Starting charging history – GxT V055-01 Diagnostic Analyzer User Manual
Page 16
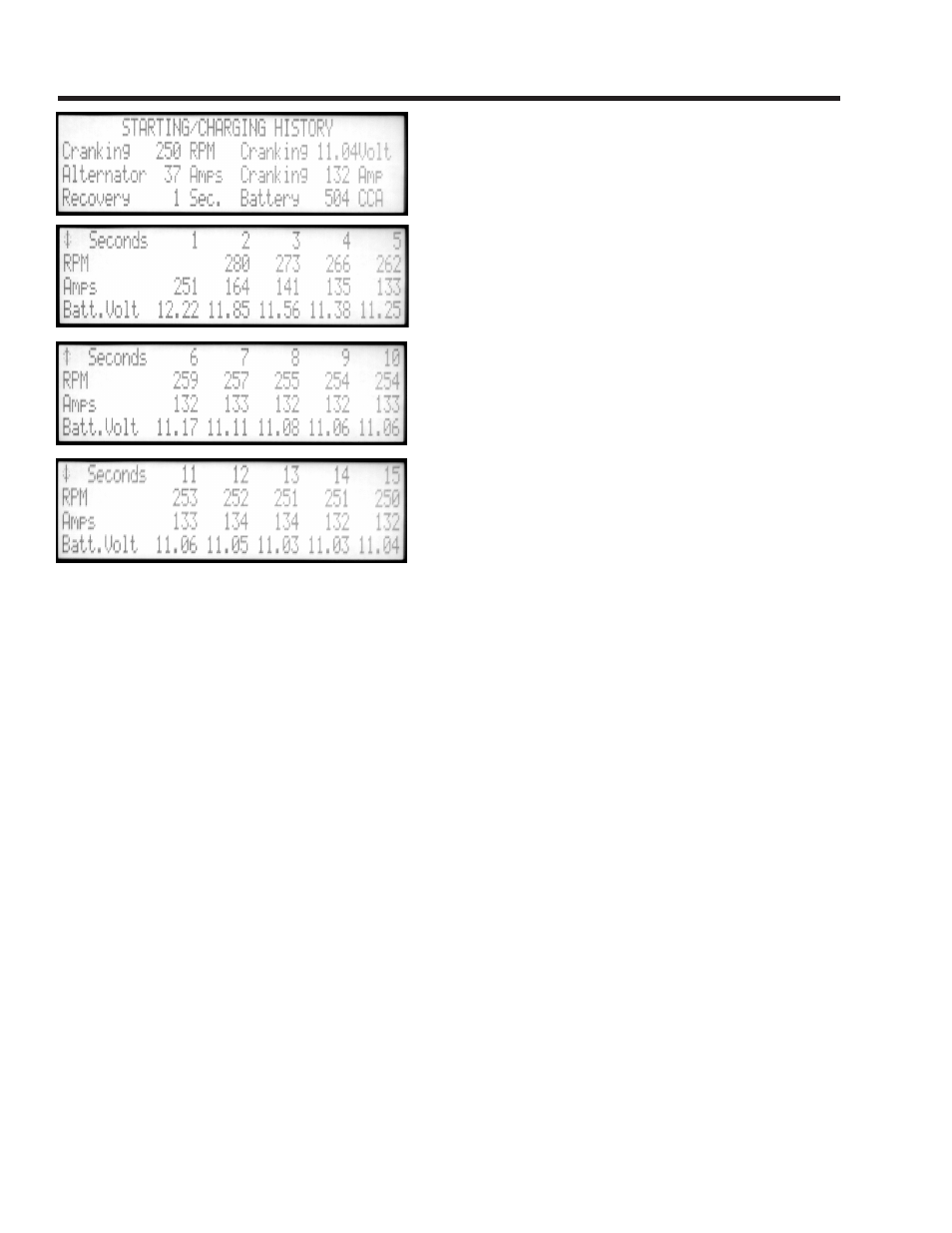
16
Starting Charging History
An electrical power system test of the engine is the primary
feature of this sequenced procedure. Performance of the
alternator, battery, and starter are evaluated.
This test records battery voltage and amps while the
starter cranks the engine for 15 seconds. Then there
is a wait to check battery recovery time, followed by a
measurement of the charging current when the engine
is run at high idle.
For accurate results, turn off all lights and accessories.
Be sure the vehicle doors are closed, as the current
drawn by dome and courtesy lights is significant and may
invalidate the test results.
If a DIS or Diesel engine type was selected during
Engine Setup, the analyzer will prompt you to disable
the fuel supply to prevent the engine from starting during
cranking. Use the recommended method to disable the
engine for compression cranking tests, from the vehicle
service manual. This is usually done by unplugging the
power wire or fuse to the fuel injectors or ignition coils.
Run the engine until it quits, to verify that fuel is cutoff.
On a distributor engine, with the Coil Primary Clip connected, the EngineLink will suppress the ignition
during cranking. If, for some reason the Diagnostic Center has difficulty suppressing a particular ignition,
the disable fuel prompt will appear.
Begin cranking when prompted. After 15 seconds, the analyzer will prompt you to stop cranking and turn
the ignition key off. (If the battery voltage drops below 9.6 volts during the test, it is too low to continue,
and the test will be aborted before 15 seconds have passed.)
When the operator stops cranking, a waiting period begins while voltage recovery time of the battery is
checked. Good batteries will spring back in 1 or 2 seconds. Worn out or undercharged batteries need
over 10 seconds to recover. Make sure all battery drains such as dome lamps are off during this test.
Keep doors closed.
Restore fuel or ignition power, as necessary, and be ready to start the engine when prompted. Run the engine
over 1500 RPM to ensure the regulator has “kicked in”, so that charging current can be measured.
The Diagnostic Center will then prompt you to SELECT a temperature range to be used in the calculation
of the battery’s Cold Cranking Amp (CCA) rating. Choose the temperature of the battery electrolyte, which
may be different from shop temperature if the battery has recently been brought in from a very hot or very
cold environment just prior to testing. The results are then displayed on this screen. Use the message
and select keys to display all measurement screens.
