Theory – PASCO CI-6539A EKG SENSOR User Manual
Page 6
EKG Sensor
012–06852A
2
Theory
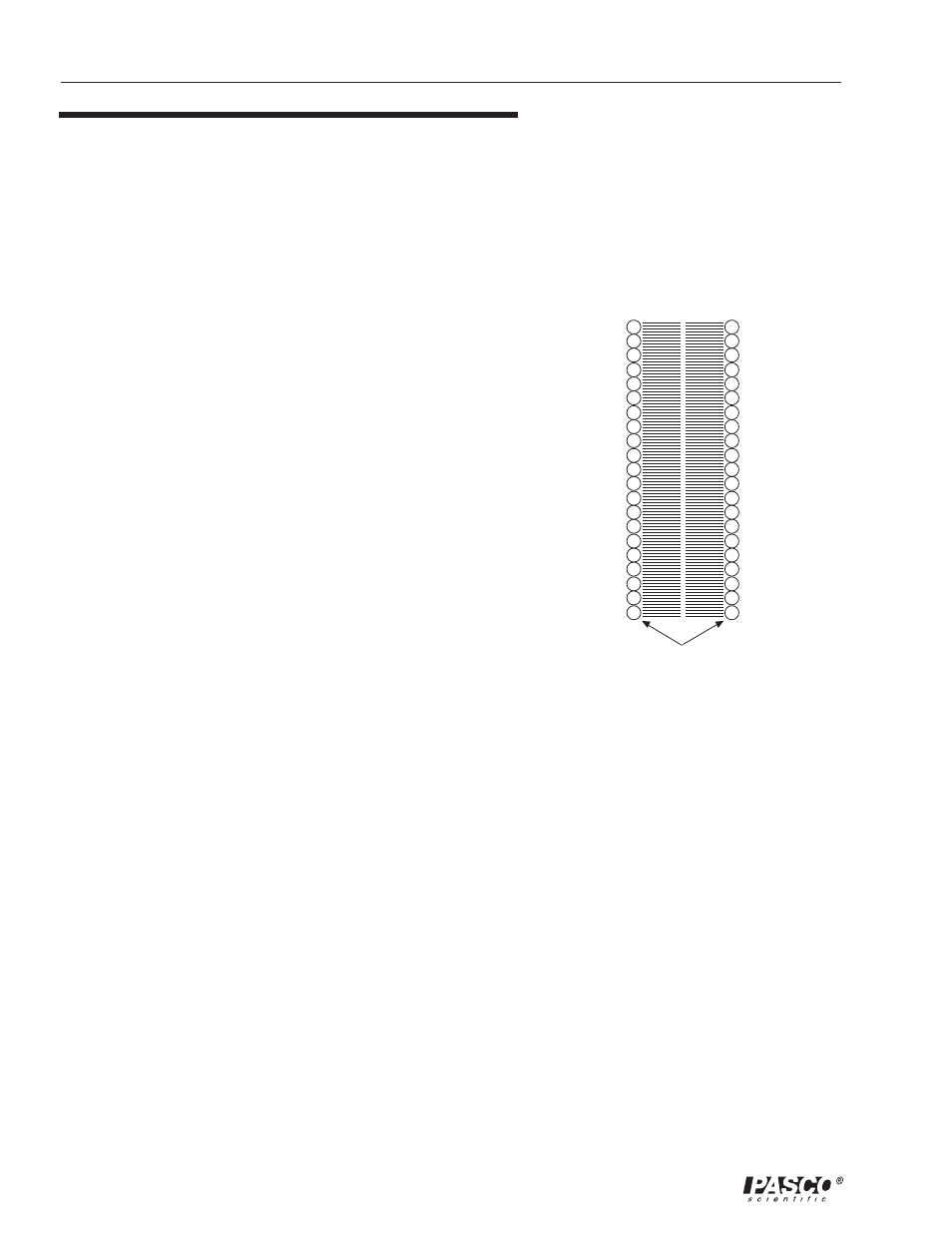
Heart muscle cells are polarized at rest. This means the cells have
slightly unequal concentrations of ions across their cell membranes.
See Figure 1. An excess of positive sodium ions on the outside of the
membrane causes the outside of the membrane to have a positive
charge relative to the inside of the membrane. The inside of the cell
is at a potential that is about 90 millivolts (mV) less than the outside
of the cell membrane. The 90 mV difference is called the resting
potential. See Figure 1.
The typical cell membrane is relatively impermeable to the entry of
sodium. However, the stimulation of a muscle cell causes an increase
in its permeability to sodium. Some sodium ions migrate into the cell.
This causes a change (depolarization) in the electrical field around
the cell. This change in cell potential from negative to positive and
back is a voltage pulse called the action potential. In muscle cells the
action potential causes a muscle contraction. Other ions and charged
molecules are involved in the depolarization and the recovery back
to the polarized state. These include potassium, calcium, chlorine
and charged protein molecules. The effect of this depolarization and
repolarization for the entire heart can be measured on the skin
surface. This is an electrocardiogram (EKG). The depolarization of
the heart also leads to the contraction of the heart muscles and
therefore the EKG is also an indicator of heart muscle contraction
(although this is an indirect measurement).
The cells of the heart will depolarize without an outside stimulus; that
is, they will depolarize spontaneously. The group of cells that
depolarize the fastest is called the pacemaker (also known as the
sinoatrial or SA node). These cell are located in the right atrium.
The cells of the atria are all connected physically and thus the
depolarization of the cells of the pacemaker cause all the cells of both
atria to depolarize and contract almost simultaneously.
The atria and the ventricles are isolated from each other electrically
by connective tissue that acts like the insulation on an electric wire.
The depolarization of the atria does not directly affect the ventricles.
There is another group of cells in the right atria, called the
atrioventricular or AV node, that will conduct the depolarization of
the atria down a special bundle of conducting fibers (called the
Bundle of His) to the ventricles. In the muscle wall of the ventricles
are the Purkinje fibers, which are a special system of muscle fibers
that bring depolarization to all parts of the ventricles almost
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Figure 1
Animal Cell Membrane (sectional view)
lipid bylayer
outside
the cell
inside
the cell
layers of protein molecules
