Functional block diagram functional block diagram – Detcon PI-600 User Manual
Page 5
3.1 P
RINCIPLE OF
O
PERATION
Ionizable target gases diffuse into the PID sensor chamber through a sintered f lame arrestor. These target gases are
exposed to UV radiation emitted by the PID lamp and this causes a fraction of the molecules to give up a free electron.
The free electrons are captured by the high voltage collection grid and provide a current signal that is directly propor-
tional to the concentration of the target gas. This change in current is completely reversible and results in the continu-
ous monitoring of ambient air conditions.
3.2 A
PPLICATION
3.2.1 Sensor Placement/Mounting
Sensor location should be reviewed by facility engineering and safety personnel. Area leak sources and perimeter mounting
are typically used to determine number and location of sensors. The sensors are generally located 2 - 4 feet above grade.
3.2.2 Interference Data
Detcon Model PI-600 series PID sensors are subject to interference from many gases. This interaction is shown in the
table in Section 3.2.3. The table shows most all gases of interest and the level of signal response they have relative to a
standard isobutylene reference gas. This measure is referred to as the Response Factor (RF). As a general rule, the lower
the RF value, the stronger the signal from the PID sensor. When determining a cross-interference from one gas to
another, f ind the RF of your target gas and then your interfering gas(es). The cross-interference will be calculated by
dividing the RF of your interfering gas by the RF of your target gas.
For example, if your target gas is benzene and you are concerned about a cross-interference to H2S then you would cal-
culate the cross interference to be 3.3/0.50 = 6.2. This shall be interpreted as: it will take 6.2 ppm of H2S to register as
1 ppm benzene on a PID sensor calibrated for benzene.
In many cases, the user will be interested in measuring a multiple of toxic VOC compounds. In this case the sensor
will produce a signal that is a composite total of each gases’ individual response, when taking into account the corre-
sponding response factors.
For example, if the target gases are benzene and isobutanol and your PID sensor was calibrated for benzene then the
presence of 5 ppm benzene and 5 ppm of isobutanol would each add to the total reading. In this case, the 5 ppm ben-
zene would register as 5 ppm, but the 5 ppm isobutanol would register as the amount of cross interference of isobu-
tanol relative to a benzene calibration. This is calculated as discussed above where you divide the RF of isobutanol by
the RF of benzene. Using the look up table this gives you 3.8/0.50 = 7.2. So it takes 7.2 ppm isobutanol to equal 1
part benzene. Since we have 5 ppm isobutanol, that will equal 0.7 ppm on the benzene scale. The total signal will be 5
+ 0.7 = 5.7 ppm.
3.2.3 Relative Response Gas Matrix (See next page)
The table shows you the response of the PID sensor to a long list of components. It includes the compound name,
synonyms/abbreviations, and chemical formula. It also lists the 10.6 eV Response Factor (the measure of how strong
the signal from the sensor is in reference to Isobutylene gas). Isobutylene gas is the standard reference used with PID
sensors, the lower the Response Factor, the stronger the signal.
NR = not reccomended (does not register)
? = measureable but no data exist
Conf irmed Value = “+” means actual gas has been used to verify RF, “blank” means it is an empirical estimate
IP = is the gases ionization potential (only gases < 10.6eV will respond to sensor)
TWA/Time Weighted Average = generally accepted limit for safe 8 hour exposure (in ppm)
PI-600 Toxic Gas Sensors PG.5
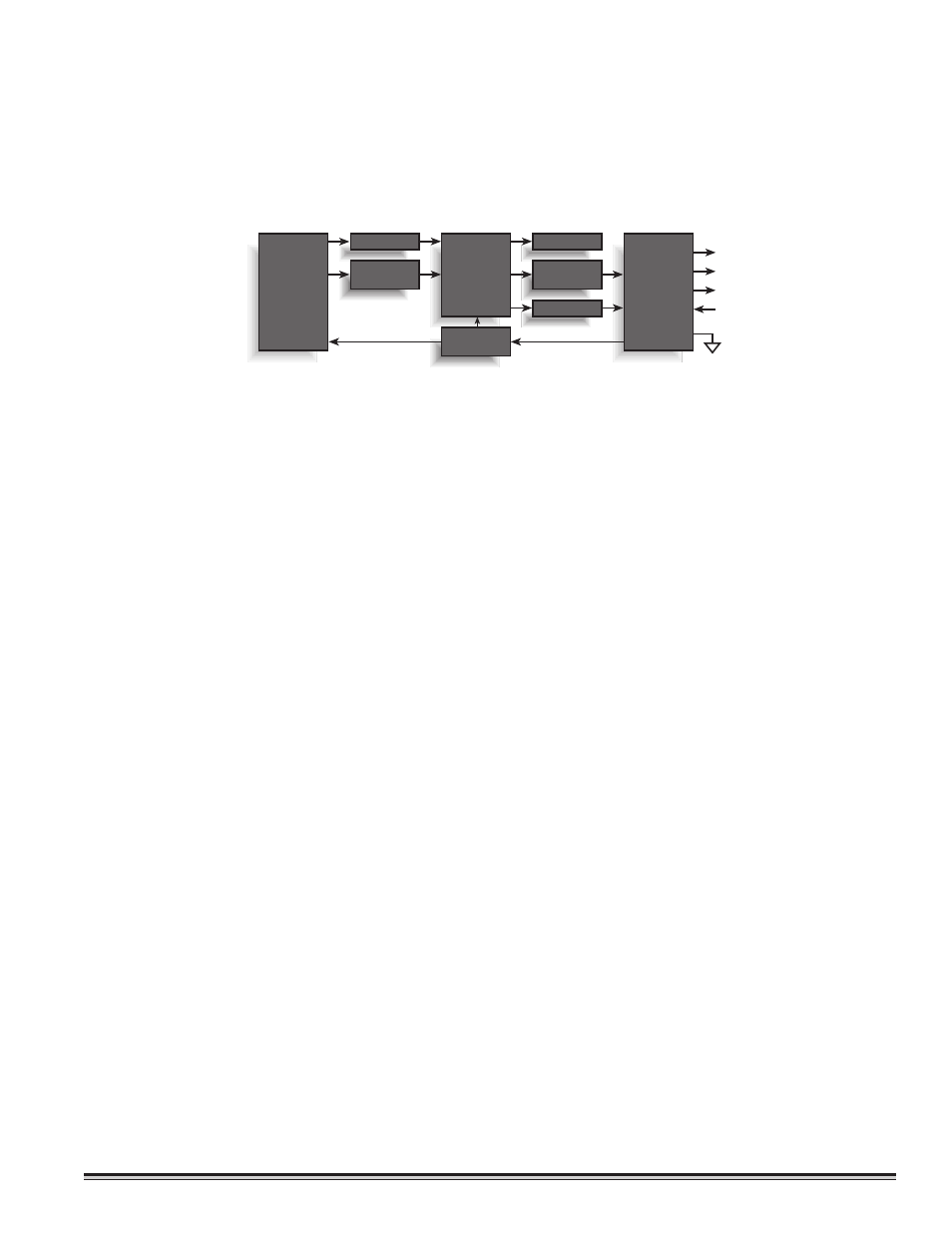
Functional
Block
Diagram
Functional
Block
Diagram
Analog 4-20 mA Out
Power In
Relays Out
Pre-Amp
Display
Temperature
Compensation
Alarm & Fault
Relays
RS-485 & 4-20mA
Micro-
processor
Transmitter
Power Supply
Sensor
Element
I/O Circuit
Protection
Serial RS-485 Out
