6 setting impeller clearance, 7 disassembly – Flowserve WUC Worthington User Manual
Page 37
WUC USER INSTRUCTIONS ENGLISH - 07/14
Page 37 of 52
M20
283
(209)
472
(348)
415
(306)
112
(83)
150
(111)
592
(437)
434
(320)
247
(182)
115
(85)
M22
387
(285)
644
(475)
567
(418)
151
(111)
202
(149)
807
(595)
473
(349)
337
(249)
157
(116)
M24
487
(359)
811
(598)
714
(527)
193
(142)
257
(190)
1017
(750)
595
(439)
426
(314)
198
(146)
M27
716
(528)
1193
(880)
1050
(774)
284
(209)
379
(280)
1496
(1103)
716
(528)
292
(215)
M30
968
(714)
1614
(1190)
1420
(1047)
386
(285)
515
(380)
2033
(1500)
968
(714)
397
(293)
M33
1315
(970)
2191
(1616)
1928
(1422)
523
(386)
697
(514)
2747
(2026)
1008 (744)
536
(395)
M36
1692
(1248)
2820
(2080)
2482
(1831)
672
(496)
897
(662)
3535
(2607)
1297 (957)
690
(509)
M39
2187
(1613)
3645
(2689)
3208
(2366)
870
(642)
1160
(856)
4569
(3370)
890
(656)
M42
2714
(2002)
3920
(2891)
3980
(2936)
1146
(845)
1447 (1067)
5670
(4182)
M45
3375
(2489)
4875
(3596)
4950
(3651)
1425 (1051) 1800 (1328)
7050
(5200)
M48
4084
(3012)
5899
(4351)
5990
(4418)
1724 (1272) 2178 (1606)
8530
(6292)
M64
9750
(7192) 14083 (10388) 14300 (10548) 4117 (3037) 5201 (3836) 20370 (15025)
M68
11768 (8680) 16998 (12538) 17260 (12731) 4969 (3665) 6277 (4630) 24580 (18130)
M76
25230 (18610) 8270 (6100)
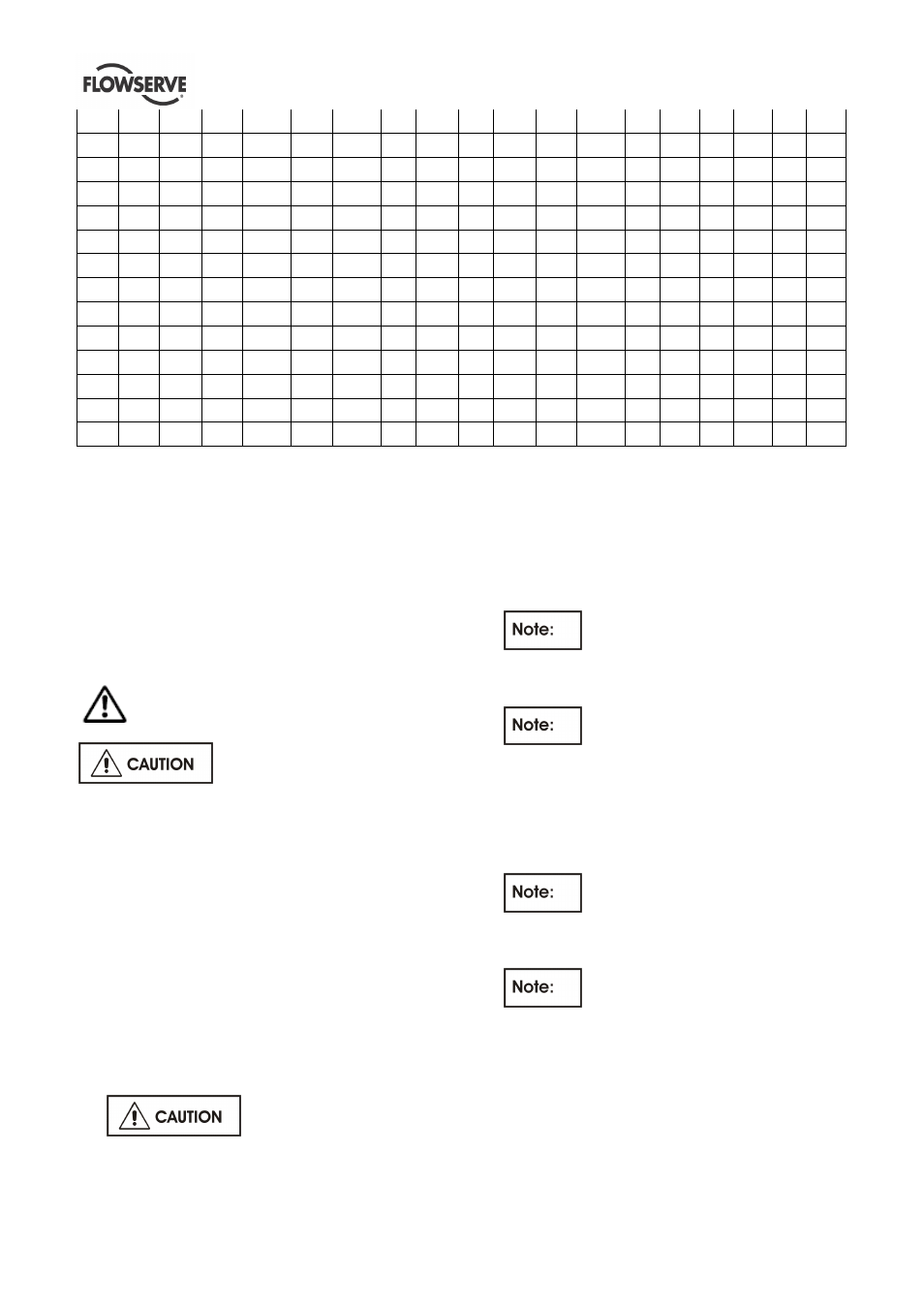
Above mentioned torques are for all screwed unions, which works under dynamical load. For all other
connections you can use a corresponding smaller torque.
Anchor bolts are usually made of 4.6 material. Tightening torques indicated in above table shall not be
exceeded.
6.6 Setting impeller clearance
For axial rotor setting see section 5 Commissioning
startup, operation and shutdown.
6.7 Disassembly
Refer to section 1.6, Safety, before
dismantling the pump.
Before dismantling the pump for
overhaul, ensure genuine Flowserve replacement
parts are available.
