5 limitations, 6 vrrp configuration – CANOGA PERKINS 9171 Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 126
CanogaOS Configuration Guide
20-3
20.5 Limitations
The VRRP RFC specifies that the master-down-timer is a fraction that is always <1. The
Linux operating system supports only timers that are multiples of 1 second. This might
result in increasing the length of time the system takes in stabilizing the master, after
master fails in the network with multiple backups.
MD5 authentication is not yet supported for VRRP.
20.6 VRRP Configuration
This section contains basic VRRP configuration examples. To see details on the
commands used in these examples, or to see the outputs of the Validation commands,
refer to the VRRP Command Reference.
20.6.1 Configuring VRRP (One Virtual Router)
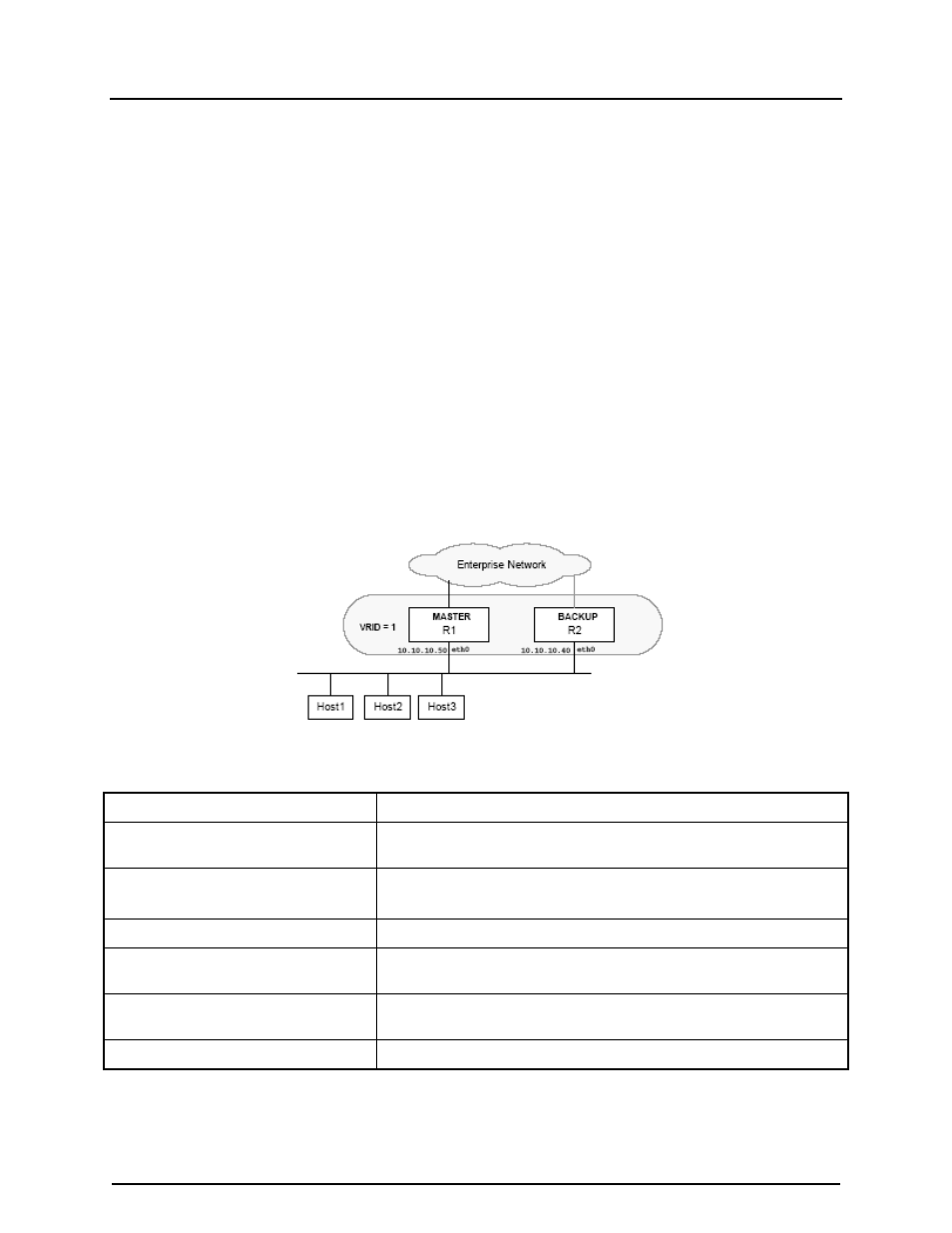
In this configuration the end-hosts install a default route to the IP address of virtual router
1(VRID = 1) and both routers R1 and R2 run VRRP. R1 is configured to be the Master for
virtual router 1 (VRID = 1) and R2 as a Backup for virtual router 1. If R1 fails, R2 will take
over virtual router 1 and its IP addresses, and provide uninterrupted service for the hosts.
Configuring only one virtual router, doubles the cost and leaves R2 idle at all times.
Figure 20-3: One VRRP Router
R1
DUT# configure terminal
Enter the Configure mode.
DUT(config)#router vrrp 1
Create a new VRRP session on the router and specify the VRID for the
session.
DUT(config-router)#virtual-ip
10.10.10.50
Set the virtual IP address for the VRRP session.
DUT(config-router)#interface eth-0-1
Specify the physical interface that will participate in virtual routing.
DUT(config-router)#preempt-mode true Set the preempt mode to specify that the highest priority will function as
a backup to master when master is unavailable
DUT(config-router)#
advertisement-interval 5
Configure the advertisement interval to 5 seconds.
DUT(config-router)# enable
Enable the VRRP session on the router.
R2
