4 power supply characteristics, 5 thermal data (48-pin lqfp) – Cirrus Logic CS485xx User Manual
Page 10
10
DS734F5
5.4 Power Supply Characteristics
5.4 Power Supply Characteristics
(Measurements performed under operating conditions)
5.5 Thermal
Data (48-pin LQFP)
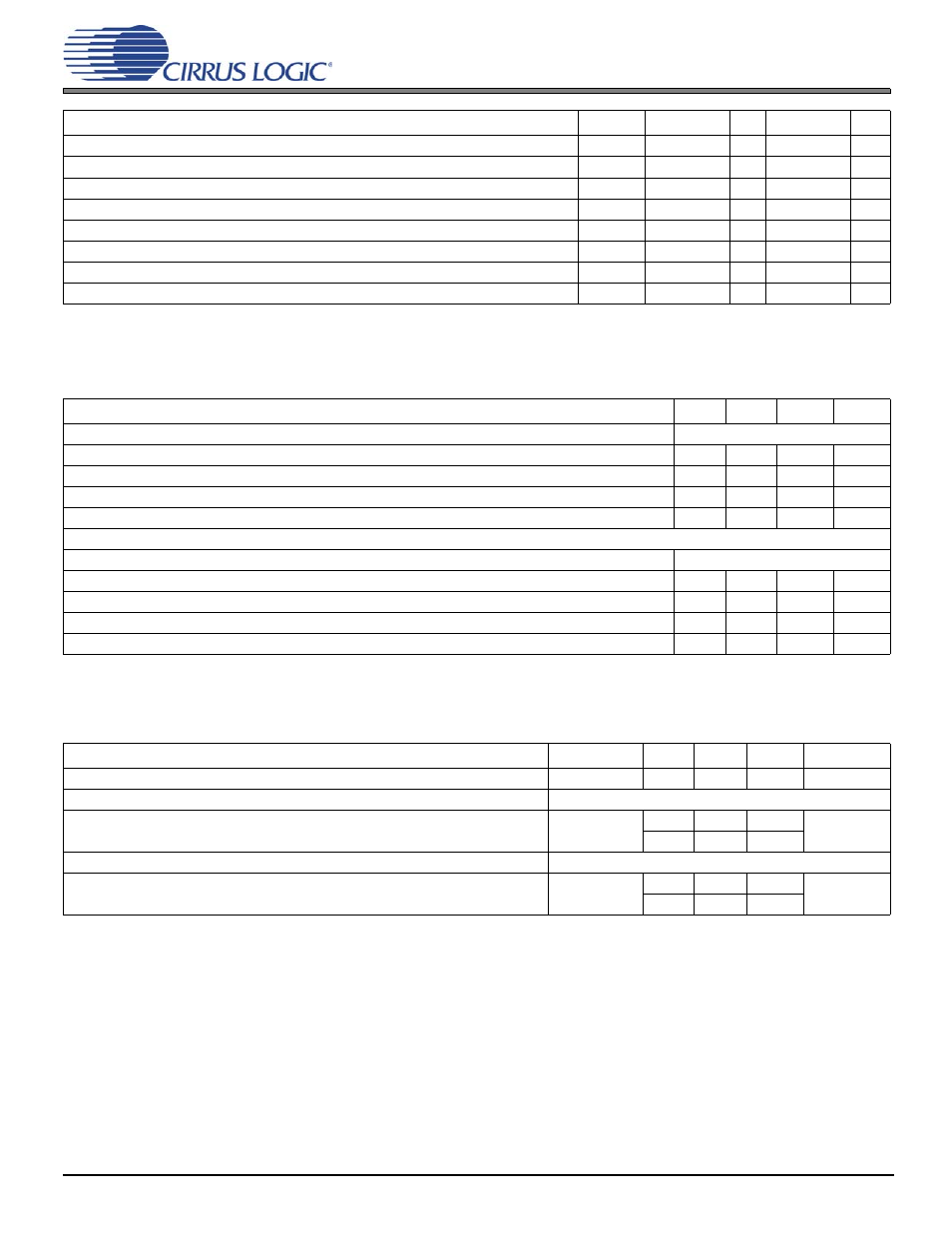
Parameter
Symbol
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
High-level input voltage
V
IH
2.0
—
—
V
Low-level input voltage, except XTI
V
IL
—
—
0.8
V
Low-level input voltage, XTI
V
ILXTI
—
—
0.6
V
Input hysteresis
V
hys
—
0.4
—
V
High-level output voltage (I
O
= –2 mA), except XTI
V
OH
VDDIO*0.9
—
—
V
Low-level output voltage (I
O
= 2 mA), except XTI
V
OL
—
—
VDDIO*0.1
V
Input leakage XTI
I
LXTI
—
—
5
µA
Input leakage current (all digital pins with internal pull-up resistors enabled)
I
LEAK
—
—
70
µA
Parameter
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Operational Power Supply Current:
VDD: Core and I/O operating
1
1.Dependent on application firmware and DSP clock speed.
—
203
—
mA
VDDA: PLL operating
—
8
—
mA
VDDIO: With most ports operating
—
27
—
mA
Total Operational Power Dissipation:
—
480
—
mW
Standby Power Supply Current:
VDD: Core and I/O not clocked
—
100
—
µA
VDDA: PLL halted
—
1
—
µA
VDDIO: All connected I/O pins 3-stated by other ICs in system
—
50
—
µA
Total Standby Power Dissipation
—
348
—
µW
Parameter
Symbol
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Junction Temperature
T
j
—
—
125
°C
Thermal Resistance (Junction to Ambient)
Two-layer board
1
Four-layer board
2
1.Two-layer board is specified as a 76 mm X 114 mm, 1.6 mm thick FR-4 material with 1 oz. copper covering 20% of the top and bottom layers.
2.Four-layer board is specified as a 76 mm X 114 mm, 1.6 mm thick FR-4 material with 1 oz. copper covering 20% of the top and bottom layers and 0.5
oz. copper covering 90 % of the internal power plane and ground plane layers.
θ
ja
—
63.5
—
°C/Watt
—
54
—
Thermal Resistance (Junction to Top of Package)
Two-layer board
3
Four-layer board
4
3.To calculate the die temperature for a given power dissipation
T
j
= Ambient Temperature + [(Power Dissipation in Watts)*
θ
ja
]
4.To calculate the case temperature for a given power dissipation
T
c
=
T
j
– [(Power Dissipation in Watts)*
ψ
jt
]
ψ
jt
—
0.70
—
°C/Watt
—
0.64
—
