Calculating the number of bc pairs if luse is used – HP XP Business Copy Software User Manual
Page 20
20
Business Copy XP (BC) for the XP10000/XP12000
If you intend to create pairs with volumes of different emulation types, the maximum number of pairs you
can create depends on the following conditions.
NOTE:
For more information about calculating total number of differential tables per pair, see
.
Calculating the number of BC pairs if LUSE is not used
Use the following equation to calculate whether the desired number of BC pairs can be created:
, where:
•
is the required number of differential tables per pair (see
).
•
(number of BC pairs) is the number of BC pairs you want to create.
•
is number of differential tables in the disk array.
•
= 13,652 when additional shared memory for differential tables is not installed.
•
= 30,718 when additional shared memory for differential tables is installed.
For example, if you create 10 pairs of OPEN-3 volumes and 20 pairs of OPEN-V volumes in a disk array
that does not have additional shared memory for differential tables, use the following equation:
.
Since 3,870 is less than 13,652, 10 pairs of OPEN-3 volumes and 20 pairs of OPEN-V volumes can be
created.
NOTE:
When the emulation type is OPEN-3, and the capacity of the volume is 2,403,360 KB, the
number of differential tables required for a pair is 1. When the emulation type is OPEN-V, and the
capacity of the volume is 3,019,898,880 KB, the number of differential tables required for a pair is193.
Calculating the number of BC pairs if LUSE is used
Use the following equation to calculate whether the desired number of BC pairs can be created:
, where:
•
is the required number of differential tables for each volume that forms the LUSE volume.
When you use LUSE volumes to create a BC pair, every volume that forms the LUSE volume uses the
differential tables as a pair. For example, if you create a BC pair by using LUSE volumes that are
created by combining two OPEN-V volumes, you need differential tables for two OPEN-V pairs.
•
is number of differential tables in the disk array.
Up to 1,811.2GB
121
Up to 2,305.1GB
154
Up to 2,799.1GB
187
Up to 1,826.1GB
122
Up to 2,320.1GB
155
Up to 2,814.1GB
188
Up to 1,841.1GB
123
Up to 2,335.1GB
156
Up to 2,829.0GB
189
Up to 1,856.1GB
124
Up to 2,350.0GB
157
Up to 2,844.0GB
190
Up to 1,871.0GB
125
Up to 2,365.0GB
158
Up to 2,859.0GB
191
Up to 1,886.0GB
126
Up to 2,380.0GB
159
Up to 2,873.9GB
192
Up to 1,901.0GB
127
Up to 2,394.9GB
160
Up to 2,880.0GB
193
Up to 1,915.9GB
128
Up to 2,409.9GB
161
Up to 1,930.9GB
129
Up to 2,424.9GB
162
1. 1 GB = 1024
3
Bytes
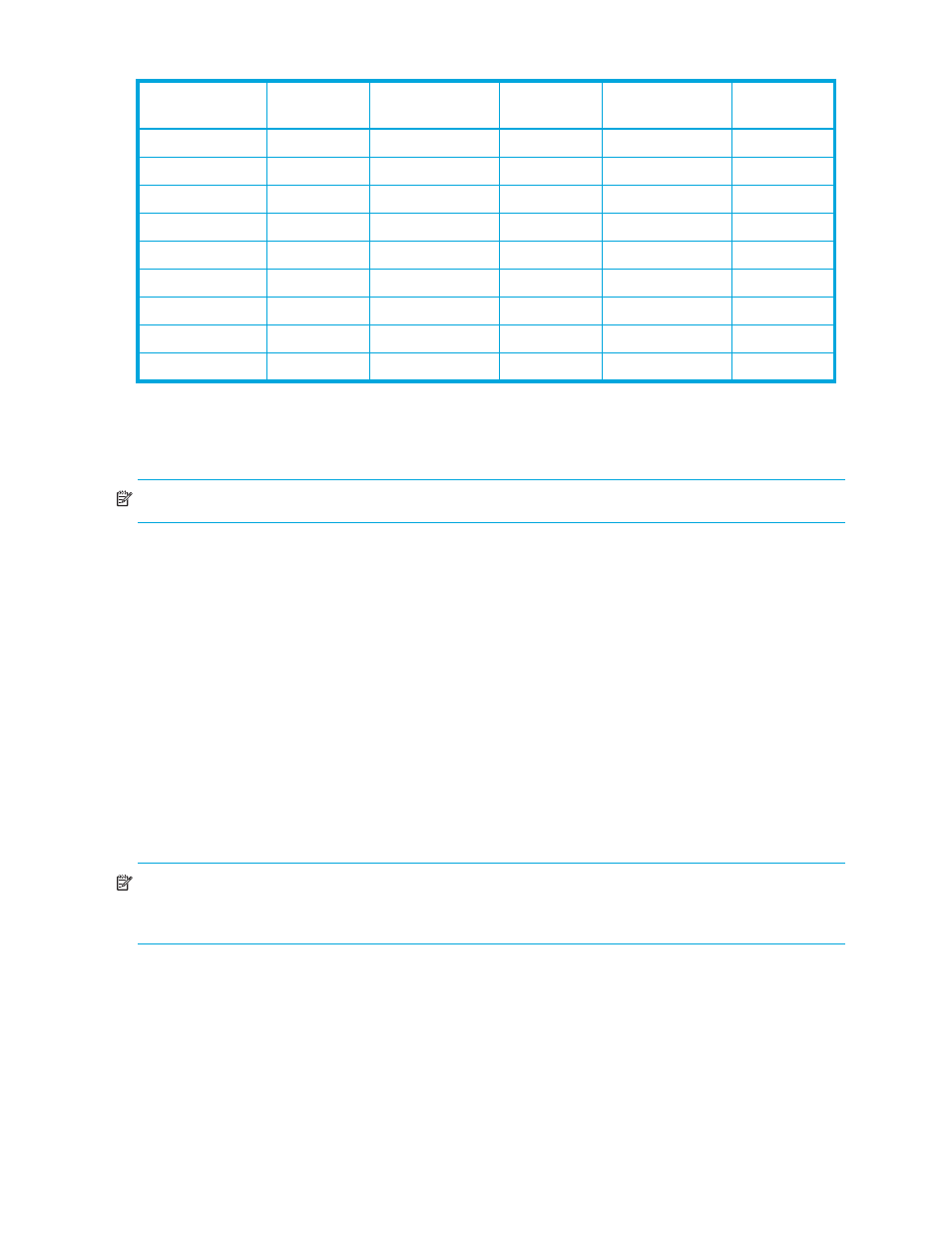
Table 7
Number of differential tables used in OPEN-V (continued)
Capacity
1
Differential
tables
Capacity
1
Differential
tables
Capacity
1
Differential
tables
Σ α
( )
number of BC Pairs
(
)
×
{
}
β
( )
≤
α
( )
β
( )
β
( )
β
( )
1 10 193 20
Ч
+
Ч
3870 13,652
≤
=
Σ Σ α
( )
number of volumes that form LUSE volumes
(
)
×
{
}
number of BC pairs
(
)
×
[
]
β
( )
≤
α
( )
β
( )
