Sap acc overview, The virtual sap landscape, 1 components to create a virtualized application – HP Storage Essentials Enterprise Edition Software User Manual
Page 14
SAP Adaptive Computing Overview
2
SAP ACC Overview
The following section provides some basic background on the structure and functionality of the SAP
Adaptive Computing Controller (SAP ACC). For more detailed information, refer to the
documentation provided by SAP on this subject. It is available at
http://service.sap.com/adaptive
.
This URL requires you to provide an SAP S-user ID.
The following topics are covered in this section:
• Control
The Virtual SAP Landscape
To create an adaptive SAP landscape, it is necessary to have a virtual application setup. The
application and all the resources belonging to the applications (network and storage) must be
grouped together into one unit that can be moved from one system to another independent from
anything else on the system.
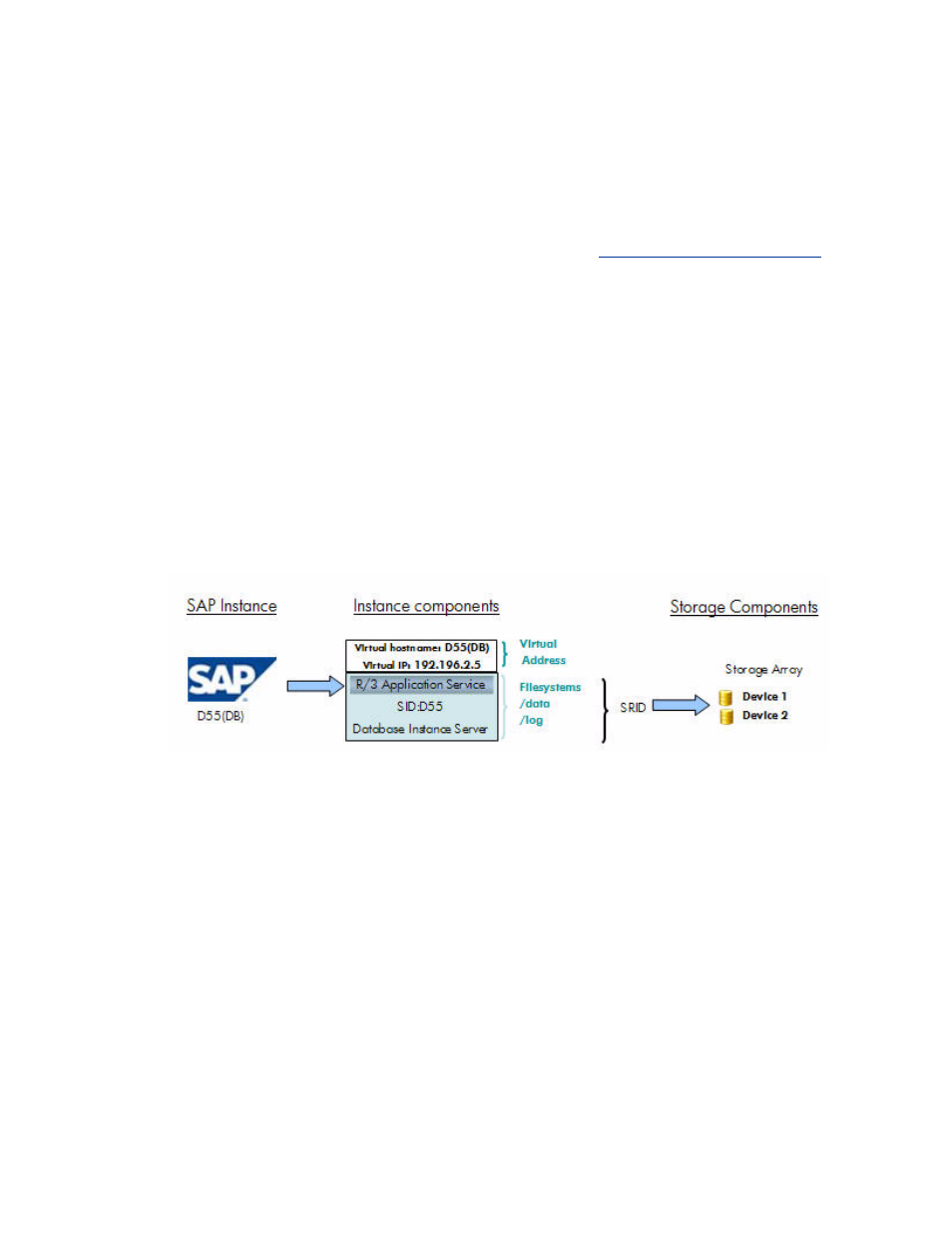
The following figure describes the components to create a virtualized application.
Figure 1
Components to create a virtualized application
A SAP instance consists of network resources that include a virtual host name and a virtual IP
address. This virtual IP address is different from the dedicated server IP address assigned to the
hardware. The virtual IP address of the application makes it possible to connect to the application,
independent of the hardware, anywhere in the landscape.
The SAP instance also consists of physical storage, either Network Attached Storage (NAS) or
Storage Area Network (SAN)-attached storage. The storage is made up of file systems located on
logical devices (Ldev) from a storage system. The SAP ACC groups all the storage components of an
instance under the Storage Resource Identifier (SRID) and lets you create a custom name for the
storage component of the instance.
The HP Storage Essentials Storage Resource Management (SRM) Enterprise Edition Application
Integration Software for SAP ACC provides a link between the SRID created in SAP and the physical
