CM-ET Prostar User Manual
Page 8
7
Figure 6A
Figure 6B
Frequent Inspections
These inspections are usually visual examinations by the
operator or other designated personnel. Frequent
inspections are to be performed daily or monthly and shall
include the following items:
a. Operate the hoist, with no load, and check for visual signs
or abnormal noises which could indicate a potential
problem - daily.
b.Brake for evidence of slippage - daily.
c. Chain for lubricant, wear, damaged links or foreign
material - daily (see below).
d.Hooks for damage, cracks, twist, latch engagement and
latch operation - daily (see below).
Any deficiencies must be corrected before the hoist is
returned to service.
Periodic Inspections
There are visual inspections by an appointed person who
records apparent external conditions to provide a basis for
continuing evaluation. Periodic inspections are to be
performed semi-annually and they should include the
following:
a. All items listed under frequent inspections.
b.External evidence of loose screws.
c. External evidence of worn, corroded, cracked or distorted
hook block, gears, bearings, chain stop and hook retainer.
d.External evidence of damage or excessive wear of the
liftwheel or sheave (double-reeved unit). Widening and
deepening of pockets may cause chain to lift-up in the
pockets and cause binding between liftwheel and chain
guide or between lower sheave and hook block. Check
chain guide for wear or burring where the chain enters the
hoist. Severely worn or damaged parts should be
replaced.
e. External evidence of excessive wear of brake parts - see
page 9.
f. Check the control station push buttons to make sure they
operate freely and spring back when released.
g.Check power cord, control cord and control station for
damaged insulation.
h. Check for pitting and any deterioration of contactor
contacts (hoists with black control station).
i. Check the chain pin or dead end pin and chain stop for
wear and cracks.
j. Check for lubricant leaks at gasket between main frame
and gear housing. Tighten gear housing screws to stop
leak. If leak persists, replace gasket.
k. Inspect splines on first pinion shaft and motor coupling for
signs of wear or deterioration. Replace splined parts if
worn or damaged.
NOTE: To perform some of the periodic inspections, it is
necessary to partially disassemble the hoist. Refer to
Disassembly - Assembly starting on page 13.
Any deficiencies noted must be corrected before the hoist is
returned to service. Also, the external conditions may show
the need for more detailed inspection which, in turn, may
require the use of nondestructive-type testing.
Any parts that are deemed unserviceable are to be replaced
with new parts before the unit is returned to service. It is very
important that the unserviceable parts be destroyed to
prevent possible future use as a repair item and properly
disposed of.
Hook Inspection
Hooks damaged from chemicals, deformations or cracks or
that have more than a 10° twist from the plane of the unbent
hook or excessive opening must be replaced.
Any hook that is twisted or has excessive throat opening
indicates abuse or overloading of the unit. Other load-
sustaining components of the hoist should be inspected for
damage.
On latch type hooks, check to make sure that the latch is not
damaged or bent and that it operates properly with sufficient
spring pressure to keep the latch tightly against the tip of the
hook and allow the latch to spring back to the tip when
released. If the latch does not operate properly. It should be
replaced. See Figure 5B, Pg. 6 to determine when the hook
must be replaced.
LOAD CHAIN
Chain should feed smoothly into and away from the hoist or
hook block Double-reeved. If chain binds, jumps or is noisy,
first clean and lubricate it (see below). If trouble persists,
inspect chain and mating parts for wear, distortion or
other damage.
Chain Inspection
First clean chain with a non-caustic/non-acid type solvent
and make a link by link inspection for nicks, gouges, twisted
links, weld spatter, corrosion pits, striations (minute parallel
lines), cracks in weld areas, wear and stretching. Chain with
any one of these defects must be replaced.
