3 soam protocols – CANOGA PERKINS 9145EMP NID Software Version 3.1 User Manual
Page 138
9145EMP NID Software User’s Manual
Service OAM
Service OAM
126
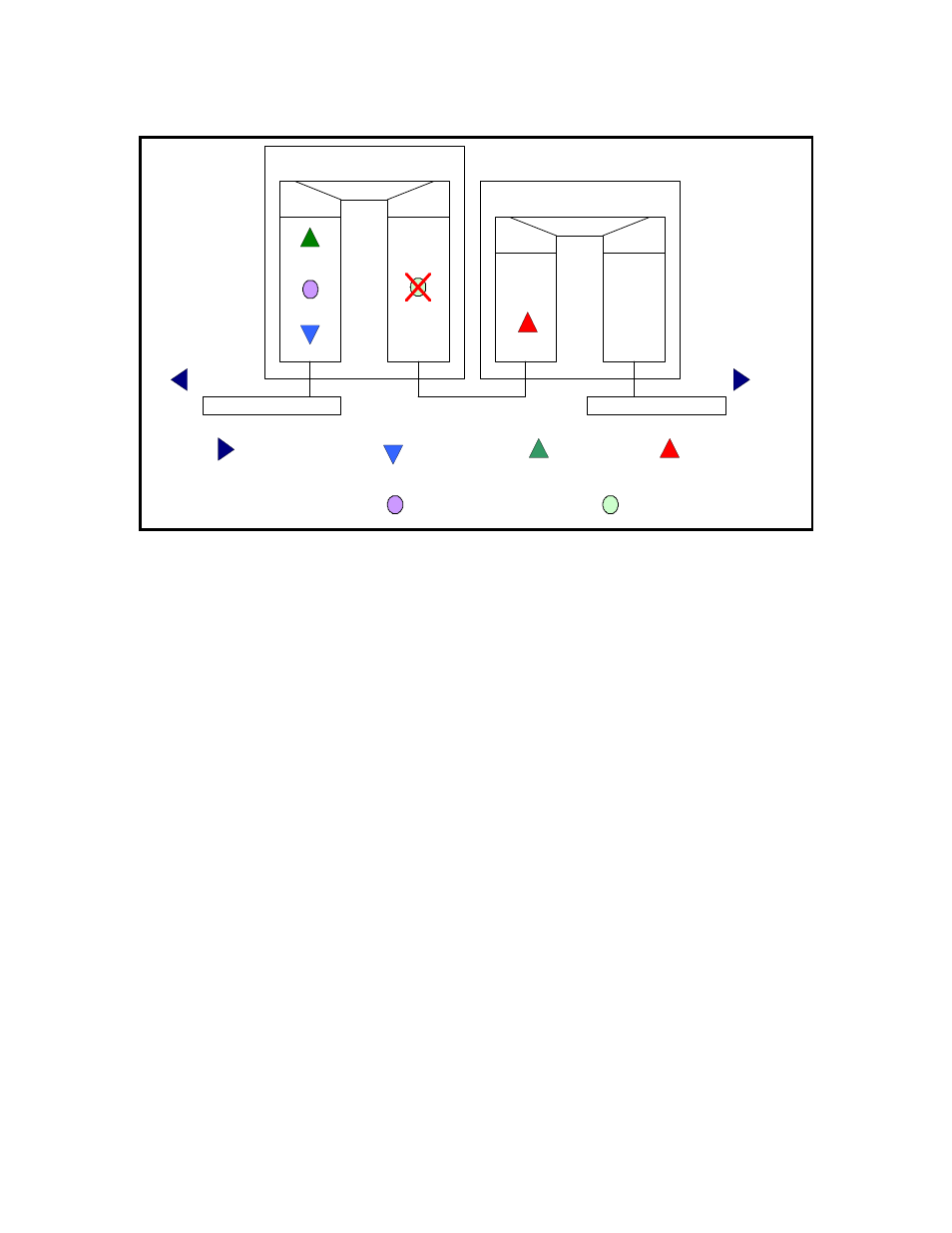
Figure 11-1 Positioning of up/down MEPs
11.1.3 SOAM Protocols
SOAM Connectivity Fault Management provides the following protocols:
•
Continuity Check Protocol: The continuity check message (CCM) is used to detect con-
nectivity failures in an MA/MEG. Each MEP can be configured to periodically transmit a
CCM. CCMs are sent to all MEPs associated with a given MA/MEG. Use of a multicast
destination address allows the discovery of remote MEP MAC addresses and the detec-
tion of leaks between MAs/MEGs. Every active MEP maintains a CCM database. As a
MEP receives CCMs, it updates the record in the database. If no CCM frames from a
peer MEP are received within the defined interval (3.5 times the CCM transmission
period), loss of continuity defect is detected.
•
Loopback Protocols: A loopback message (LBM) is used to identify the specific fault
location. The MEP generates a loopback message addressed to a specific maintenance
point within an MA/MEG. The destination MIP or MEP must respond with a loopback reply
(LBR).
A single, multicast LBM can be generated by a Y.1731 MEP, and every far-end MEP in
the MA/MEG responds with a loopback reply; hence, the originating MEP will know all the
far end MEPs that have connectivity.
A sweep loopback procedure is used to detect the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size
for a given end-to-end connection. Loopback messages are sent continuously,
incrementing the MTU size for each new request (by increasing the size of the data type-
User Port
Network Port
S-Component
C-Component
Untagged MEP
Down C-
tagged MEP
UP C-tagged
MEP
UP S-tagged
MEP
C-tagged MIP
on user port
C-tagged MIP on network port
(by proxy) –
not supported
