Lonworks network transceivers, Router function, Figure 2 ncb network combiner block diagram – CTI Products NCB/FL with Fiber Interface User Manual
Page 6: Network transceivers
CTI Products, Inc.
NCB-EL/FL User Guide
2. Installation
3
LONWORKS
NETWORK
Side
A
ROUTER
LONWORKS
TRANSCEIVER
“DC IN”
Connector
“NETWORK”
Connector
“10BaseT”
Connector
Side
B
SMX
TRANSCEIVER
POWER
SUPPLY
CONTROL
NEURON
PROCESSOR
To
Ethernet
Channel
“AUI”
Connector
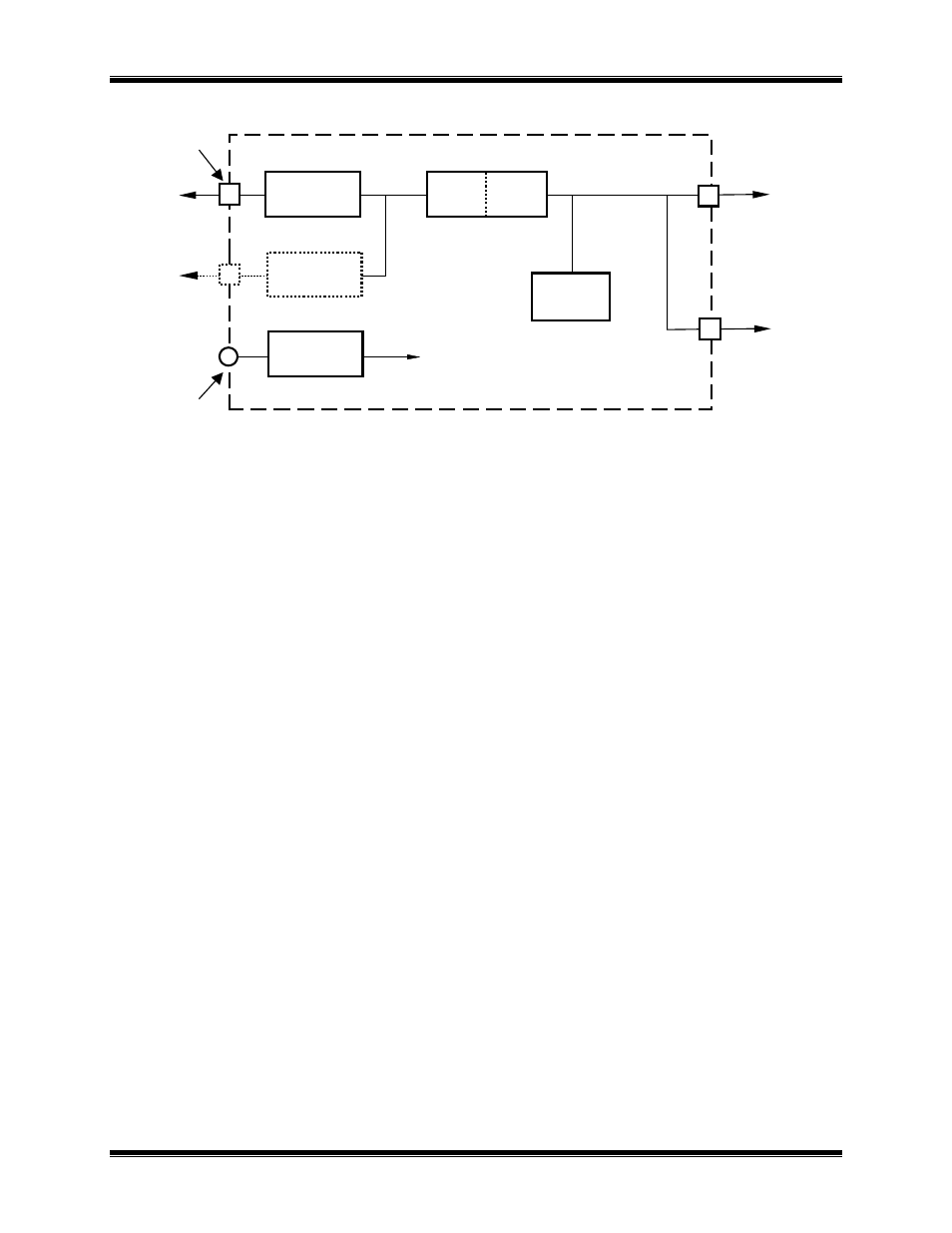
Figure 2 NCB Network Combiner Block Diagram
•
The “NETWORK” connector attaches to the local L
ON
W
ORKS
network using a compatible transceiver
internal to the NCB module and is associated with Side B of the internal router.
•
One of the Ethernet connectors attaches to the Ethernet channel, providing communication to additional
NCB modules at remote sites. These ports are associated with Side A of the internal router.
•
The Control Neuron Processor allows network management messages to be sent to the NCB module for
control and status monitoring and is associated with Side A of the internal router.
L
ON
W
ORKS
Network Transceivers
The local L
ON
W
ORKS
networks at different sites do not need to use the same network transceiver type. For
example, an FTT-10A network, a TPT/XF-78 network, and a PLT-22 network can all be interconnected by
using NCB modules with network transceivers matching the local network at each site.
NCB units are available with an option for L
ON
W
ORKS
network transceiver type. The ordering code on the rear
of the NCB lists the installed options. For NCB-Etherlons, this ordering code is of the form:
NCB/EL-Txxx, where ‘T’ indicates the transceiver type.
For NCB-Fiberlons, this ordering code is of the form:
NCB/FL-Txxx, where ‘T’ indicates the transceiver type.
The following L
ON
W
ORKS
network transceiver options are available:
A = FTT-10A
K = SMX RS485
B = TPT/XF-78
M = SMX PL22
C = TPT/XF-1250
X = None (SMX ready)
Router Function
The router contained in each NCB module may be configured as a repeater, bridge, or configured router. The
easiest configuration is as a repeater, where all messages which enter the NCB module (via any of the three data
sources described above) are simply passed to the other two sources, regardless of the domain, subnet/node, or
group destination address. A bridge forwards only messages that match one of the two domain IDs configured
on the router. A configured router forwards only messages that match a domain ID as well as a set of subnet or
group numbers. The proper choice of router mode depends on desired simplicity of installation versus required
system performance.
