4 operation, 1 measuring principle, measuring behavior – INFICON HPG400 ATM to High-Vacuum Gauge User Manual
Page 23
tina31e1 (2004-05) HPG400 v1.om
23
4 Operation
The HPG400 consists of two separate measuring systems (high pressure (HP) hot
cathode and Pirani).
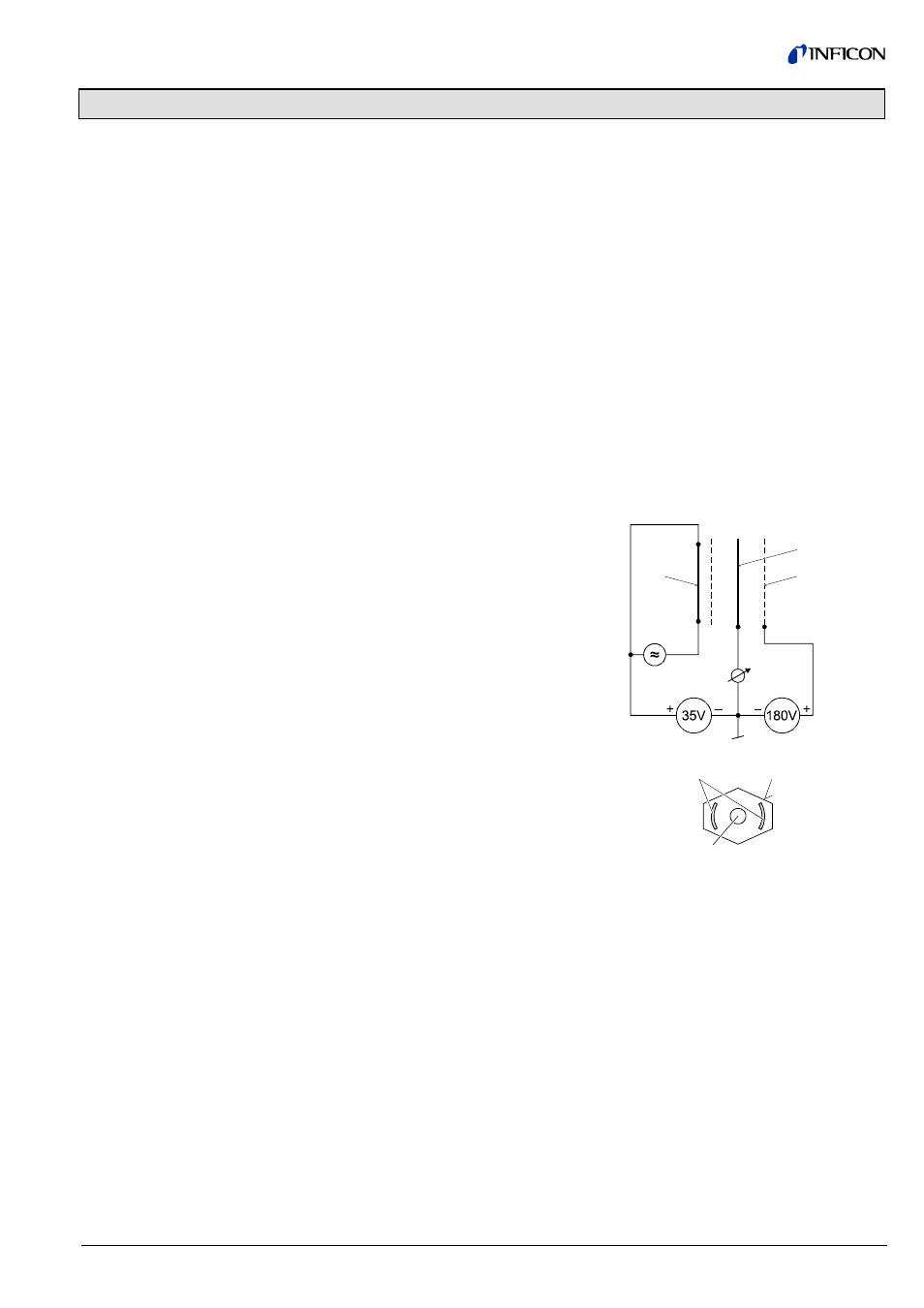
The HP hot cathode measuring system is based on the electrode arrangement
shown in the figure below, which grants sensitivity, linearity, and stability even at
high pressures.
The measuring principle of this system is based on gas ionization. Electrons emit-
ted by the hot cathode (F) ionize a number of molecules proportional to the pres-
sure in the measuring chamber. The ion collector (IC) collects the thus generated
ion current I
+
and feeds it to the electrometer amplifier of the measuring instrument.
The ion current is dependent on the emission current I
e
, the gas type, and the gas
pressure p according to the following relationship:
I
+
= I
e
× p × C
Factor C represents the sensitivity of the gauge. It is generally specified for N
2
.
The lower measurement limit is 2×10
-6
mbar.
In order for the entire range of 2×10
-6
mbar … 1 mbar to be covered, the emission
current is continually increased from 4 µA at 1 mbar to 130 µA at 2×10
-6
mbar (no
transients due to switching of the emission current).
Diagram of the HP measuring system
F
hot cathode (filament)
IC
ion collector
EC
electron collector (anode)
EC
IC
F
IC
EC
F
4.1 Measuring Principle,
Measuring Behavior
High pressure (HP) hot cathode
