Mma-303 direct/indirect charge - installation, Equipment grounding / safe- ty recommendations – Ransburg MMA-303 Direct_Ind Charge Atomizer A12870 User Manual
Page 44
MMA-303 Direct/Indirect Charge - Installation
41
LN-9269-11.3
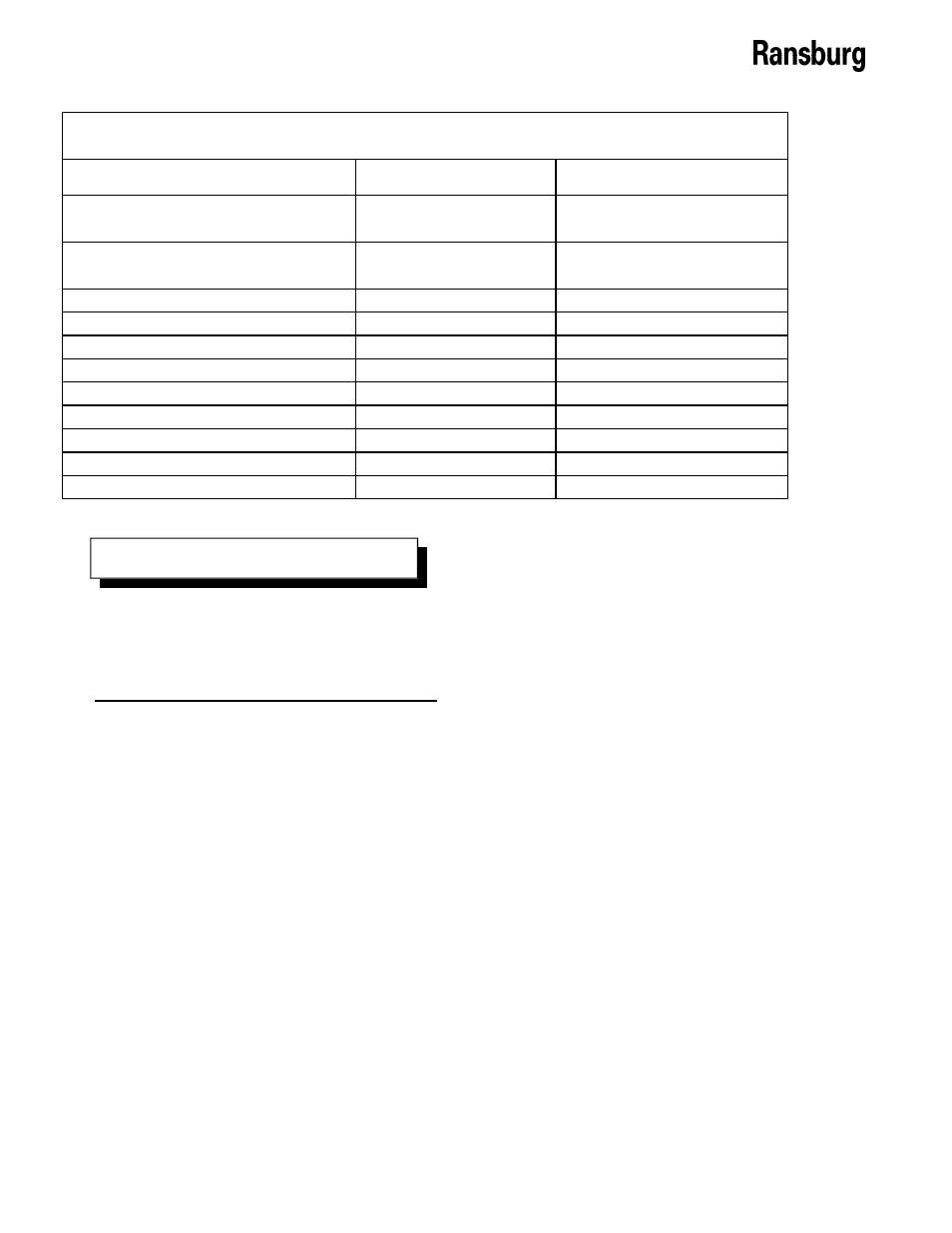
AIR TUBING C0NNECTIONS
Tube Size
Air Pressure Requirements
Bearing Air Supply (B.A.)
6 X 4mm (Yellow)
90 psi +/- 10 kPa)
(621 +/- 69 kPa)
Bearing Air Return (BRG RTN)
4mm (5/32") OD (Yellow)
90 psi +/- 10 (at atomizer card
(621 +/- 69 kPa)
Turbine Air (T.A.)
12 x 10mm
Variable
Cut-In Air (SAO)
10 X 8mm
Variable
Pattern Control Air (SAI)
8 X 6mm (Blue)
Variable
Brake Air (BRK) (if used)
6 X 4mm (Orange)
60-100 psi (414-689 kPa)
Paint Valve Control (PT)
4mm (5/32") OD (Natural)
80 psi +/- 10 (552 +/- 70 kPa)
Dump Valve Control (PD)
4mm (5/32") OD (Gray)
80 psi +/- 10 (352 +/- 70 kPa)
Cup Wash Solvent Valve Control (ST)
4mm (5/32") OD (Blue)
80 psi +/- 10 (352 +/- 70 kPa)
Cup Wash Air Valve Control (ATI)
4mm (5/32") OD (Orange)
80 psi +/- 10 (352 +/- 70 kPa)
Cup Wash Air (CWA)
6 X 4mm (Green)
80-100 psi (551-689 kPa)
N O T E
With the exception of fluid, dump, and bearing
air, all other pilot and air supply lines should
be bulkheaded and their diameters increased
one size.
EQUIPMENT GROUNDING / SAFE-
TY RECOMMENDATIONS
In electrostatic coating systems, the flow of
high voltage power from the power supply to
the atomizer is insulated from ground and iso-
lated from all other functions equipment.
When the voltage reaches the atomizer, it is
transferred to the coating material where, by
introducing a negative charge, it causes the
atomized fluid to seek the nearest positive
ground. In a properly constructed and operat-
ed system, that ground will be the target ob-
ject.
The directed conduction of the electric charge,
through its array of wires, cables, and equip-
ment, is accompanied by a variety of stray
electrical charges passing through the air by
various means such as: air ionization,
charged particles in the air and radiated ener-
gy. Such charges may be attracted to any
conductive material in the spray area. If the
conductive material does not provide a safe
drain to electrical ground, which will allow the
charge to dissipate as fast as it accumulates, it
may store the charge. When its electrical stor-
age limit is reached, or when it is breached by
external circumstances (such as the approach
of a grounded object or person, or one at low-
er potential), it may discharge its stored
charge to the nearest ground. If there is no
safe path to ground (such as a ground wire or
braided cable) it may discharge through the air
as a spark. A spark may ignite the flammable
atmosphere of a spray area. The hazard area
extend from the point of origin up to as much
as a twenty-foot radius. (See the NFPA-33 for
definition and limitations of a hazard area.)
