Bio-Rad Nuvia™ IMAC Resin User Manual
Page 15
Bio-Scale Mini Nuvia IMAC Ni-Charged 11
2. Load the sample lysate at 1 ml/min.
3. Wash the cartridge with 6 CV of wash buffer 1 at 1 ml/min.
4. Wash the cartridge with 6 CV of wash buffer 2 at 2 ml/min.
Note: equivalent to 5% buffer B/elution buffer wash.
5. Elute the purified protein with 10 CV of elution buffer at
2 ml/min.
6. Prior to quantitation of the protein concentration, the purified
protein should be exchanged into a non-imidazole buffer
(imidazole can absorb at 280 nm). Purified protein from
denaturing purifications should be exchanged into another
buffer through dialysis.
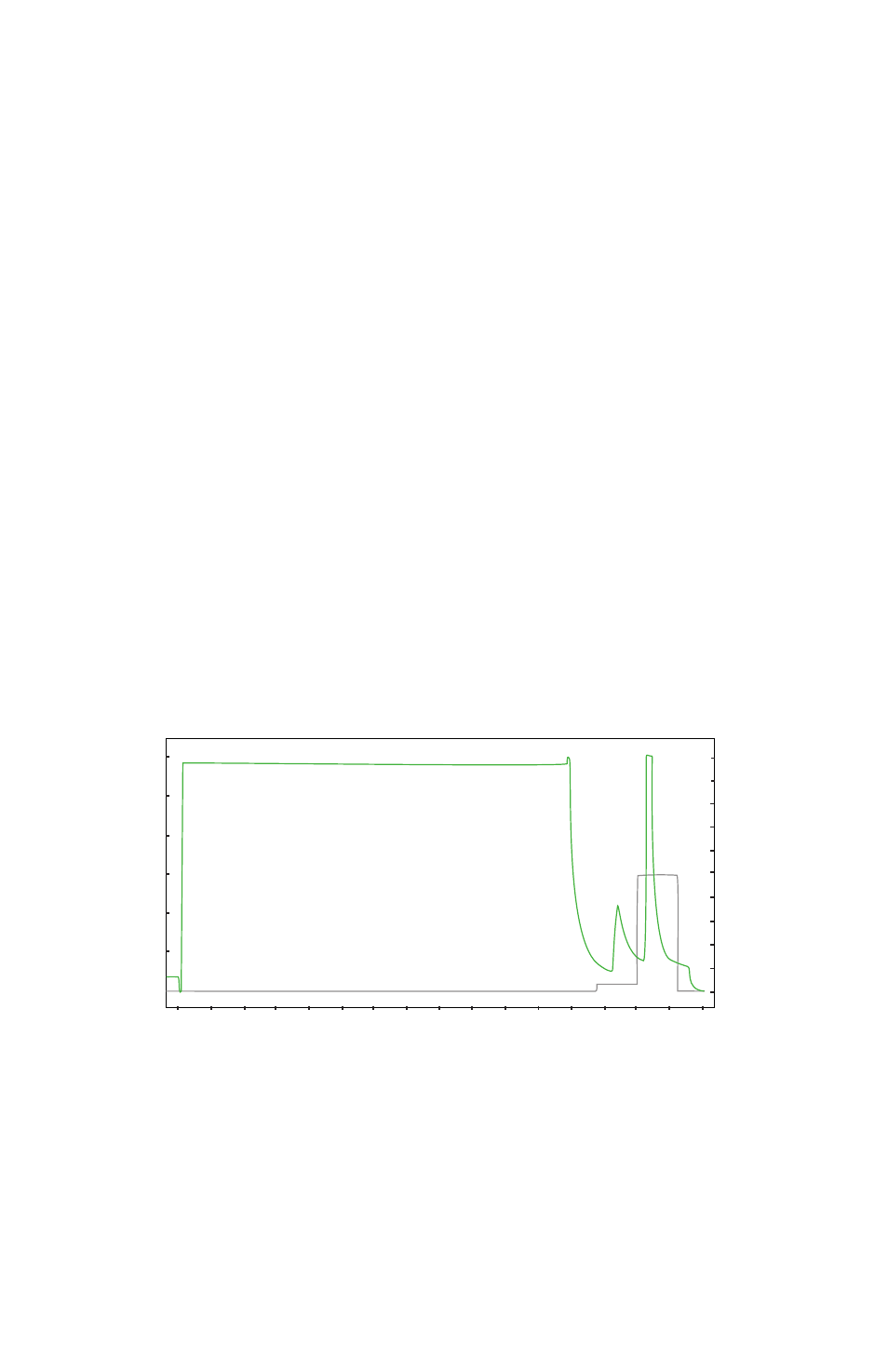
The chromatogram in Figure 1 illustrates a representative
purification of a high-expressing soluble protein purified using the
native buffer set and method describe
d in Table 5.
Note: IMAC buffers made with potassium salts are more stable
than sodium salt–based buffers. However, potassium will complex
with SDS in Laemmli buffer and precipitate out of solution. Prior to
analyzing IMAC samples on gels, the samples must be diluted at
least 1:7 with Laemmli buffer to prevent precipitation.
Fig. 1. Typical IMAC purification: A histidine-tagged protein was purified from the soluble
fraction using the standard Nuvia IMAC native purification protocol. Clarified E. coli lysate was
loaded onto a 5 ml Nuvia IMAC Ni-Charged Cartridge. The cartridge was washed with 6 CV
of wash buffer 1 followed by 6 CV of wash buffer 2. Purified protein was eluted with 5 CV of
elution buffer.
3000
2000
1000
0
100
80
60
40
20
0
0
40
80
120
160
200
240
280
320
%B (%)
λ (280 nm, mAU)
Volume, ml
