Lifetime expectancy and mtbf, Functional diagram, L2 l3 l1 – Rockwell Automation 1606-XLS960F-3 Power Supply Reference Manual User Manual
Page 12
All parameters are specified at 24V, 2.5A, 230Vac input, 25ªC ambient and after a 5 minutes run-in time unless noted otherwise.
12
Rockwell Automation Publication 1606-RM032A-EN-P — April 2014
Bulletin 1606 Switched Mode Power Supplies
13. Lifetime Expectancy and MTBF
3AC
400V
3AC 480V
Calculated lifetime expectancy
*)
314
000h
*)
294
000h
*)
at 48V, 10A and 25°C
111 000h
104 000h
at 48V, 10A and 40°C
179
000h
*)
174
000h
*)
at 48V, 20A and 25°C
63 000h
62 000h
at 48V, 20A and 40°C
MTBF
**)
SN 29500, IEC 61709
375 000h
369 000h
at 48V, 20A and 40°C
685 000h
678 000h
at 48V, 20A and 25°C
MTBF
**)
MIL HDBK 217F
158 000h
157 000h
at 48V, 20A and 40°C; Ground Benign GB40
211 000h
210 000h
at 48V, 20A and 25°C; Ground Benign GB25
*) The calculated lifetime expectancy shown in the table indicates the minimum operating hours (service life) and is determined by the
lifetime expectancy of the built-in electrolytic capacitors. Lifetime expectancy is specified in operational hours and is calculated according
to the capacitor’s manufacturer specification. The manufacturer of the electrolytic capacitors only guarantees a maximum life of up to 15
years (131 400h). Any number exceeding this value is a calculated theoretical lifetime which can be used to compare devices.
**) MTBF stands for Mean Time Between Failure, which is calculated according to statistical device failures, and indicates reliability of a
device. It is the statistical representation of the likelihood of a unit to fail and does not necessarily represent the life of a product.
The MTBF figure is a statistical representation of the likelihood of a device to fail. A MTBF figure of e.g. 1 000 000h means that
statistically one unit will fail every 100 hours if 10 000 units are installed in the field. However, it can not be determined if the failed unit
has been running for 50 000h or only for 100h.
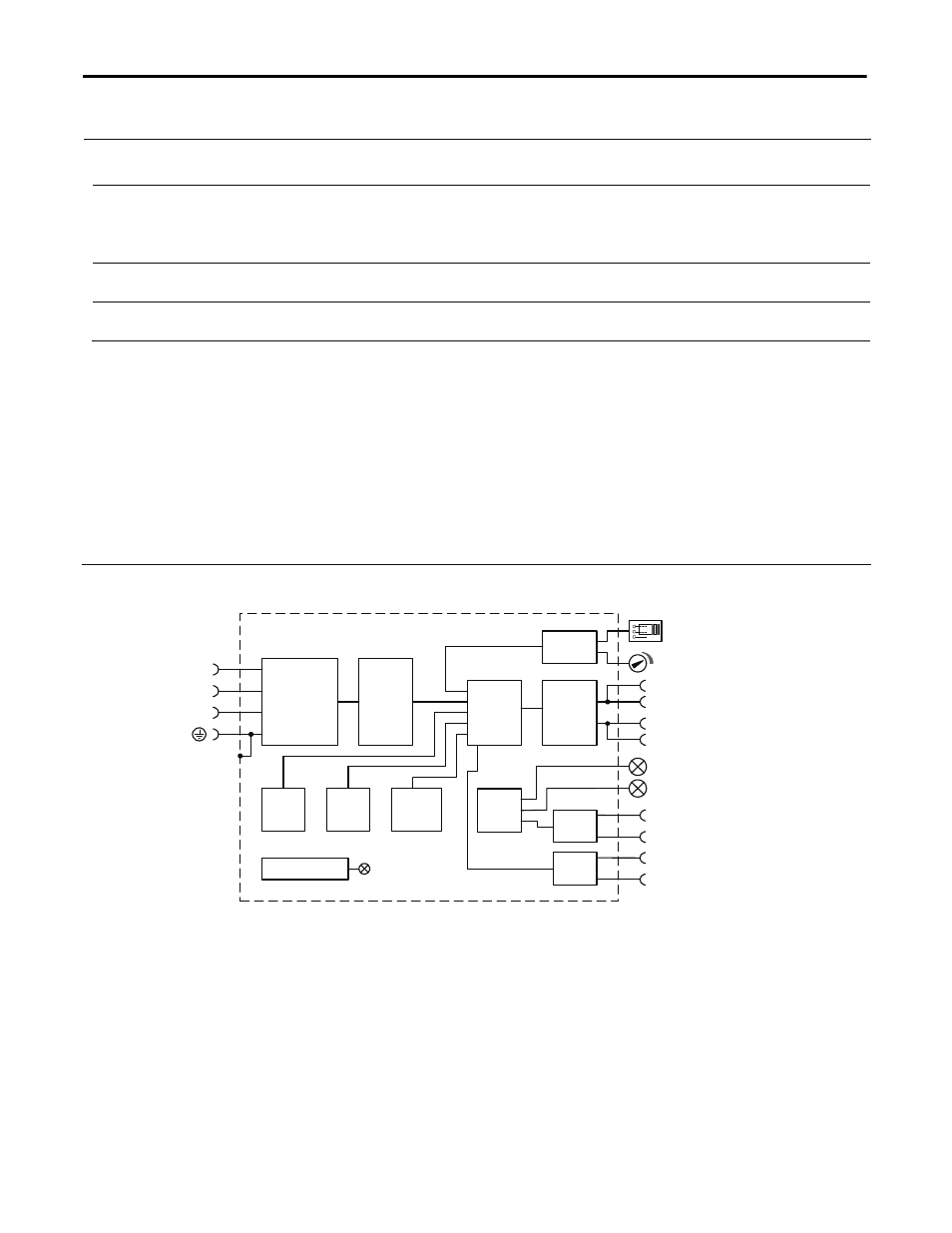
14. Functional Diagram
Fig. 14-1 Functional diagram
+
+
-
-
V
OUT
DC-ok
Contact
Output
Over-
Voltage
Protection
PFC
Converter
Input Fuses
Input Filter
Input Rectifier
Inrush Limiter
Transient Filter
Output
Voltage
Regulator
Power
Converter
Output
Filter
DC ok
Relay
Output
Voltage
Monitor
Output
Power
Manager
Temper-
ature
Shut-
down
Overload
LED
DC-ok
LED
L2
L3
L1
Single /
Parallel
Shut-
down
Input
Shut-
down
13
14
15
16
Event Datalogger
