GxT V055-01 Diagnostic Analyzer User Manual
Page 17
17
TPS Test
O2 Sensor Test
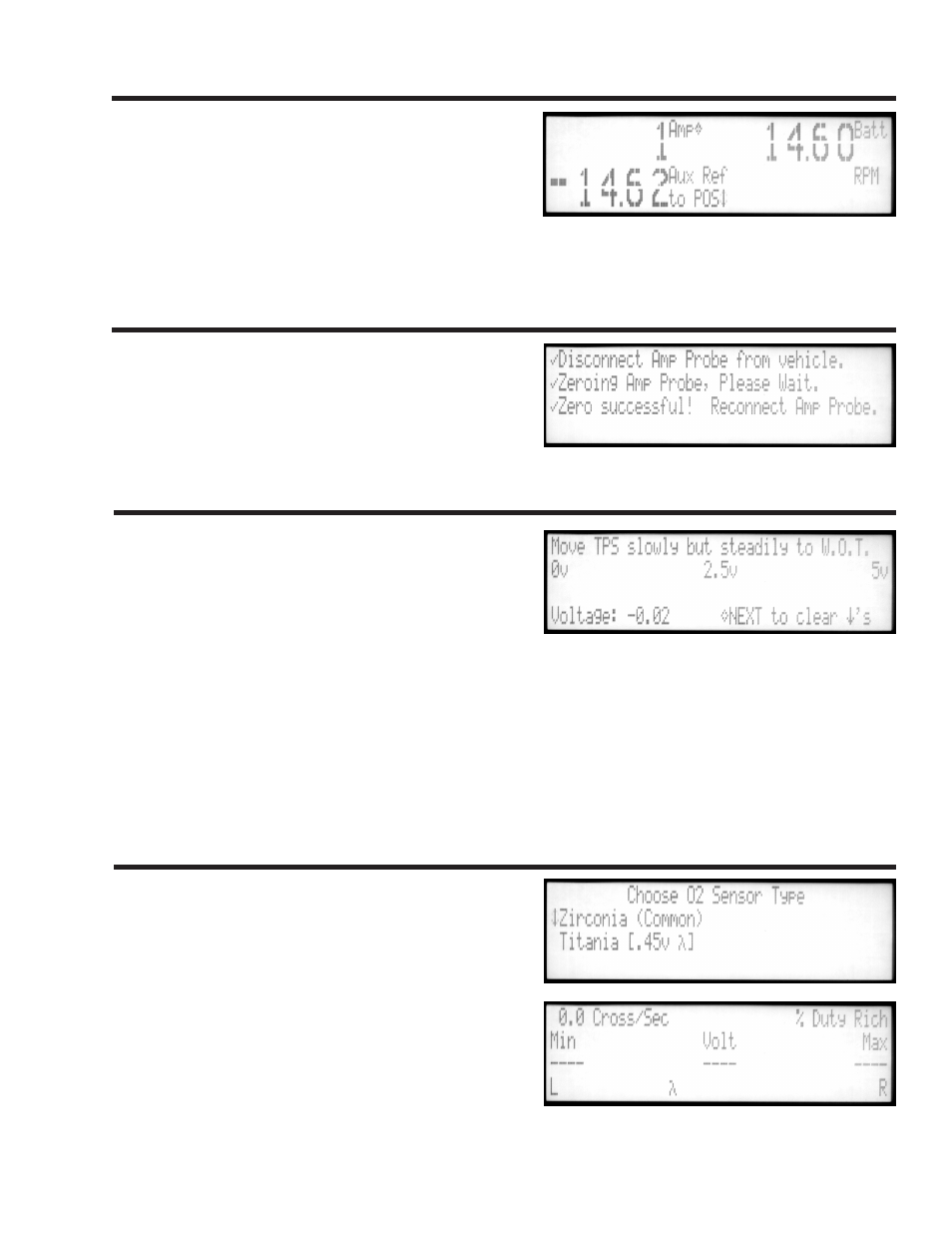
Volt Amp Meter
Zero Amp Probe
Amps are measured by the Inductive Amp Probe.
Battery voltage is measured at the Battery Power Clips.
Auxiliary volts are read with the Auxiliary Meter Lead and
referenced to either Battery Power Clip. Press SELECT
to change the reference between POS and NEG. Large
digits are displayed for enhanced readability. If excessive
alternator ripple is detected a message signal will appear on the display. Press the MESSAGE key to
display the text.
Whenever zeroing of the amp probe is desired, select this
function. A prompt will remind you that the amp probe
should be disconnected. The menu will reappear a few
seconds after a successful zero.
This is a computer aided test to check for glitches in
a position sensor signal. When a position sensor on a
throttle or air flow vane is moved from the rest position
to the top, the output voltage should move just like the
position shaft. A dedicated glitch detector operates
continuously and is not dependent upon sample rate.
Connect the Auxiliary Meter Lead to the throttle position sensor output wire. Switch the ignition key to the
ON position. The test screen will appear with a prompt to move the sensor slowly through its range.
Slowly move the sensor shaft through its full range. Using the voltmeter display, check that the output
responds to a typical range of 1 to 4 volts. If glitches are detected, arrows will appear in place of the
prompt, showing the voltage location of each glitch. Recheck the sensor for intermittent faults near the
indicated problem voltages. The arrows can be cleared by pressing the NEXT key.
Connect at the sensor harness plug or ECM. Do not
penetrate wire insulation where moisture could cause
corrosion or electrical leakage to ground.
Voltage from the vehicle O2 sensor is monitored for
crossings per second through the stoichiometric point
(0.45v), indicating rich and lean conditions. Recent
minimums and maximums are shown and used to
generate a graph. The number of crossings per second
indicates the activity level of the system. When the signal
is active (more than 2 crossings per second), the percent
of time in the rich zone is given.
Typical cross count readings for warm engines running
at a steady fast idle are in the 1 to 3 range. Low rates may indicate a damaged O2 sensor. Multiports
usually cross count fastest, and carbureted engines the slowest.
