Matrix Orbital GLK19264-7T-1U User Manual
Page 25
(b) Height (1 byte)
(c) ASCII Start Value (1 byte)
(d) ASCII End Value (1 byte)
2. Character Table (3 bytes for every character between the ASCII Start and End values inclusive)
(a) High Offset MSB (1 byte)
(b) Low Offset LSB(1 byte)
(c) Character Width (1 byte)
3. Bitmap Data
5.1.2
Creating a Font
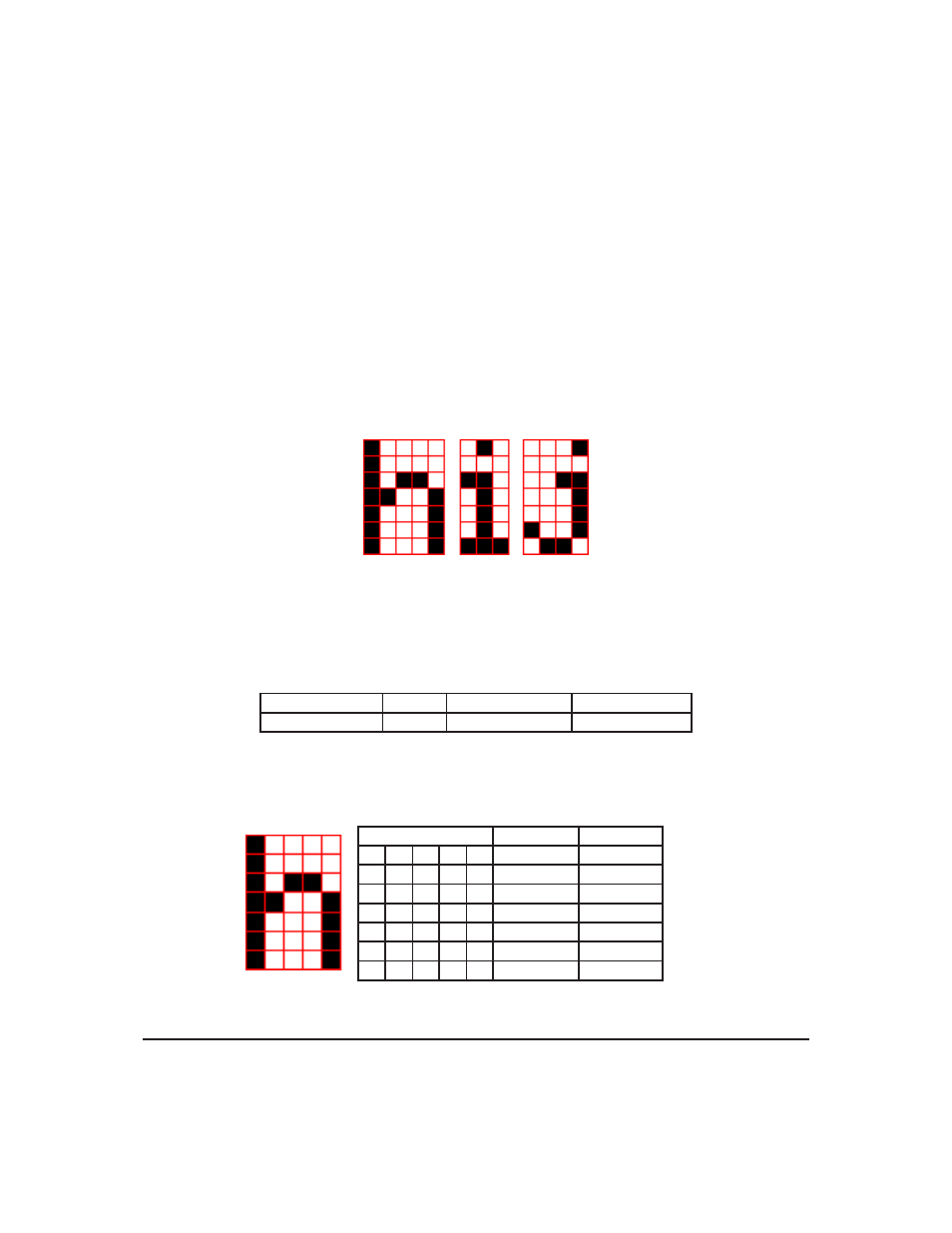
The following is an example of how to create a font file for the letters h, i and j.
First you must create the bitmaps containing the character data in bitmap form. Figure 21 below illus-
trates the bit pattern for the h, i and j bitmap data.
Figure 21: Bitmaps for h, i, and j
Second you may begin to create the font file starting with the header. The header will contain the nominal
width, the height and the ASCII start and end values inclusive that you wish to create characters for.
Table 8: Font File Header
Nominal Width
Height
ASCII Start Val
ASCII End Val
0x05
0x07
0x68
0x6A
Next we will have to find out how many bytes each character will use up, in order to create the character
table. The bitmaps are encoded horizontally and may have variable widths, h has a width of five, i a width
of three and j a width of four, see the figure below for an example of encoding the first letter h:
Bitmap Data
Byte
Hex Value
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
10000100
0x84
1
0
1
1
0
00101101
0x2D
1
1
0
0
1
10011000
0x98
1
0
0
0
1
11000110
0xC6
1
0
0
0
1
00100000
0x20
1
0
0
0
1
Figure 22: Bitmap Encoding
Matrix Orbital
GLK19264-7T-1U
20
