KROHNE GFM 700 EN User Manual
Page 6
6
3 Measuring
principle
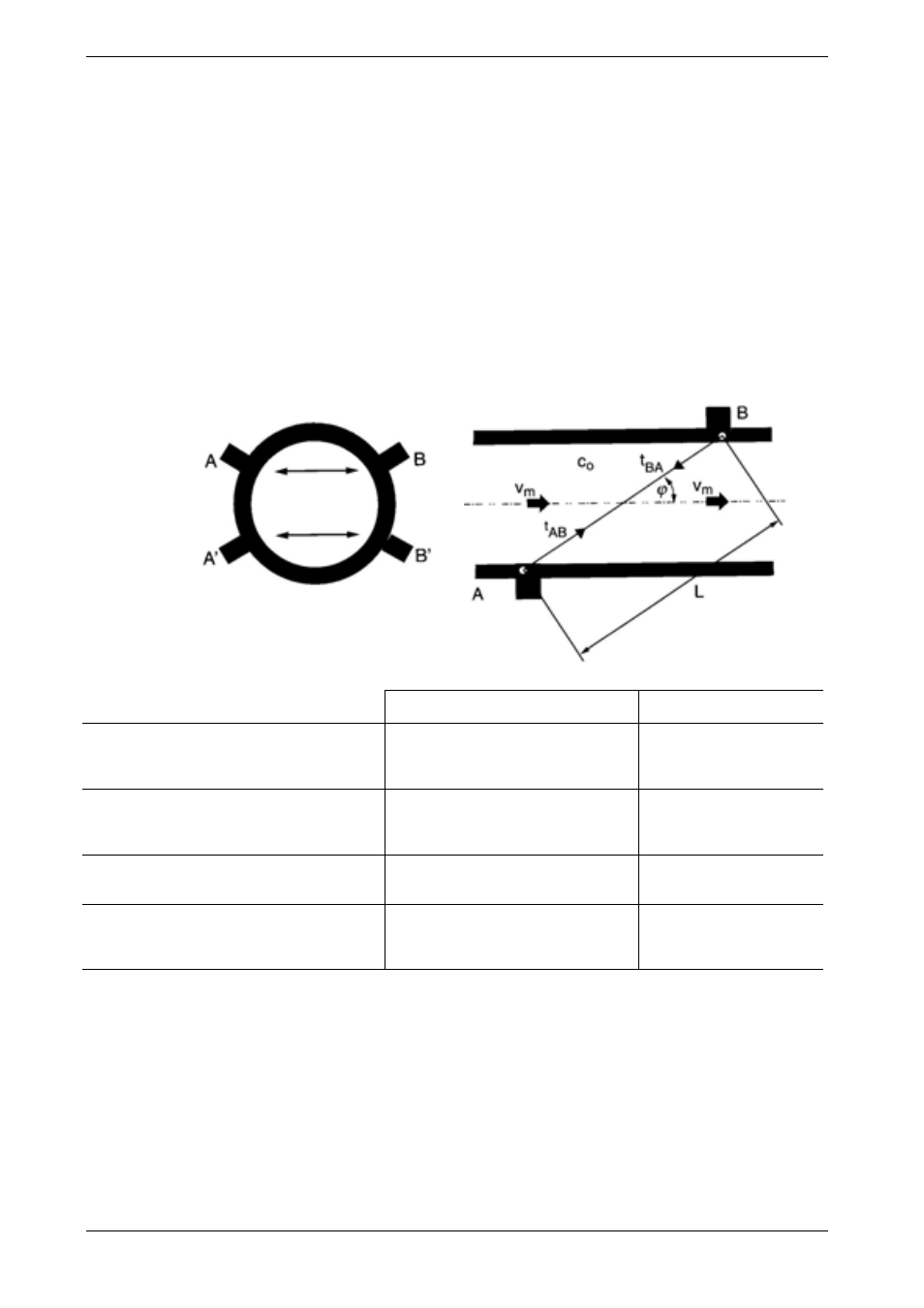
All KROHNE ultrasonic flowmeters operate using the
transit-time differential method.
Transit-time differential measurement is based on a
simple physical fact.
Imagine two canoes crossing a river on the same
diagonal line, one with the flow and the other against the
flow. The canoe moving with the flow needs much less
time to reach the opposite bank.
Ultrasonic waves behave exactly the same way. A sound
wave travelling in the direction of flow of the product is
propagated at a faster rate than one travelling against the
flow (v
AB
> v
BA
).
Transit times t
AB
and t
BA
are measured continuously. The
difference (t
BA
- t
AB
) in time travelled by the two ultrasonic
waves is directly proportional to the mean flow velocity
(v
m
) of the product.
The volumetric flowrate per unit time is the product of the
mean flow velocity (v
m
) multiplied by the pipe cross-
section.
A liquid product is identified by direct measurement of the
transit time of ultrasonic waves. Assuming the same path
length (L), the transit time in water is shorter than in crude
oil, for example.
Propagation
rate
of ultrasonic waves . . .
Transit time
of ultrasonic waves …
… in direction of flow
of product from sensor A to B
v
AB
= c
o
+ v
m
x cos
ϕ
L
t
AB
= ---------------------
c
o
+ v
m
x cos
ϕ
… counter to direction of flow
of product
from sensor A to B
v
BA
= c
o
– vm × cos
ϕ
L
t
AB
= --------------------
c
o
- v
m
x cos
ϕ
with the given product
flow direction
v
AB
> v
BA
t
AB
< t
BA
mean flow velocity v
m
of liquid product
(t
BA
– t
AB
)
v
m
= GK x ---------------
(t
AB
x t
BA
)
A (A’)
Sensor A, transmitter and receiver
t
AB
Transit time of ultrasonic waves
from sensor A to sensor B
B (B’)
Sensor B, transmitter and receiver
t
BA
Transit time of ultrasonic waves
from sensor B to sensor A
c
o
Sound velocity in the product
v
AB
Propagation rate of ultrasonic waves between
sensor A and sensor B
GK
A calibration constant
v
BA
Propagation rate of ultrasonic waves between
sensor B and sensor A
L
Length of measuring beam,
distance between sensors A and B
v
m
Mean flow velocity of liquid product
ϕ
Angle between pipe axis and
measuring beam
