Introduction – Teledyne 6650 - Fluorescence Probe - Oil in Water analysis system User Manual
Page 9
UV-Photo-X
Introduction
Teledyne
Analytical
Instruments
1
Introduction
1.1 Theory of Operation
The ability to monitor the concentration of an analyte in a process
stream is critical for accurate and reliable process control. There are
many techniques used to determine the analyte concentration of interest.
One of the most sensitive sensing techniques is molecular fluorescence.
Fluorescence occurs when a molecule absorbs light energy, either
ultraviolet or visible, and rapidly emits light, at some longer wavelength.
Fluorescence of this type is referred to as Stokes fluorescence.
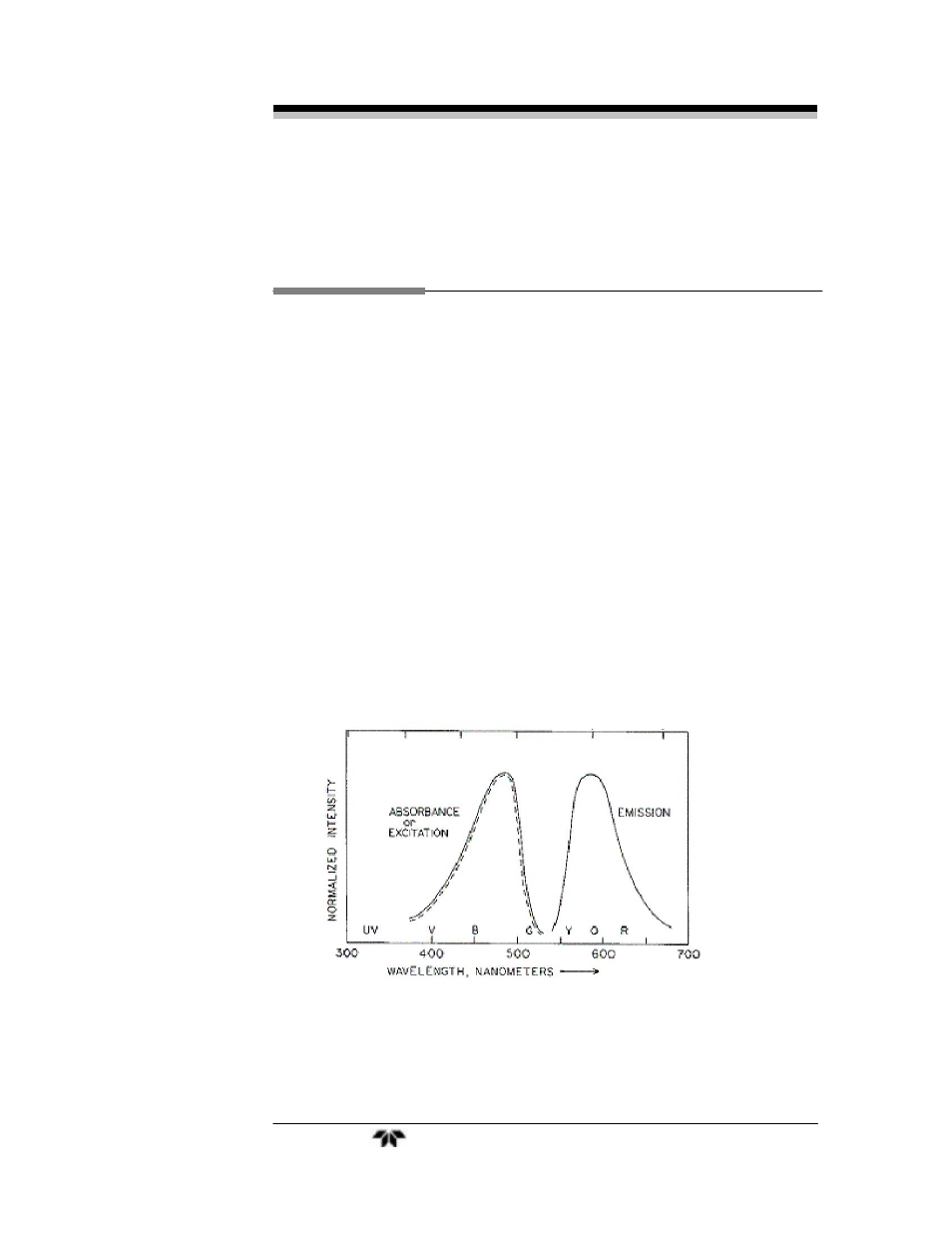
Fluorimetry characterizes the excitation and emission properties of the
molecular species. Figure 1-1 shows an example of the excitation and
emission spectrum from a hypothetical fluorophore.
