Tos/diffserv priority, 1p/q priority tagging – Contemporary Control Systems EISC Configurable Switches User Manual User Manual
Page 27
TD021000-0MB
27
When this EISC option is enabled, VLAN
“tagged” frame priority is recognized. In the data link header, the 802.1p supplement
provides priority coding which was never specified in the 802.1Q VLAN-tagging
standard. Within the VLAN tag space, a 3-bit code is applied so that “tagged” frames
can specify priority. Values 4–7 are assigned to the EISC High-priority queue and
values 0–3 to the Low-priority queue. Switches and other network equipment, can set
these priority bits.
7.2.7.4
ToS/DiffServ Priority.
Differentiated Services can offer:
• Expedited Forwarding (EF) for low loss, low latency, low jitter and assured bandwidth;
• Assured Forwarding (AF) specifies drop precedence to apply when traffic becomes congested;
• Best Effort, which uses any bandwidth not allocated to EF and AF.
DiffServ allows nodes that are either ignorant of or incapable of DS coding to use the
network with best-effort forwarding by using the default value in the DS field.
If ToS/DiffServ priority is applied, the EISC can read this information (defined in
RFC2474) from the DS field byte. Recommended codepoints are defined in RFC2597
to distinguish traffic by different service classes. The EISC can read this 6-bit value —
in either IPv4 or IPv6 frames — and can then identify the incoming packet priority as
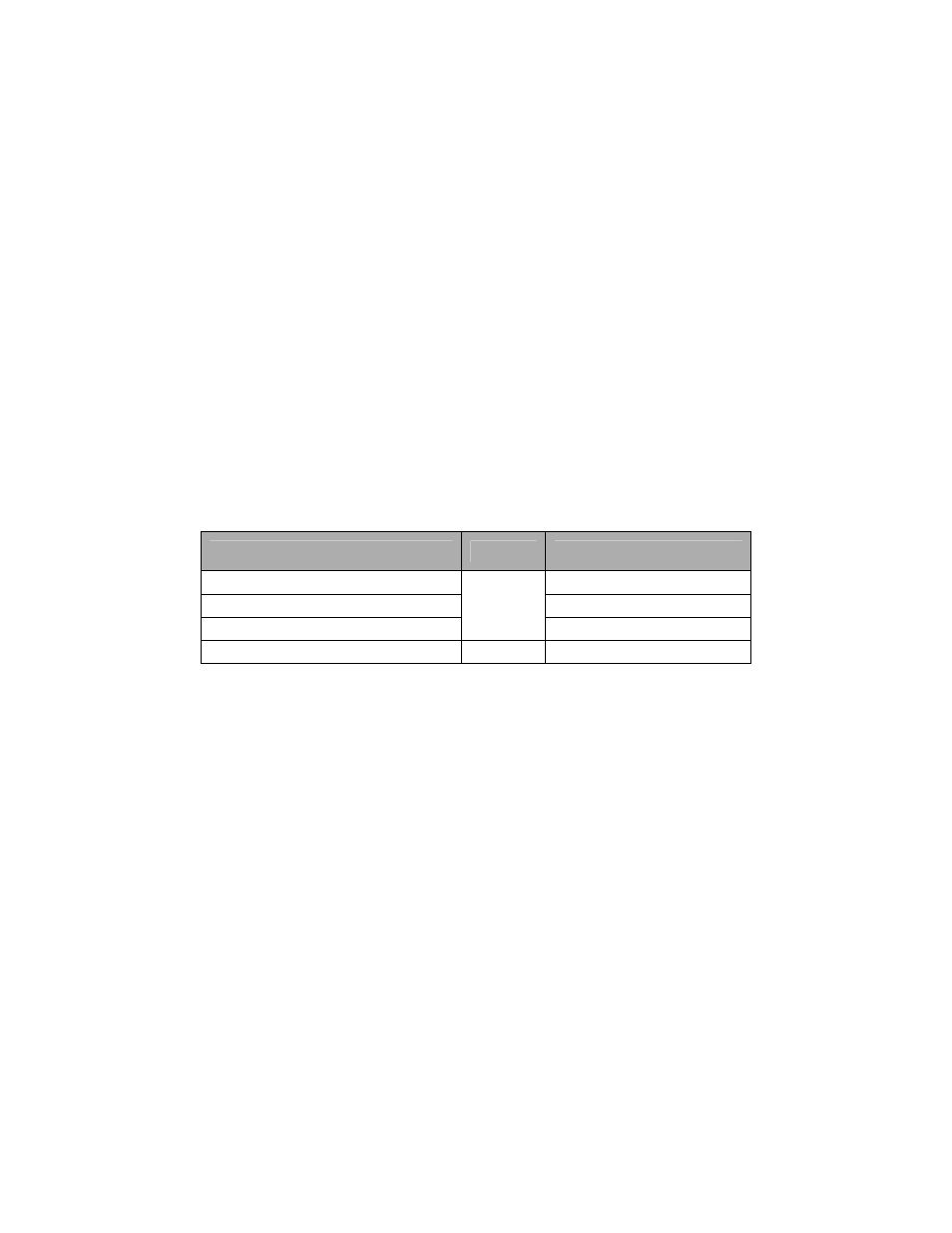
shown in Table 2:
DS Field Value
Priority
Per Hop Behavior
101110
EF (Expected Forwarding)
001010, 010010, 011010, 100010
AF (Assured Forwarding)
110000, 111000
High
Network Control
All others values
Low
Uncharacterized
Table 2 — DiffServ Packet Priority
7.2.7.5
802.1p/Q Priority Tagging.
The IEEE suggests a priority scheme, but does not mandate a definition. This method
represents a simple, best-effort Layer 2 prioritization for network adapters and switches
— requiring no bandwidth reservation.
Note: Since the data link header is only read at the switch level, networks which have
routers cannot use this method unless special mapping is implemented.
IP protocol frames include in their network headers
an 8-bit Type of Service (ToS) field for packet prioritization. The first three of these bits
specify 8 levels of priority. The next three bits provide the QoS refinement known as
Differentiated Services (DiffServ or DS) which efficiently manages traffic by categorizing
packets into classes to apply rules for packet delay and discarding. The two remaining
bits of the ToS octet are not yet defined.
