Solid wire flux cored wire, Fabricator 251 – Tweco 251 Thermal Arc Fabricator User Manual
Page 50
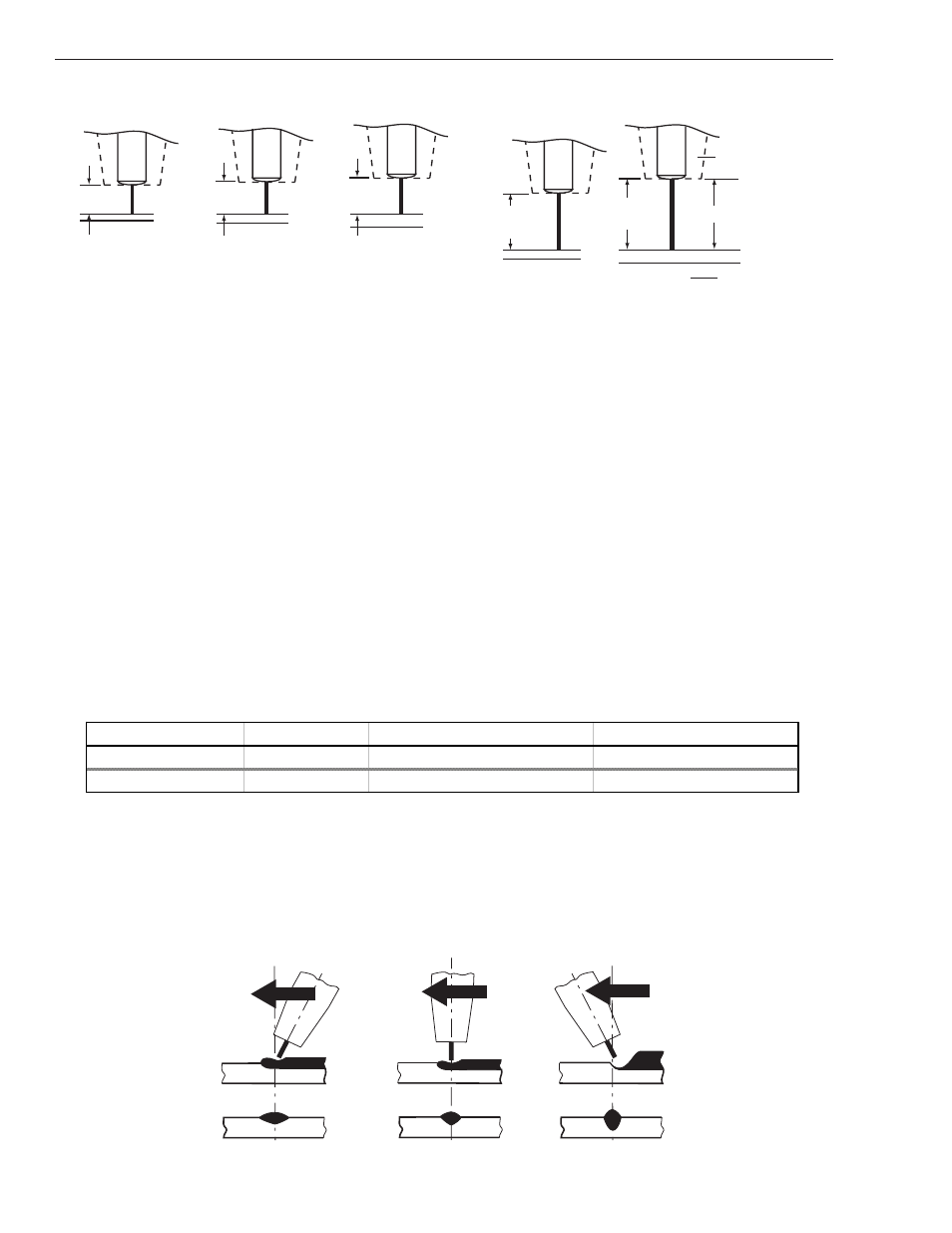
FABRICATOR 251
OPERATION
4-12
Manual No. 0-4847
Contact
Ti
p
Gas
Nozzle
Solid Wire
Flux Cored Wire
.023”
(.6mm)
1/4” (6.4mm)
5/16” (7.9mm)
3/8” (9.5mm)
9/16”
(14.3mm)
11/16”
(17.5mm)
.030”
(.8mm)
.035”
(.9mm)
.035”
(.9mm)
.045”
(1.1mm)
Art # A-07186
Wire Diameter
Distance: ±1/16”
Figure 4-16: Optimum Contact Tip to Work Distances
Electrode Wire Size Selection
The choice of electrode wire size in conjunction with shielding gas used depends on:
- Thickness of the metal to be welded,
- Type of joint,
- Capacity of the wire feed unit and power supply,
- The amount of penetration required,
- The deposition rate required,
- The bead profile desired,
- The position of welding and
- Cost of the electrode wire.
Weld metal deposition rate is proportional to current density. Current density is defined as the current per cross
sectional area of the electrode wire and is normally expressed as amps per mm
2
. An example is in Table 4-3 below.
Electrode Wire Size Current (Amps) Current Density(Amps/mm2) Deposition Rate(lbs/hour)
.035”( 0.9mm)
200
314
7.0
.045”(1.2mm)
200
177
6.2
Table 4-3: .035"(0.9mm) , .045"(1.2mm) Wire Deposition Rate
Advantages of MIG welding forehand:
- Allows superior visibility of the weld zone
- Flatter weld bead
- Shallower penetration
Forehand
Vertical
Backhand
Art # A-07185
Figure 4-17: MIG Gun Angle
