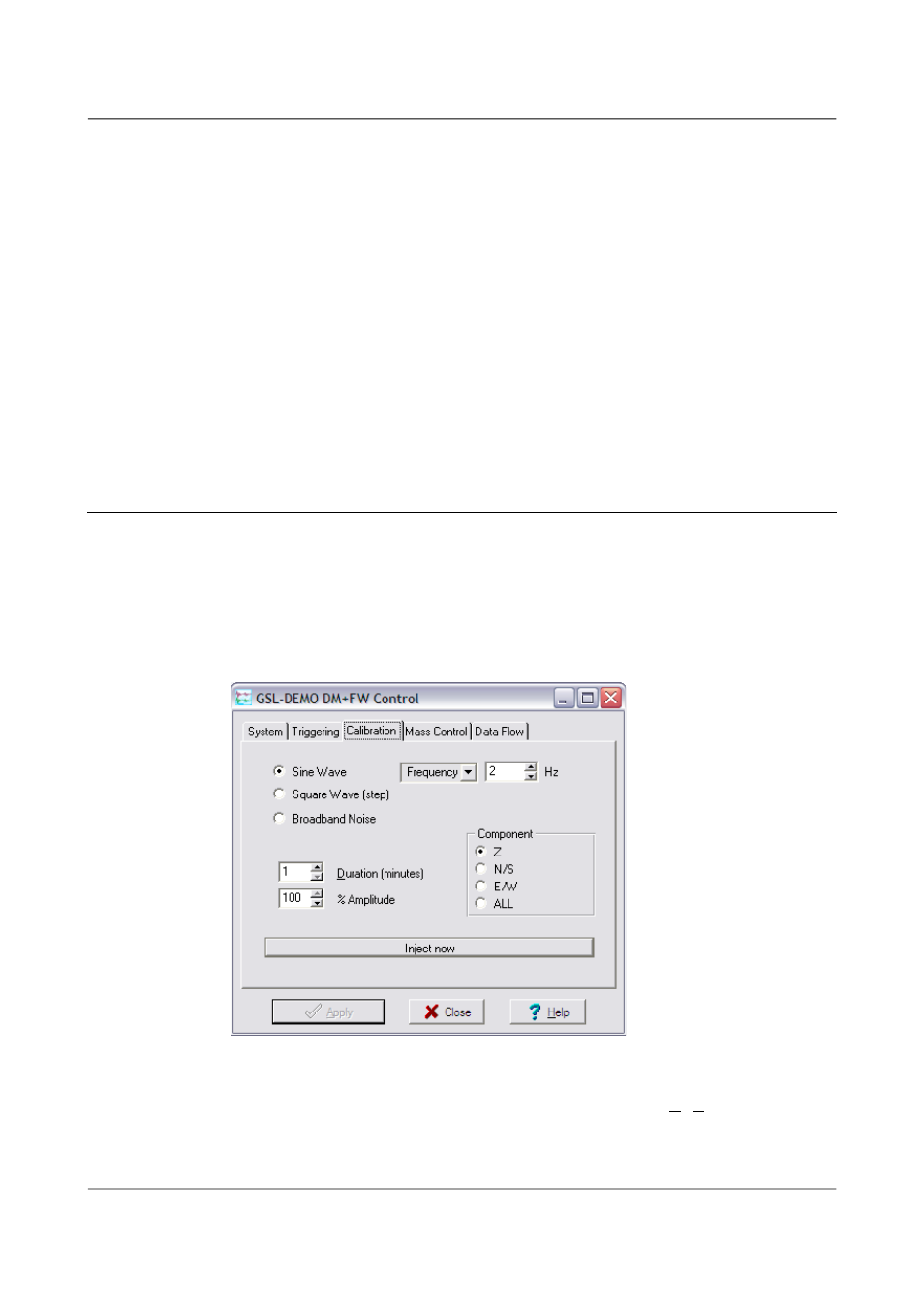
Calibration with Scream!
Calibration is most easily done using a PC running Güralp's Scream! Software.
In this section, broadband noise calibration will be used to determine the
complete sensor response in one action. Please refer to the CMG-DM24 and
Scream manuals for information on other calibration methods.
1. In Scream!'s main window, right-click on the digitiser's icon and select
Control.... Open the Calibration pane.
2. Select the calibration channel corresponding to the instrument, and
choose Broadband Noise. Select a suitable duration and amplitude,
and click Inject now. A new data stream, ending Cn (n = 0 – 7) or MB,
should appear in Scream!'s main window containing the returned
calibration signal.
32
Issue D - April 2013