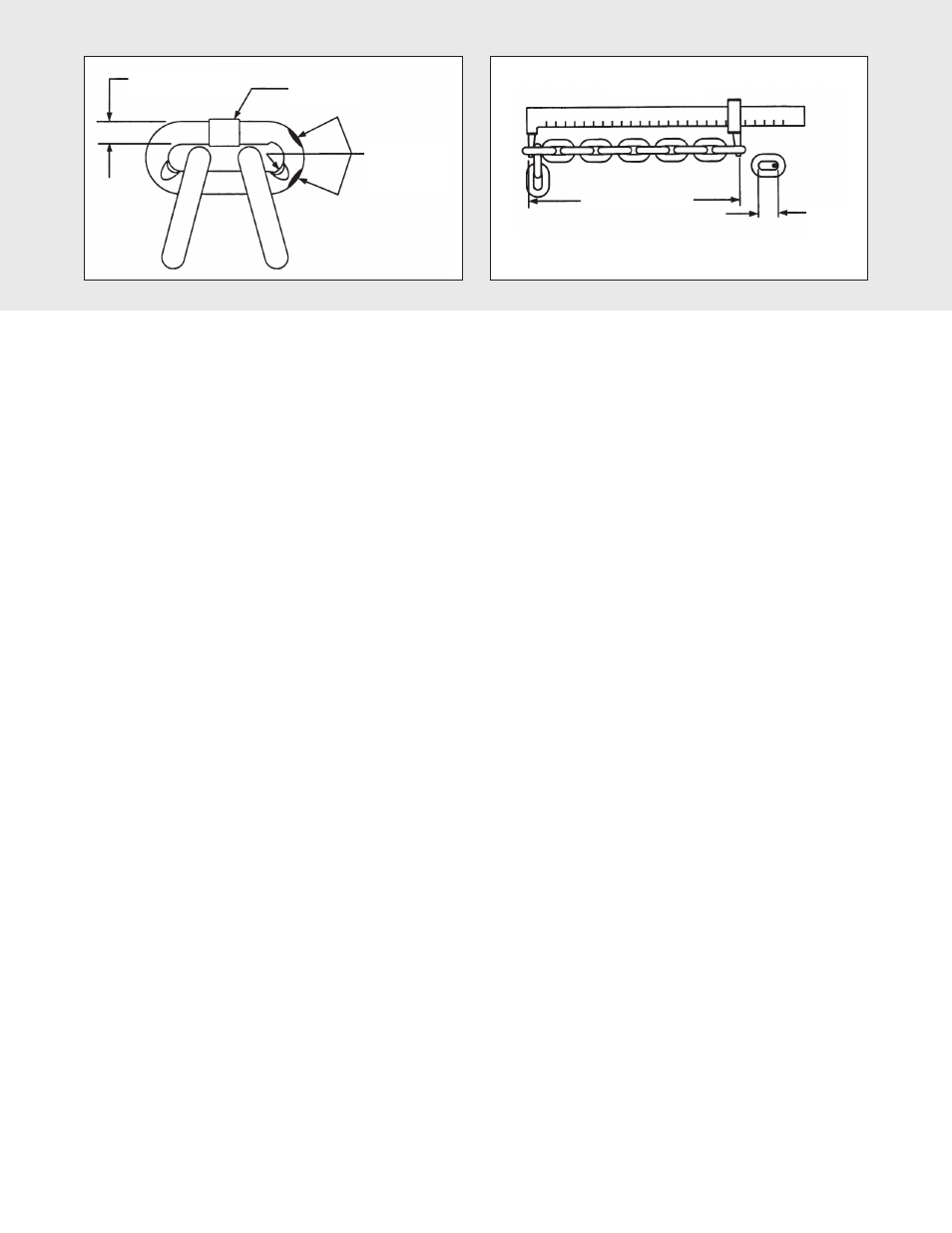
Slack the portion of the chain that normally passes over the
liftwheel. Examine the interlink area for the point of maximum
wear (polishing see Figure 6A). Measure and record the
stock diameter at this point of the link. Then measure stock
diameter in the same area on a link that does not pass over
the liftwheel (use the link adjacent to the loose end link for
this purpose). Compare these two measurements.
Weld
.157 Inches
(4 mm) Diameter
Wear in These
Areas
Vernier Caliper
Measure 11 Pitches
One
Pitch
