KB Electronics KBRG-212D User Manual
Page 24
24
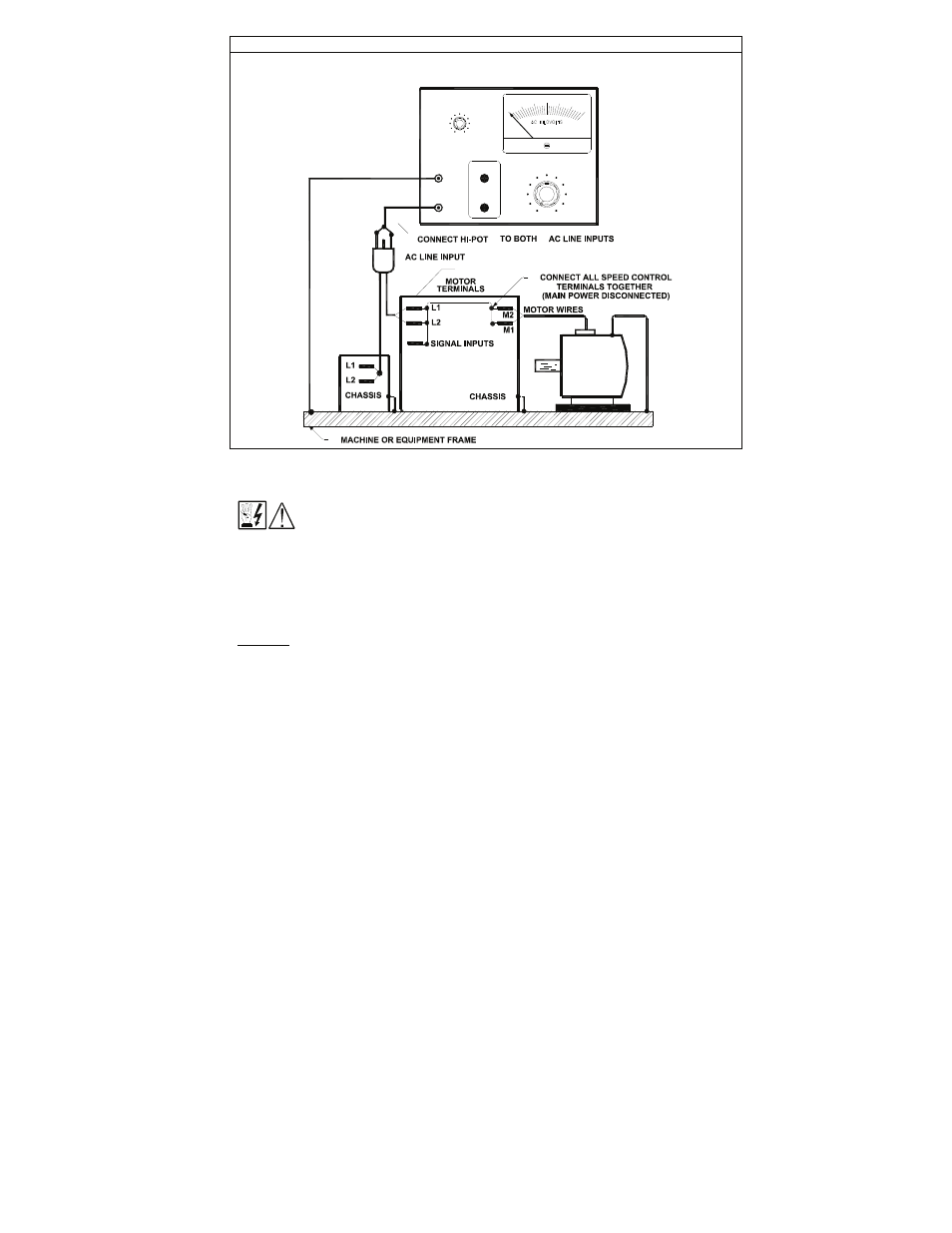
FIGURE 19 - TYPICAL HI-POT TEST SETUP
AUX. EQUPT.
FRAME
MOTOR SPEED CONTROL
HIGH VOLTAGE DIELECTRIC WITHSTAND TESTER
ZERO
(HI-POT TESTER)
RETURN
H. V.
RESET
TEST
LEAKAGE
0mA 10mA
0
VOLTAGE
MAX
1
2
3
9 DRIVE OPERATION
WARNING! READ SAFETY WARNING ON PAGE 5 BEFORE ATTEMPTING TO
OPERATE OR SEVERE INJURY OR DEATH CAN RESULT.
The input voltage can be derived from the wiper of the Main Speed Potentiometer or from an
analog input (voltage following mode). Since the KBRG-212D is a 4-quadrant regenerative
drives, the motor speed will follow both a positive and negative wiper voltage and drive the
motor in both the forward direction and reverse direction. In addition, it will apply both forward
and reverse torque in order to stabilize motor speed.
Example: To understand the concept of a regenerative drive, the operation of an elevator can
be used. If one were to enter the elevator on the first floor and press 10, the motor and control
would have to lift the elevator against gravity. In this mode, the drive would operate like a
conventional speed control which is called "motoring" (the applied load is opposite to the
direction of motor speed).
When the elevator is at floor 10 and floor 1 is pressed, gravity will try to pull the elevator car
down faster than the speed for which it is set. The control will then provide reverse torque to
keep the car form falling faster than the set speed. This operation is regeneration (the applied
load is in the same direction as the direction of motor rotation). Table 10, on page 25
summarizes the different modes of regen operation.