Fluorimetry is concerned with two types of information: 1) The
(spectral) wavelength distribution, which is characteristic of the
electronic properties of the molecule, and 2) The intensity of the
fluorescence, which is typically correlated to the concentration of the
fluorescent molecule in the solution.
Figure 1-1: Molecular Fluorescence Example
- 1220 - Multipoint flammable gas and vapor detection system (50 pages)
- 212R - Thermal conductivity analyzer (28 pages)
- 235 - Thermal conductivity analyzer (38 pages)
- 275R - Portable turbine generator purge gas analyzer (21 pages)
- 2000A-EU - General purpose thermal conductivity analyzer (86 pages)
- 2000XTC - Thermal conductivity analyzer (40 pages)
- 2010A - Split architecture thermal conductivity analyzer (110 pages)
- 2010B - Split architecture thermal conductivity analyzer (98 pages)
- 2020 - Explosion proof thermal conductivity analyzer (80 pages)
- 2120 - Trace Nitrogen in Argon Analyzer (66 pages)
- 2120XL - Trace Nitrogen Analyzer (85 pages)
- 2230R - Process Hydrogen Analyzer (26 pages)
- 2240 – Portable Handheld Hydrogen Leak Detector, 3rd generation (updated 1/31/11) (30 pages)
- 2240 - Portable Handheld Hydrogen Leak Detector, 3rd generation (revision 2/29/08) (40 pages)
- 2240 – Portable Handheld Hydrogen Leak Detector, 2nd generation (13 pages)
- 2750 - Portable turbine generator gas analzyer (40 pages)
- 300P - Percent oxygen analyzer (24 pages)
- 306WA - Analog trace oxygen analyzer (46 pages)
- 311 - Portable trace oxygen analyzer (19 pages)
- 311D - Portable trace oxygen analyzer with digital meter (18 pages)
- 311XL - Portable trace oxygen analyzer (18 pages)
- 316RA / RB / RAD / RBD - Oxygen analyzers (24 pages)
- 319R - Oxygen analyzer (23 pages)
- 320 Series - Portable oxygen detectors (24 pages)
- 326, 327 and 328 - Oxygen analyzers (45 pages)
- 329R - Oxygen analyzer (22 pages)
- 335 - Analog control room monitor for personnel safety (24 pages)
- 356WA - Analog trace oxygen analyzer (42 pages)
- 3000MA - Paramagnetic oxygen analyzer (63 pages)
- 3000MA - Paramagnetic oxygen analyzer Addendum (2 pages)
- 3000MB - Paramagnetic oxygen analyzer (59 pages)
- 3000PA - General purpose percent oxygen analyzer (69 pages)
- 3000PAEU - General purpose percent oxygen analyzer (78 pages)
- 3000PB - Bulkhead mount percent oxygen analyzer (82 pages)
- 3000TA - General purpose trace oxygen analyzer (75 pages)
- 3000TA-EU - General purpose trace oxygen analyzer (89 pages)
- 3000TA-XLEU - Trace oxygen analyzer (108 pages)
- 3000TB - Bulkhead mount trace oxygen analyzer (78 pages)
- 3000TB-XL - Trace oxygen analyzer (78 pages)
- 3000ZA - Trace oxygen analyzer (81 pages)
- 3000ZA-3X - Trace oxygen analyzer (72 pages)
- 3000ZA2G - Zirconium oxide analyzer (72 pages)
- 3000 Ultra Trace - PPB oxygen analyzer (72 pages)
- 3010MA - Paramagnetic oxygen analyzer, includes 0-100% range (88 pages)
- 3010MA – Paramagnetic oxygen analyzer, no 0-100% range – (superceded) (88 pages)
