Fig.26 – KYORITSU 6016 User Manual
Page 34
31
Max value of Zs for this example is 1.44 Ω (MCB 16A, characteristic C), the instrument
reads 1.14 Ω (or 202 A on Fault current range) it means that the condition
Zs x Ia ≤ Uo is respected.
In fact the Zs of 1.14 Ω is less than 1.44 Ω (or the Fault current of 202 A is more than Ia
of 160A).
In other words, in case of fault between phase and earth, the wall socket tested in this
example is protected because the MCB will trip within the disconnection time required.
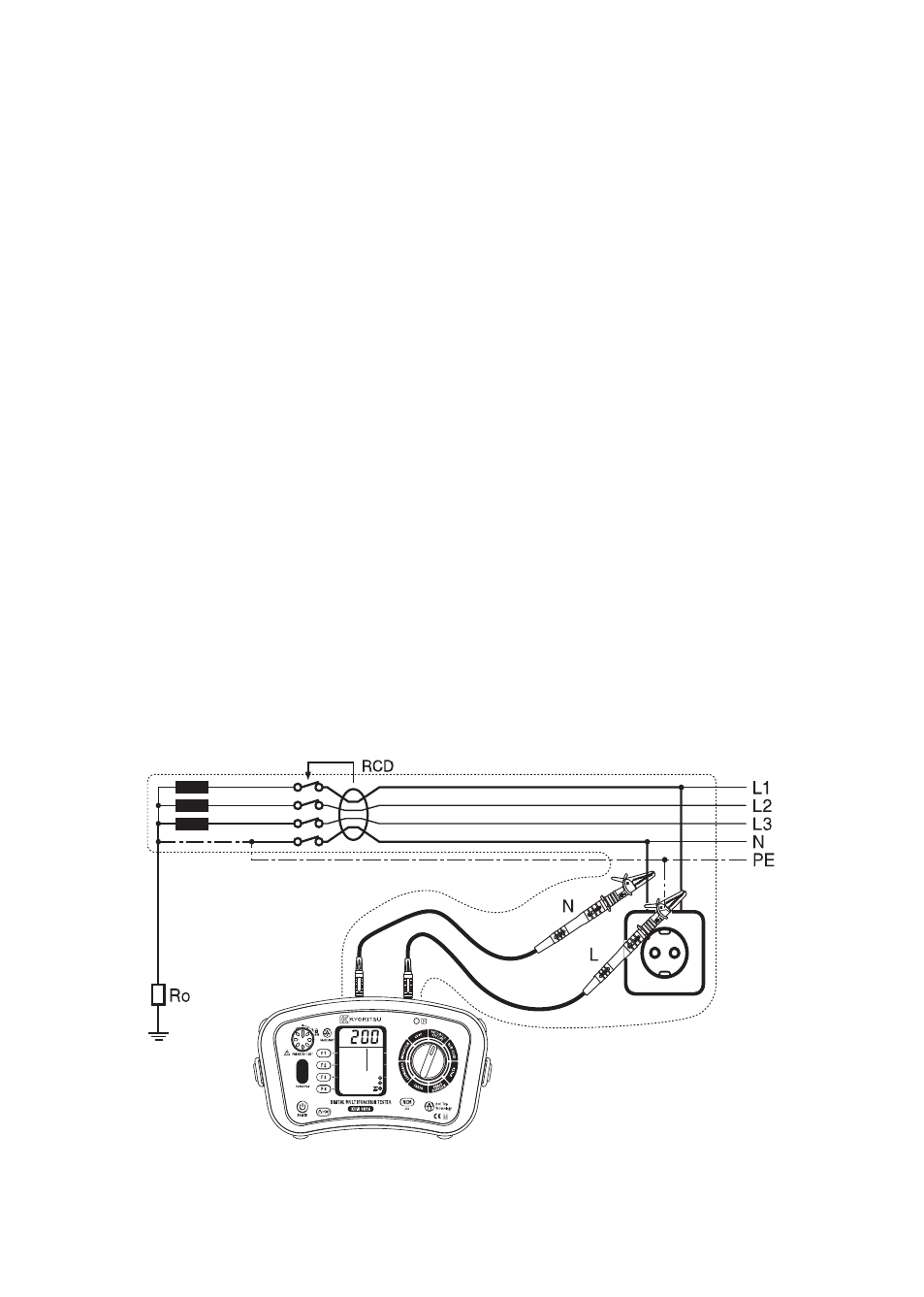
9.2 Principles of the measurement of line impedance and PSC
The method for measuring Line – neutral impedance and line-line impedance is exactly
the same as for earth fault loop impedance measurement with the exception that the
measurement is carried out between line and neutral or line and line.
Prospective short circuit or fault current at any point within an electrical installation
is the current that would flow in the circuit if no circuit protection operated and a
complete (very low impedance) short circuit occurred. The value of this fault current
is determined by the supply voltage and the impedance of the path taken by the fault
current. Measurement of prospective short circuit current can be used to check that the
protective devices within the system will operate within safety limits and in accordance
with the safe design of the installation. The breaking current capacity of any installed
protective device should be always higher than the prospective short circuit current.
PSC
A
230
V
L-N
50.0Hz
L-PE
L-N
!
Fig.26
