Cnr4 performance and measurements under – Campbell Scientific CNR4 Net Radiometer User Manual
Page 43
Appendix A. CNR4 Performance and
Measurements under Different
Conditions
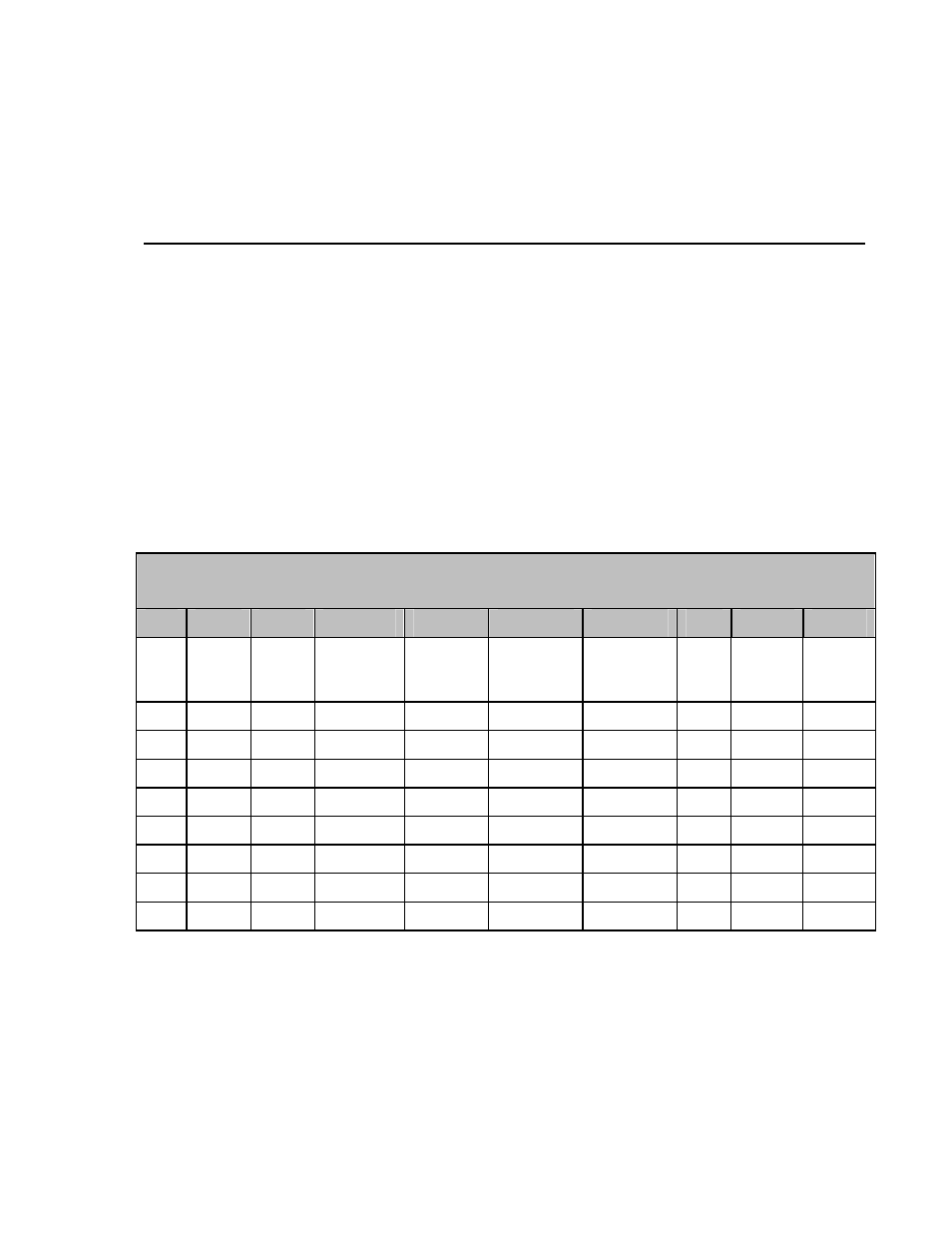
TABLE A-1 shows what one might typically expect to measure under different
meteorological conditions.
The first parameter is day and night. At night, the solar radiation is zero. The
second column shows if it is cloudy or clear. A cloud acts like a blanket,
absorbing part of the solar radiation, and keeping net far infrared radiation
close to zero. The third parameter is ambient temperature; this is included to
show that the sky temperature, column nine, “sky T”, tracks the ambient
temperature. Under cloudy conditions this is logical; cloud bases will be colder
than the ambient temperature. At instrument level, the temperature difference
depends roughly on cloud altitude.
Under clear sky conditions, it is less obvious that sky temperature “adjusts” to
the ambient temperature. This can roughly be attributed to the water vapor in
the air, which is a major contributor to the far infrared radiation.
TABLE A-1. Typical output signals of CNR4 under different meteorological conditions.
Explanation can be found in the text.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Day
night
Cloudy
clear
+20ºC
–20ºC
Pyrgeo–
meter
Up
Pyrgeo–
meter
low
Pyrano–
meter
up
Pyrano–
meter
low
Pt
100
sky T
ground
T
d cloud +20
0
0
0–500
0–150 20 20
20
d cloud –20
0
0
0–500
0–150 –20 –20 –20
d clear +20 –100*
0
0–1300 0–400 20 1*
20
d clear –20 –100*
0
0–1300 0–400 –20 –53* –20
n cloud +20
0
0
0
0
20 20
20
n cloud –20
0
0
0
0
–20 –20 –20
n clear +20 –100***
0
0**
0
20 1*** 20
n clear –20 –100***
0
0**
0
–20
–53*** –20
* Values may suffer from the so-called window heating offset; the sun heats the pyrgeometer window causing a
measurement error of +10 Watts per square meter (maximum).
** Values may suffer from negative infrared offsets, caused by cooling off of the pyranometer dome by far
infrared radiation. The maximum expected offset value is 15 Watts per square meter.
*** Values may suffer from dew deposition. This causes the pyrgeometer-up values to rise from –100 to 0 Watts
per square meter.
A-1
