Flint & Walling Commander Pro 300 User Manual
Page 5
5
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755
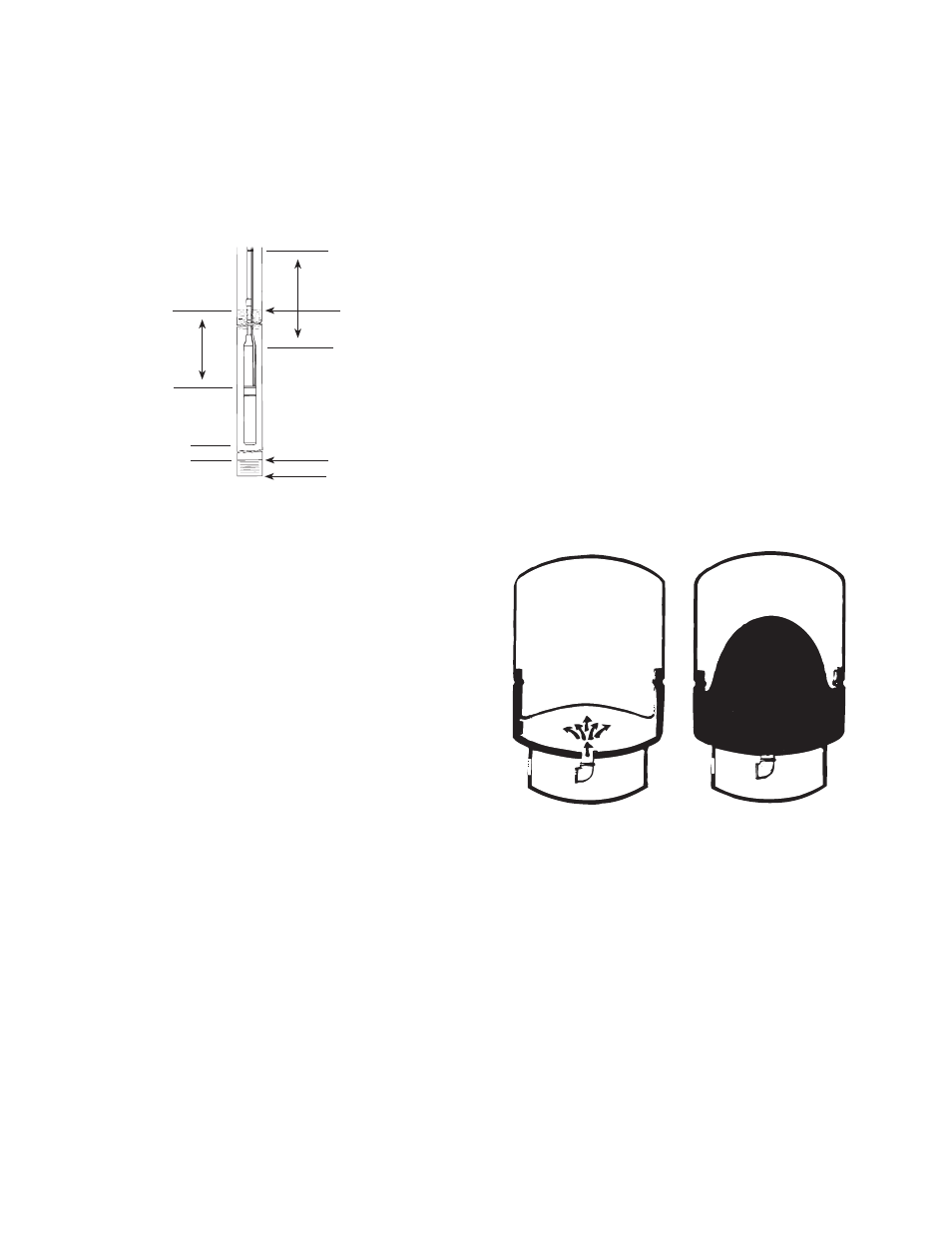
8. The complete pump and motor should be
submerged at least ten feet below the draw
down level of the well, and the motor should be
a minimum of ten feet off the bottom of the well
(Figure 4).
9. The Piping — Install the pump with pipe of the
same diameter as the discharge port of the pump
or larger.
IL0077
Figure 4
10 ft.
10 ft.
10 ft. Min.
Drawn Down Water
Level
Top of Well Screen
Bottom of Well
NOTE: Use of pipe smaller that the discharge port
of the pump will restrict the capacity of the pump and
lower its operating performance.
10. Check Valve — A check valve is required on all
submersible installations. This valve maintains
water within the pipe when the pump is running. A
line check should be installed within 25 feet of the
pump and below the draw down level of the water
supply.
a. For well depths exceeding 200 feet, it is
suggested that an additional check valve be
installed every 125 feet.
b. An additional check valve should be installed in
the horizontal line between the well top and the
pressure tank (See Figures 1 & 2).
CAUTION: Make certain that the check valve is
pointing in the right direction, arrow pointing towards
the tank.
11. Torque Arrester — To center the pump as it is
being lowered into the well, a torque arrester is
recommended. This will also minimize the pump
whipping due to the starting torque of the motor
(See Figure 2).
NOTE: On plastic pipe installations a torque
arrester must be installed. Cable guards should also
be installed.
12. Pressure Tank — The purpose of the pressure
tank is to allow an amount of water to be drawn
before the pressure drops enough to cause the
pump to start. Without a pressure tank, the pump
would start and stop continuously when water is
drawn. There are two types of pressure tanks,
the standard tank that requires an air volume
control and the pre-charged tank.
a. On a standard pneumatic tank system, air
is introduced to compensate for that which
is absorbed by the water. Each time the
pump cycles air is added to the tank through
a bleeder and snifter valve. The excess air
is released by a float assembly (air volume
control) in the upper side tapping of the tank
(See Figure 2).
b. In a pre-charged tank, a flexible diaphragm
or bladder separates the air and water areas
of the tank. The air chamber is pre-charged
by means of a tire valve with pressure 2 PSI
less than the cut-on pressure of the pump.
Because the air is not in contact with the
water, it cannot be absorbed by the water.
Therefore, the original charge of air is never
lost.
13. In pre-charged tank systems, none of the
fittings for air introduction or air level control are
required (Figure 1). The piping in the well is also
different for the two systems. The pre-charged
tank system does not require a bleeder orifice
assembly, which simplifies the installation.
IL0096
Figure 5
Pump On. Water Enters
The Reservoir
System Filled.
Pump Off
14. The tank size should be selected to keep
the pump starts per day as low as practical
for maximum life. Excessive motor cycling
accelerates motor bearing and spline wear, pump
wear and contact erosion. Use as a guide, 100
starts per day (24 hours) on single phase motors
and 300 starts per day on three phase units.
15. Pressure Switch — The pressure switch provides
for automatic operation. The pump starts when
the pressure drops to the switch cut-in setting
and stops when the pressure reaches the switch
cut-out setting. The pressure switch must be
installed as close to the tank as possible (Figures
1 & 2).
16. Pressure Relief Valve — A properly sized
pressure relief valve must be installed on any
