Banner’s surecross™ wireless network, Network basics, Network id – Banner SureCross DX80 Wireless Networks User Manual
Page 4
4
P/N 136689
Banner Engineering Corp. • Minneapolis, MN U.S.A.
www.bannerengineering.com • Tel: 763.544.3164
DX80
Reference Guide
Network Basics
Banner’s SureCross™ Wireless Network
To balance reliable communication with efficient power management, the SureCross™ wireless network uses a star network topology.
Each node within a network communicates only with the gateway, or master device. To ensure each node can reliably send and receive
data to the master device, a TDMA architecture is employed.
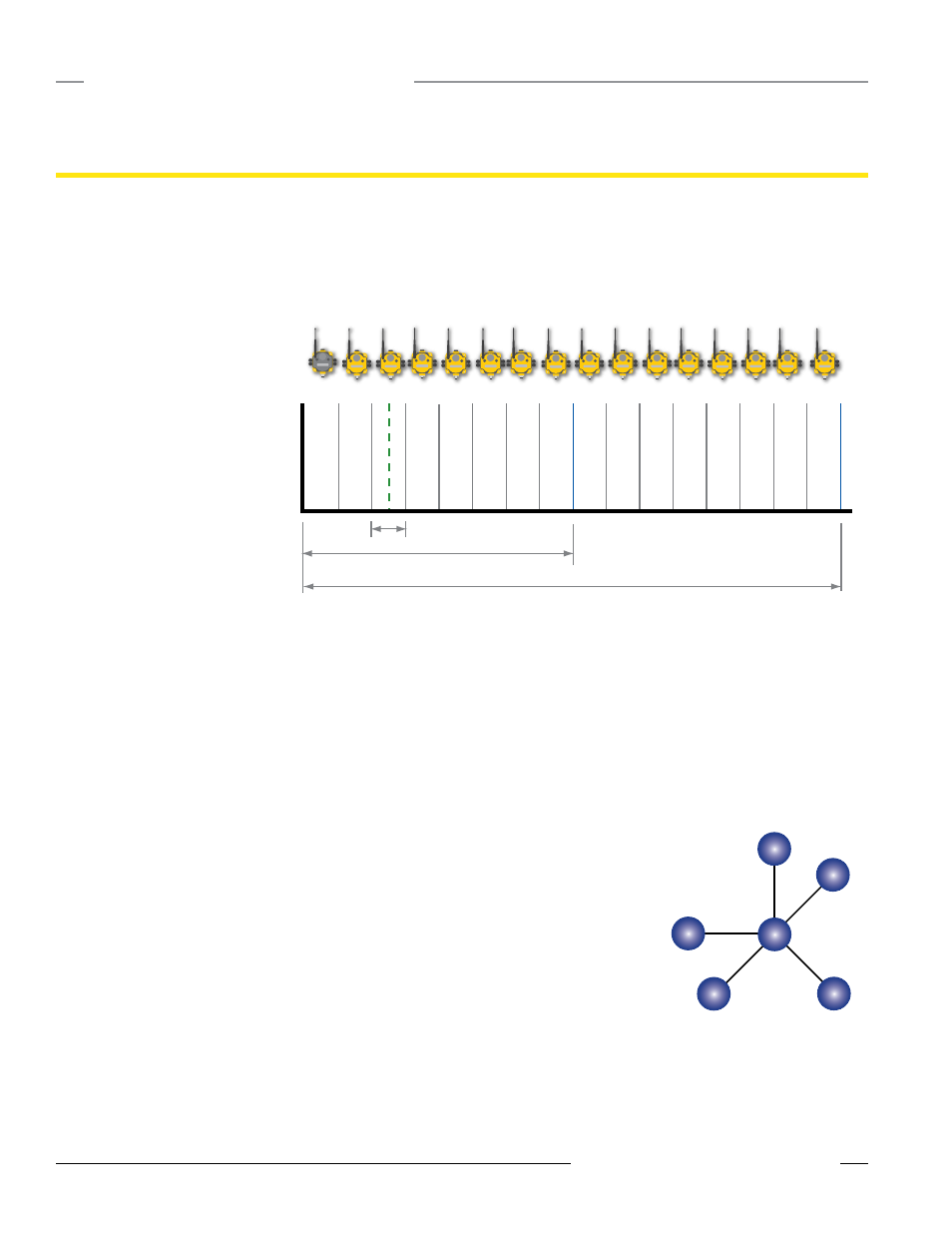
TDMA, or Time Division Multiple Access, architecture assigns each node, including the master device, a specific time period in which to
send and receive data .
By establishing specific intervals when
each node sends and receives data,
nodes do not conflict with each other
to send and the gateway never has to
receive data from more than one node
simultaneously .
As the network master device, the
Gateway initiates all communications
within the network . Each Node may
only communicate with the Gateway,
and only during that Node’s specific
transmit and receive timing periods .
Because the Node can send and
receive only in specific time intervals,
the Node’s power usage can be
managed efficiently, allowing Nodes
to operate from 3 .6V lithium batteries
when necessary .
Assigning send and receive times between the Gateway and Nodes involves using unique device identifiers .
Having multiple independent networks networks within range of each other requires unique network identifiers . These unique network
identifiers, or network IDs, use different FHSS hop sequences for the networks, preventing the Gateway from one network from
accidentally transmitting to a Node on another network .
Network ID
Because the radio network operates over the air, there are limited ways to electrically separate collocated networks. To keep collocated
networks separated, Banner uses a network ID number, sometimes abbreviated as NID. Each wireless network operating within radio
range is assigned a unique network ID number using the rotary dials on the DX80 devices . Up to 16
unique network identification numbers are available using the rotary dial . Additional Network IDs are
possible using advanced features of the DX80 devices .
All devices within a network are assigned the same network identification number, which defines a
unique frequency hop table. Because networks 1 and 2 use a different sequence of frequency changes,
they are not on the same frequency at the same time . This prevents communication between the
networks even when they share the same transmission medium .
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
time
Network Devices
Send and receive interval for Node 2
TDMA frame for a network of 8 devices
TDMA frame for a network of 16 devices
Rx
Tx
node 1
node 2
node 3
node 4
node 5
node 0
