Bandwidth pools – Comtech EF Data MIDAS 4 System and Design User Manual
Page 47
System and Design Manual, Revision 2
Theory of Operation 3–5
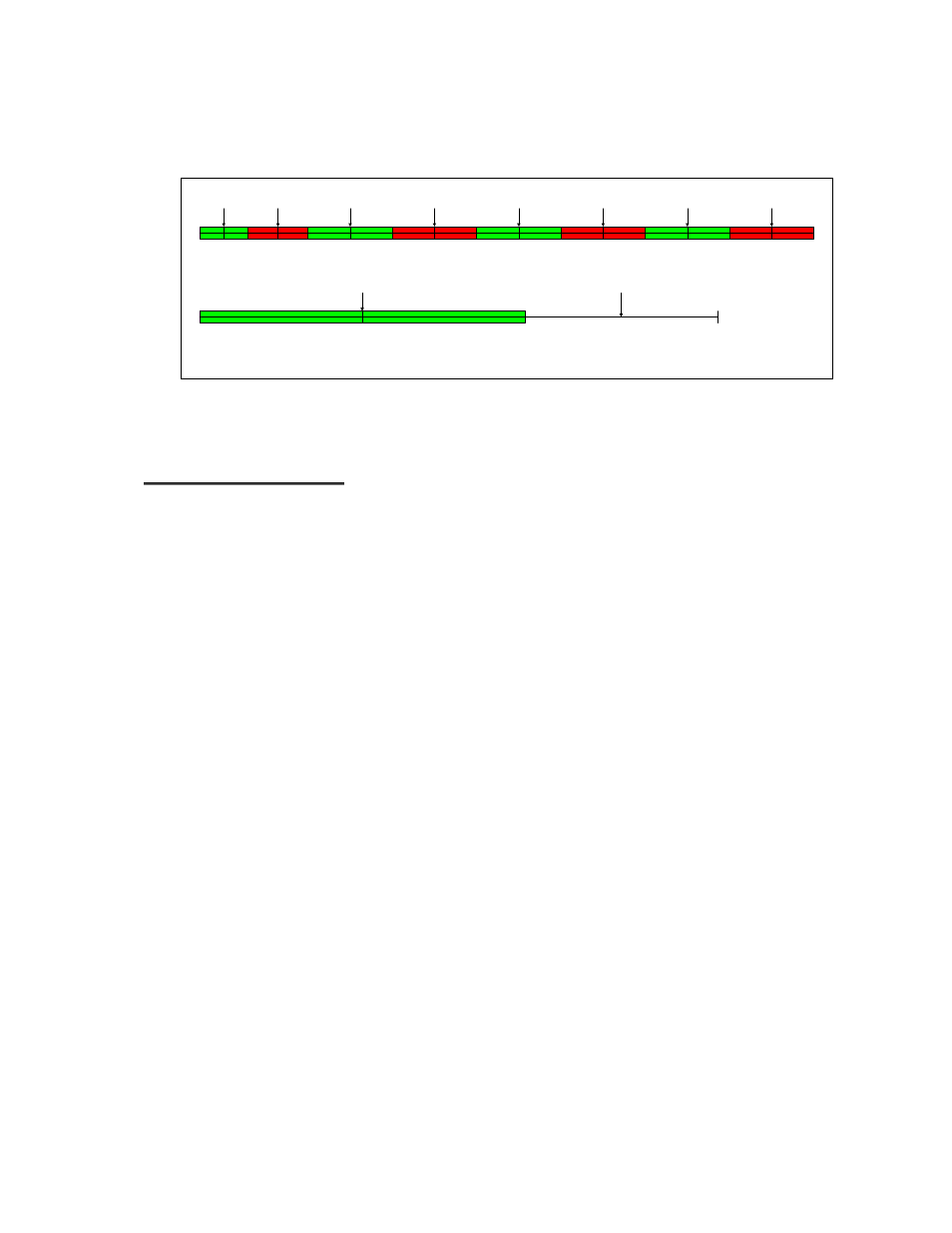
allocated to the simplex data circuit, leaving 185 kHz for other traffic. Figure
3-1 illustrates the frequency allocation (center frequencies) for this example.
12.5
747.5
OUTBOUND
CONTROL
CHANNEL
CIRCUIT4
CHANNEL1
(256 kbit/s, SIMPLEX DATA)
ALL FREQUENCIES ARE IN kHz
580.0
0.0
47.5
INBOUND
CONTROL
CHANNEL
197.5
112.5
282.5
367.5
452.5
580.0
CIRCUIT1
CHANNEL1
(64 kbit/s, DATA)
CIRCUIT1
CHANNEL2
(64 kbit/s, DATA)
CIRCUIT2
CHANNEL2
(64 kbit/s, DATA)
CIRCUIT3
CHANNEL1
(64 kbit/s, DATA)
CIRCUIT2
CHANNEL1
(64 kbit/s, DATA)
537.5
CIRCUIT3
CHANNEL2
(64 kbit/s, DATA)
1100.0
AVAILABLE
FOR ALLOCATION
915.0
Figure 3-1. (Center) Frequency Allocation
B
B
a
a
n
n
d
d
w
w
i
i
d
d
t
t
h
h
P
P
o
o
o
o
l
l
s
s
The MIDAS Controller allows for partitioning the owned (managed)
bandwidth for exclusive use by the customers. Owned bandwidth can be
divided into one or more private pools and a public pool. A private pool is
then assigned to a customer for exclusive use. The public pool is available to
all customers that do not have an assigned private pool. Customers with
assigned private pools also have the option of overflowing to the public pool,
if space is not available within their private pool. Space from the public pool is
allocated on a first-come first-served basis to the requesting customers.
Access to the pools is assigned on a per-traffic-channel basis. Different traffic
channels in a traffic node can be assigned to different bandwidth pools. By
default, all new bandwidth is added to the public pool. If a private pool is
deleted, the bandwidth is returned to the public pool. The MIDAS operator
can add/delete private pools and transfer bandwidth between pools. Usage
statistics are also available on a pool basis.
The key features of the bandwidth pools can be summarized as:
• The owned bandwidth can be divided into private pools.
• Owned bandwidth not assigned to private pools is referred to as the
public pool.
• The public pool always exists.
• The control channels are allocated bandwidth from the public pool.
• Each customer can have access to one private pool and/or the public
pool.
• A customer has exclusive access to the private pool.
• Bandwidth cannot be shared between pools.
• The call detail record indicates which pool an allocated bandwidth
came from.
