Altera Device-Specific Power Delivery Network User Manual
Page 29
Chapter 1: User Guide for the Device-Specific Power Delivery Network (PDN) Tool
1–25
Design PCB Decoupling Using the PDN Tool
September 2012
Altera Corporation
Device-Specific Power Delivery Network (PDN) Tool User Guide
1
Some power rails are sensitive to noise, such as PLL-related power supplies. They are
isolated from other rails by a power filter (usually ferrite bead) although they connect
to the same VRM module. These isolated rails usually have their own PCB power
plane. In this scenario, you must treat each group of isolated power rails as an
individual power supply and decouple each power supply individually following the
procedures described in this User Guide.
When deriving decoupling capacitors for multiple FPGAs sharing the same power
plane, each FPGA should be analyzed separately using the PDN tool. For each FPGA
design, combine the required power rails as described above and analyze the
decoupling scheme as if the FPGA was the only device on the power rail. Then repeat
for each of the remaining FPGAs on the board.
High frequency decoupling capacitors are meant to provide the current needed for
AC transitions and must be placed in a close proximity to the FPGA power pins. Thus,
the PDN tool should be used to derive the required decoupling capacitors for the
unique power requirements for each FPGA on the board.
The power regulators must be able to supply the total combined current requirements
for each load on the supply, but the decoupling capacitor selections should be
analyzed on a single FPGA basis.
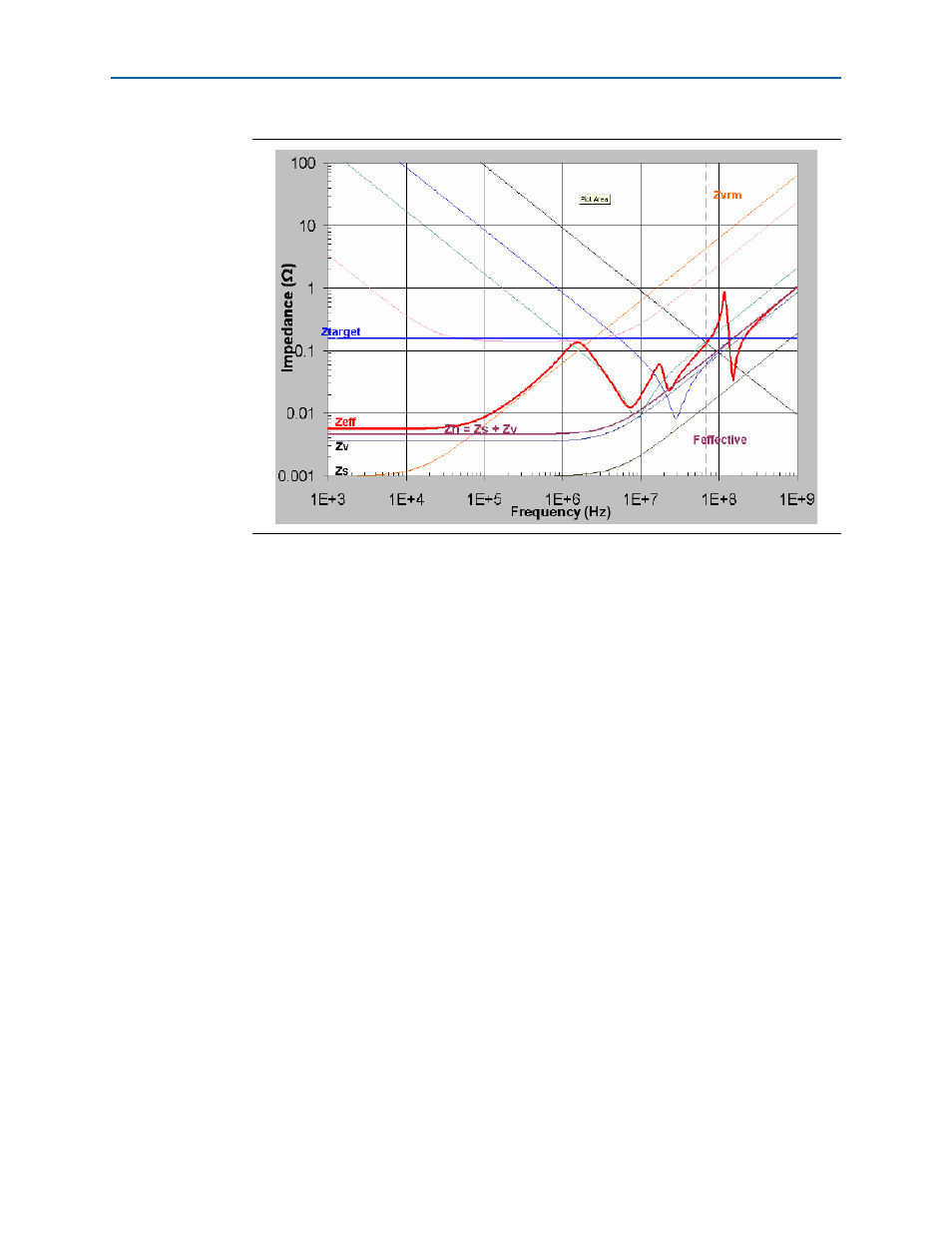
Figure 1–18. Enlarged Plot of Zeff Using the Figure 1-18 Design
