Deviation alarm, Manual tracking, Trusted – Rockwell Automation T8019 Trusted Process Control Algorithm Software Package User Manual
Page 19: Process control algorithms t8019
Trusted
TM
Process Control Algorithms T8019
Issue 8 Sep 07
PD-T8019
19
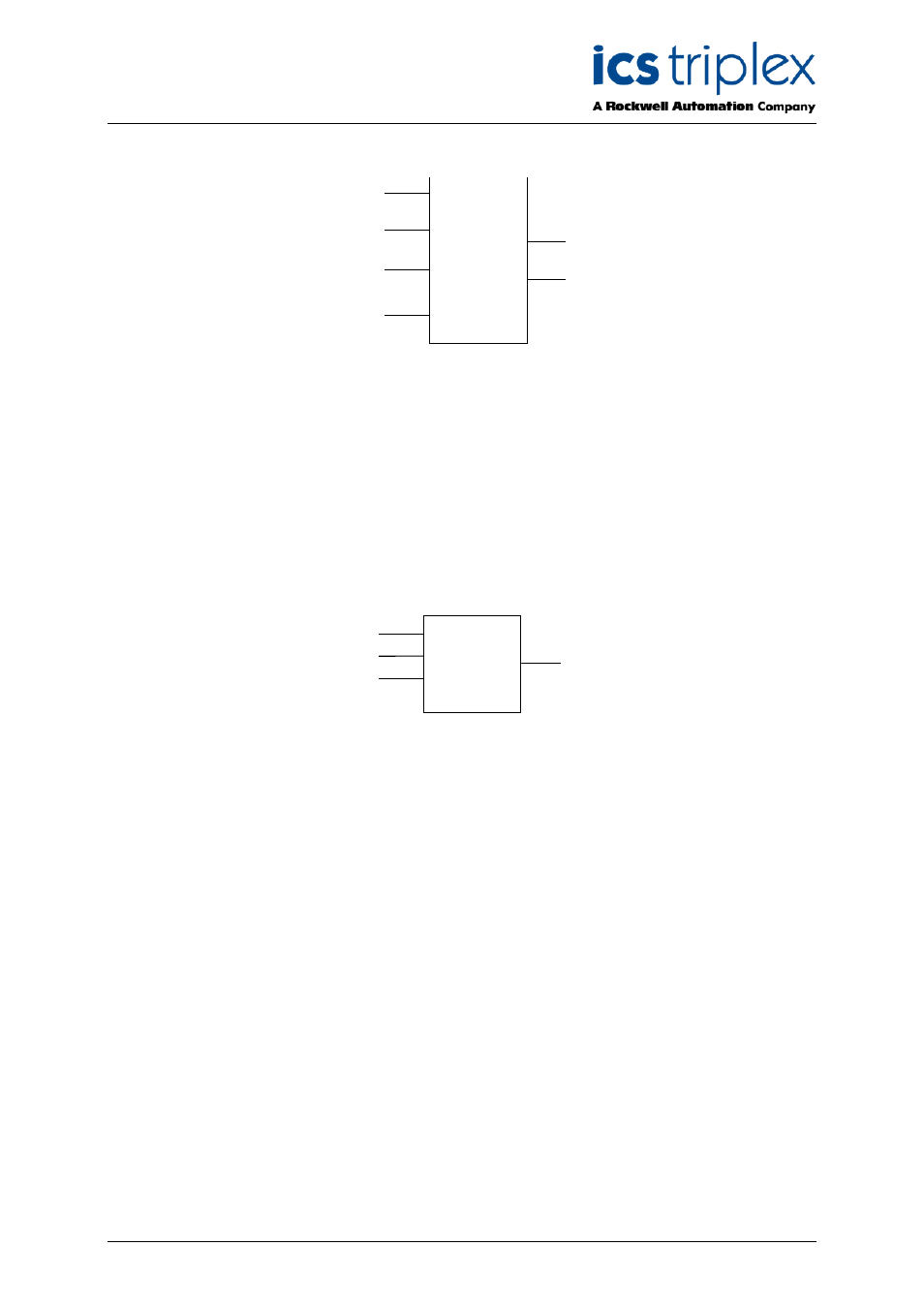
2.8. Deviation Alarm
DEV_AL
PV
SP
DEV
US
DEV
DS
DEV
HI
DEV
LO
The deviation alarm function block takes the current process variable (PV) and set-point (SP), together
with the up-scale and down-scale deviation between the PV and SP (DEV
US
and DEV
DS
respectively).
PV, SP, DEV
US
and DEV
DS
are of type REAL, both outputs (DEV
HI
and DEV
LO
) are of type Boolean.
DEV
HI
= ( (PV – SP) DEV
US
)
DEV
LO
= ( (SP – PV) DEV
DS
)
If an overflow condition occurs during the execution of the function, DEV
HI
is to be set to PV>0, DEV
LO
to PV<0 and the “overflow” error counter is to be incremented.
PV, SP, DEV
US
and DEV
DS
must be finite, i.e. not ±infinities or NaNs.
2.9. Manual Tracking
MANTRK
X
OUT
XO
OUT
XO
AUTO
The manual tracking function requires the current PID function output (X
OUT
), the manual set-point
(XO) and auto/manual mode control (AUTO). Xout, XO and XO
OUT
are of type REAL, AUTO is
BOOLEAN.
Whilst AUTO is TRUE XO
OUT
will be set to the current value of X
OUT
. On a transition to manual mode,
i.e. AUTO changes to FALSE, the XO
OUT
value will remain at its previous value until the value of the
manual set-point input (XO) changes. Following a change to the manual set-point, the value of XO
OUT
will reflect the value of XO whilst AUTO is FALSE.