Refer to sectional drawings for part numbers and
identification.
6.7.1 Dismantling of radial flow impeller pump
types
1) Completely drain the pump by using the drain
connection. By pumping explosive or toxic media,
flush it with Nitrogen.
2) Uncouple the pump from the motor and remove the
motor after disconnecting it from the electrical net.
3) Pull off the coupling hub from the pump shaft
[2110] and take out the key [6700.1].
4) Secure the mechanical seal by putting the tool into
the groove of the shaft sleeve. Loose the shrunk
ring, and disconnect the seal piping.
Drain the seal system, if
applicable.
5) Drain the oil from the bearing housing using the
plug [6569.1]. Loose the studs [6572.4] and pull out
the pump from it’s can.
6) Loose the socket head cap screw [6579.1] and slip
down the rotor by turning the shaft nut [2910] and
remove it.
If applicable pull off the fan [8161]
after loosing the grub screw [6814.3].
Use an anaerobic adhesive for securing the
socket set screw for reassembly.
If the pump is equipped with a rigid
spacer coupling open the socket head cap screws
[6579.3] move the coupling half [7200], remove
the intermediate coupling [7021], coupling ring
splits [7415], coupling half [7200] and keys
[6700.8].
7) Loose the studs [6572.1], take off the bearing
cover [3260.1] and remove key [6700.2].
Take care of the springs [4260
].
Pull off the bearing housing [3200]. Loose the
studs [6572.2] and pull off the mechanical seal
cartridge.
To disassemble only the hydraulic
section, start with point 11.
8) Open the hexagon head bolt [6577.4] and
disconnect the first column pipe from the
headstock [1141].
9) Pull out the complete bowl assembly together with
shafts and column pipes. Disconnect the first
column pipe.
10) Open the socket head cap screws [6579.2] and slip
upwards the shaft coupling [7020]. Remove the
coupling shell split [7240]. Now the shafts are
uncoupled and you can proceed the same way
